Ancient Greek sculpture briefly. Sculpture of the classic era: Beauty without whimination and wisdom without a lot
The heroic era of the Greco-Persian wars and years, followed by them, were the time of the rapid growth of slave-owned policies. In the fight against the Persians, they proved their viability and strength and joined after the time of their highest power. A period of widespread construction of public architectural structures, the creation of monumental sculptures and frescoes, which argued the strength and significance of the Greek states-states, the dignity, the greatness and beauty of man. There was a decisive fracture in the development of art.
The features of the archaic conventionity were still allowed to know about themselves in Vazopysis and especially in sculpture. But it was now only rapidly leaving the past relics of archaic tradition. All Greek art for the first third of the 5th century. BC. It was permeated with tense search for the methods of a realistic image of a person, first of all, the truthful transmission of movement, as well as the creation of a group composition, free from the principles of decorative symmetry. In vasopysis, and then in sculpture and monumental painting defeated realism. Resolutely expanded the circle of topics and plots. The synthesis of sculpture and architecture began to be understood as a free community and complemention of equal and self-concrete arts.
Monumental and social character of architecture greek classics, Its close connection with the life of the team of free citizens, with state cults of the gods, personified the unity of the policy, found their bright and strong expression already during the early classics.
A leading role at this time was playing a Doric Order. The advanced features of the Greek architecture of the preceding, the archaic period was now wide and free development. The deep correspondence of the entire figurative building of the Doric Orders of the Spirit of Civil Heroic 5 V. BC. Especially helped the disclosure of all the arts laid in it.
The peripter became the dominant type of building in the Greek monumental architecture. The classic type of periptera and the entire system of its proportions received their development in these years.
In their proportions, temples have become less elongated, more integridewrd, the disproportion and heavyness of archaic architectural proportions were overcome. In large temples interior - Naos - usually divided by two longitudinal rows of columns into three parts. In small temples, architects were carried out without inner columns supporting the overlap of the Naos. The use of column on the end facades has disappeared with an odd number of columns that interfere with the location of the entrance to the temple in the center of the facade. The usual ratio of the number of columns of the end and lateral facades was 6 to 13 or 8 to 17; The number of the side of the side was equal to the doubled number of the columns of the end facade plus one column.
In the depths of the central part of the Naos framed by the inner colonnades, the statue of the Divine was directly against the entrance. The layout of the temple received logically clear harness and monumental solemnity. A strictly thought-out system of location and the ratio of all elements of the design of the temple led to creating an image of a magnitude, clear and simple.
Arching early classics finely felt the connection of the system of proportions of architectural forms with the absolute scale of the building and with its size relative to the person and the surrounding landscape. The development of a permanent system of parts of the order and their shape occurs simultaneously with increasingly free and diverse construction of their proportional ratios. Minor changes of proportions caused appropriate changes in the equilibrium of irrevocable and carrier parts. Modifying the ratio of the proportions of all parts of the building, the architects were modified and the whole nature of its figurative expression. Therefore, each temple of the classics period combined the principles of an inexperial experience of a canonical solution with the moments inherent in particular only to this temple. This attached to him an individual originality and made it a unique work of art. This was achieved and the solution of the task of the relationship of the church with the environment was achieved and its very character was determined, then powerful and magnificent, then light and elegant.
This feature of Greek architecture is characteristic of the entire structure of an ancient Greek artistic consciousness. So, for example, the Greek tragedy also developed in the traditional and strict forms of theatrical canons. At the same time, the same playwright, such as Eschila or Sofokla, in each drama in accordance with the nature of the conflict depicted and with the figurative system of this drama, the ratio of the prologue, epilogue, choral parties, building the poetic speech of the main characters, etc. was significantly modified.
A monument to transitional from late Archaica to early classics was built about 490 BC. Afiah Athens Temple on the island of Egina. Its dimensions are small. The ratio of columns is 6 to 12. The columns are set to proportions, but the antablement is still unresarior. The temple was built from limestone and covered with painted plaster. Frontones were decorated with sculptural groups made from marble (now located in Munich Glipotek). The location of the temple on the top of the high bank slope well shows how the Greek architects were able to associate a strict doric architecture with the surrounding space of nature.
Transitional character also had the Temple of "E" in Selinunt (Sicily). From the temple on the island of Egina, he was distinguished by an excessive exposure of proportions (the ratio of columns 6 to 15). The columns of its squathers and are often located; The antablement is very high, its height is almost equal to half the height of the column. In general, he resembles the churches of the 6th century. BC, although the processing of parts, the membership of the forms is already already greater clarity and rigor of execution.
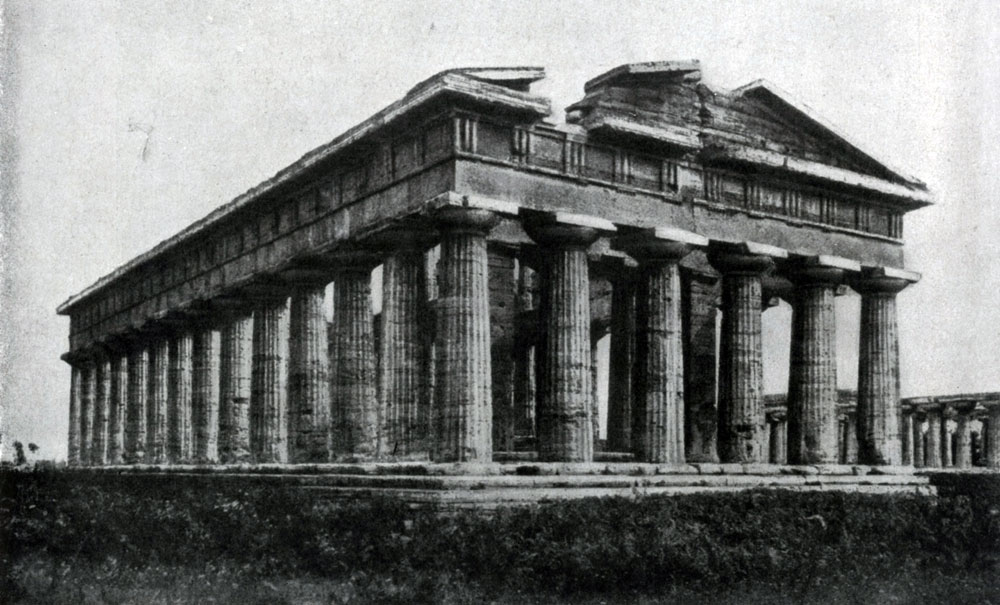
The most complete typical features of the architecture of early classics were embodied in the temple of Poseidon in Pestum (Great Greece) and in the temple of Zeus in Olympia (Peloponnes).

![]()
Poseidon Temple in Pestum, built in the second quarter of the 5th century. BC, well preserved. Full of strict greatness, powerful and somewhat heavy, it is towers on a three-step base. The low stylobate, low, but wide steps emphasize the impression of a calm, balanced strength. Columns (ratio 6 to 14; see drawing with a plan of Poseidon Temple in Pestum) relatively massive; The strong entazis creates a feeling of elastic tension of the column, as if with an effort of the chipping overlap. The entire colonnade performs against the background of the shaded space; Deep horizontal shadows from far-speaking abacks fall on the columns, emphasizing the collision line of carriers and irreversible parts. All the main elements of the architectural composition are sharply pronounced, architectural details only identify the main relationship of architectural system, and this also enhances the impression of concentrated power.
The temple was designed to perceive from different distances. Missed the temple with its relatively low columns seems somewhat smaller than in reality, and at the same time very compact and strict forms. Near the sizes of columns and tangible common sizes of the temple are clearly becoming clear compared to the person; Details (including more frequent than usual flutes), putting well visible, the massiveness of proportions and the magnitude of the building. Contrast of impressions from distant and close points of view contributes to increasing as the feeling of the power and the grandeur of the entire structure approached. This method of comparing several points of view is extremely characteristic of the principles of the architecture of the classics. The Greek architect of classical pores has always sought to create an architectural image, oriented on human perception, taking into account the organizing path of the viewer's movement.
Zeus Temple in Olympia, built between 468 and 456. BC. Architect Libon, had the meaning of the generallyls of the sanctuary and was the largest temple of the entire half anex. The temple is almost completely destroyed, but on the basis of excavations and descriptions of the ancient authors, its general view can be quite accurately reconstructed.
It was a classic doric peripter (column ratio of 6 to 13), built of solid limestone rock (sewer), which made it possible to achieve almost chased accuracy and purity of the performance of parts. The proportions of the temple differed with rigor and clarity. Their severity softened to the festive in its nature of the color. The temple was decorated with large sculptural groups on the front. Methods of external frieze, as in most temples of early classics, were deprived of sculptural jewelry. 3A outer colonnada over the porticors of Pronaos and Optiotoma on the Metops of triglyphic frieze was placed by sculptural compositions, six on each frieze. The plots of these reliefs were closely related to the public appointment of the temple, the former center of the extensive architectural ensemble of Olympia - the Sacred Center of Obchelinsky Sports Compete. The legendary contest on the chariots of Pelops and Enonaya and the Battle of Greeks (Lapiphov) with Centaurs were depicted on the frontal and the Battle of the Greeks (Lapiphs). Inside the temple from the middle of the 5th century. BC. The statue of the work of the work of Fidiya was made of gold and ivory.
Thus, in the temple of Zeus in Olympia, it has already found its embodiment characteristic classical Greece The synthesis of architecture and sculpture, which will be discussed in detail, with the description of Parfenon, and the principles of architectural classics were finally approved.
A very important part of the Greek art in the classical period was a vasopcript in which his vivid expression of the realism of the classics was.
The heyday of the city-state was and a period of heyday of artistic crafts of various types of applied and decorative art. The leading place among them continued to maintain ceramics decorated with highly artistic painting.
The vase was imbued with the traditions of folk artistic craft with his sense of artistic value of each thing created by the creative work of man. Although the best vases performed by the largest and leading artists, for the most part and were intended for religious offerings or served to decorate festive pirms - still it was the living and permanent connection with the folk art of potential masters and painter masters determined their high artistic perfection.
In the period of early classics, the realistic trends of advanced artists-Vasopisians of the Late Archaika received rapid and deep development, becoming more in the years of Greco-Persian wars dominating. Red-breeding technician at that time finally displaced blackfoot. She gave the opportunity to realistically depict the volume and movement, build any rickers, naturally and freely simulate human body.
The artistic worldview of the classics, based on the deep interest in the surrounding life and to a real person, quickly expanded the range of the possibilities of a realistic image, enclosed in red-breeding technique. Instead of a plane silhouette of black-deficient vases, artists began to build three-dimensional bodies taken in a wide variety of live turns and rockets. This free and convincing transmission of motion, far from the conditional game of black spots and scratched through black lacques of lines, was supplemented by a greater naturalness of the reddish color of clay, which was now used for the image of human figures, since he was incomparably closer was the appearance of a tanned naked body than Brilliant black varnish color. The black lines of the drawing on the light background of clay were now transferred now the muscles and details of the body, allowing realistic to reproduce the structure of the human body and its movement. It gave a powerful impetus to the development of art drawing.
The masters of redfigure vazopysi sought not only specifically to depict the body and the movement of a person - they came to a new, realistic understanding of the composition, constantly drawing complex scenes of mythological and domestic content. In some respects, the development of vases was ahead of the development of sculpture. In Vasopysi, many realistic discoveries similar to the discoveries of sculptures of the second quarter of the 5th century. BC, the 6th century appeared already in recent years. And in the first decades of the 5th century. BC, that is, in the period after the reforms of Clisphen and during the war years.
The composition of the injury of early classics was becoming more complete and holistic, it was naturally limited by the inner surface of a flat bowl or side surface between the vase handles. With a variety of scenes of everyday life, the most diverse scenes of everyday life passed the most diverse scenes of everyday life, as well as the heroic events of the myths and the Homer Epos. Traditional mythical plots rethought, saturated with new motifs, hoped from life.
Vasopy's prominent masters of this time were Euphronium, Duris and Brig, who worked in Athens. All of them were typical of the image of the image. But the degree of novelty, that is, liberation from the archaic convention and the conquest of realistic freedom, they had an unequal.
More than others were associated with the archaic pattern and ornamentality senior of these masters - Euphronium (worked at the very end of the 6th century. BC; later he became the owner of the workshop, where other handselkers worked).
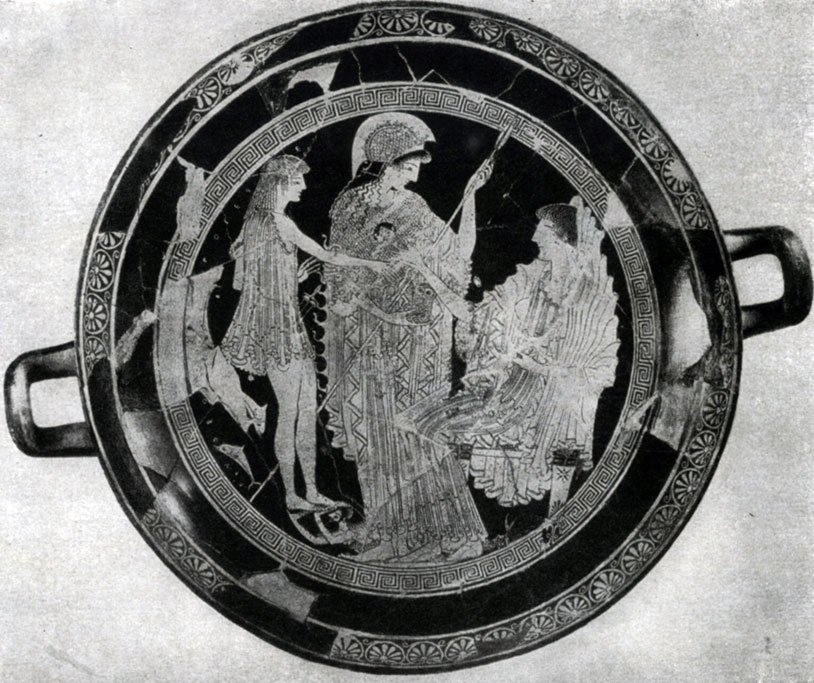


In the vases painted by Euphronem, with the image of the Teza in amphitrite or heter, playing in the Cottab, the desire to be too free and sophisticated rickers and movements, in the absence of another developed method of realistic figure, led to the conditional flatness of some parts; Many places in Euphronia occupy a purely decorative elements: patterns on clothes, etc.
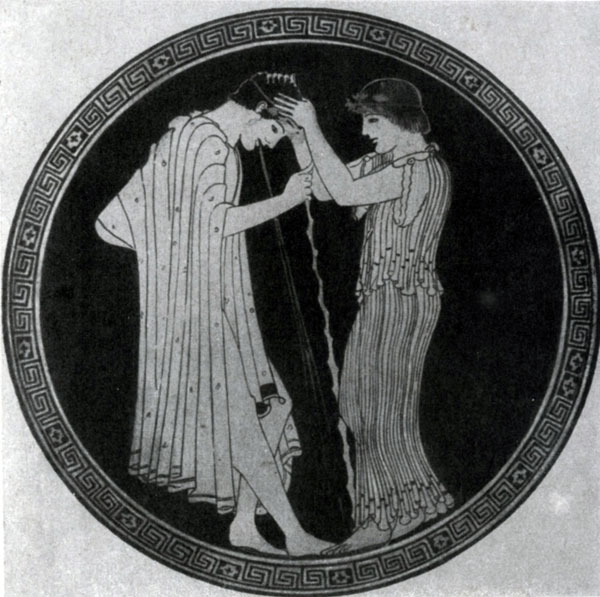
Later, in the first quarter of the 5th century. BC. The masters have learned to find such artistic means of the movement, which could, without destroying the integrity of the vessel surface, give a feeling of three-dimensional spatiality of the pattern, and this led to the final overcoming of the archaic principle of the image flatness. True, vasopisa all over 5 V. BC. Operated in the main graphics of the image, without pursuing the actual scenic tasks (for example, transmission of lighting). From the archaic remained for some time only elements of elements, a sophisticated linear contour, who played to some extent a purely decorative role. It is these echoes of archaic art that are in some works of Duris - one of the most remarkable draftsmen of early classics.

In vases, the drawings of which are filled with Duris, the dependence of its artistic techniques on the nature of the plot is felt; More elegacity and ornamental rhythm in the figures on mythological topics ("EOS with the body of Memnon"), more simplicity and casual freedom in drawings on the themes of everyday life ("School scene"). The lightness and virtuosity of building an artist of any complex poses, any real gesture (for example, in the image of a sitting teacher) are striking.

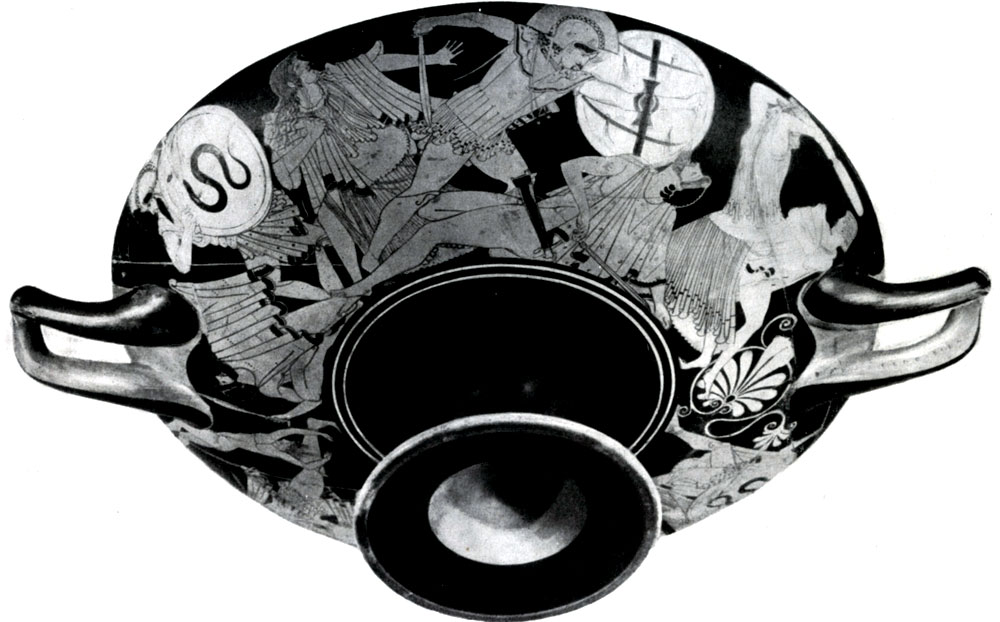
Closer to the beginning of the second quarter of the 5th century. BC. Compositions consciously put the task of organic communication of a vital image with a form and rhythmic system of the vessel are becoming more numerous and perfect. Wipers of Vazopysi more clearly began to imagine that the architectural beauty of the forms of the vessel should never collapse with the image that their close connection should serve to their mutual benefit. This is a drawing of the work of the Brig (about 480 BC), decorating the bottom of the bowl for wine stored in the Würzburg Museum. By the way, the very topic of the last drawing is directly related to the appointment of the vessel: a kind girl supports the tilt head of the young man in the guilt. The owner of the bowl, which causing her, had the opportunity to contemplate at her day. This is a humorous reminder of the need to know the measure to all things. Two standing figures are perfectly inscribed in a round bottom of the bowl, and at the same time they differ in the rare bold and simple construction of a three-dimensional form. Deep respect for the value and beauty of real human life gave the opportunity to brow to fill even such prosaic theme with a genuine grace.
Brig was a bold foreman of new paths, and his discoveries played a crucial role in the formation of realistic principles of classics. Compared to Euphronem Brig in his work, I made a big step forward. His drawings, very diverse on topics, genre and mythological, not only differ in vitality and natural simplicity, but also solve many tasks of dramatic construction. His vase dedicated to the Trojan War is distinguished by a genuine pathos of the image of the battle, resembling contemporaries Brig's events of Greco-Persian wars.

The smaller dependence of the artist-vasopisters from the mating archaic tradition and their immediate connection with the artistic craft led to the fact that the realistic character of the artistic culture of early classics affected Vazopysis not only earlier, but also in broader appeal to everyday life than it could take place in monumental sculpture. It can even be assumed that the monumental sculpture masters used the experience of best masters of Vasopysi, which at the beginning of the 5th century. BC. Ahead of sculptors in the field of transmission of action and movement of a person.
Very interesting image of a sculptor's workshop on a bowl of an unknown master of the 480s., Full of deep severity and respect for work. True, artistic craft is shown here, more respected due to the value of its products. The work of the sculptor is described in very detailed and accurately: the masters work around the oven for casting bronze, the finished statue is mounted, the tools and bronze reliefs are hung. But the situation is given only by these objects - the homeworn does not depict the walls on which they hang: in Vasopysi, as in sculpture or monumental painting, the environment has not been interested in the artist, who showed only people - their actions, expressive meaning, the feasibility of their movements and Acts. Even the tools that the person acts, and the fruits of his work were shown only to understand the meaning of action, things, like nature, occupied the artist only in their attitude towards a person. This explains the absence of a landscape in Greek vazopysis - both early and high classics. The attitude of a person to nature, to its forces and phenomena was transmitted through the image of the person himself, through his reaction to the phenomenon of nature.
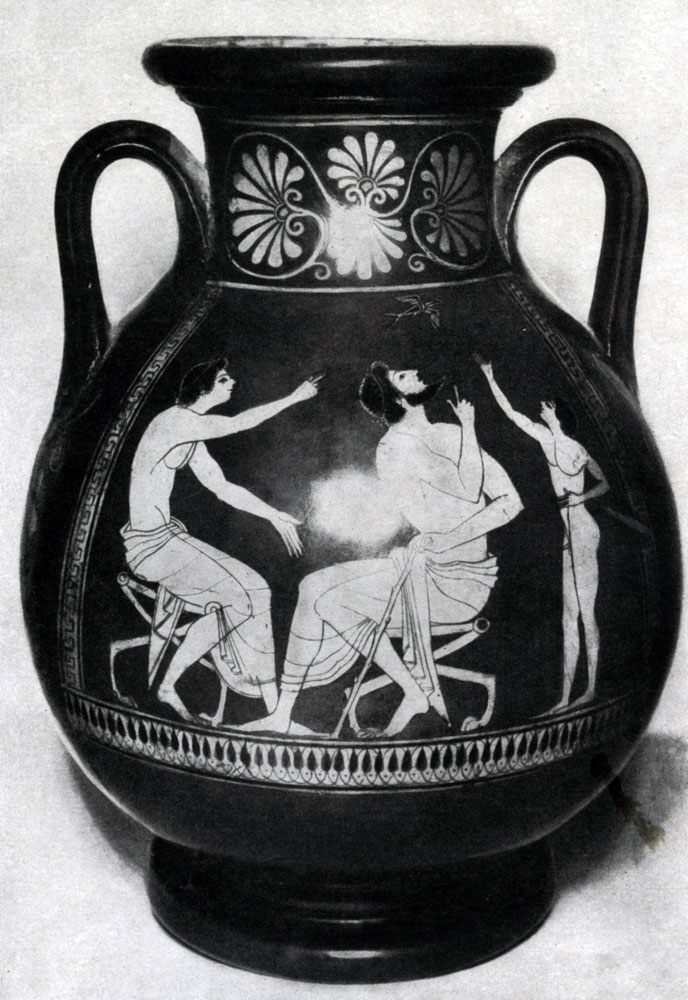

Thus, the advancing spring lyrics are embodied on a red-chicken "vase (pelica) with a swallow" (end 6 - the beginning of the 5th century BC. BC; State Hermitage) in the image of a boy, boys and an adult who saw the spring of Spring - flying swallow. Three figures, various and by their addition and in their own possessions, are associated with one action and form a holistic and living group. The overall feeling that unites these people looking up onto the swallow is expressed in the inscriptions accompanying each figure and connected in a short dialogue. The young man, who first saw the swallow, says: "Look, swallow"; His senior interlocutor confirms: "True, I swear Hercules"; The boy happily exclaims, by entering into a conversation: "Here it is already spring!"
In the second quarter of the 5th century. BC. Greek vazopisa acquires an unprecedented strict and clear harmony, but at the same time to some extent loses the immediate sharpness and brightness, which differences in the work of the first vases of classical art - Duris or Brig. But the Vazopis of this time, as well as monumental painting, it is more expedient to consider with the art of the pericla era - the art of high classics.
In the northern part of Peloponnes, in the Argos-Sikion school, the most significant of the schools of doric directions, the sculpture of the folding classics developed basically the task of creating a calmly standing human figure. The old Doric traditions in the light of new artistic tasks in the light of new artistic tasks, the largest Master of Agelade School already at the beginning of the 5th century. BC. It sought to solve the problem of revitalizing a calmly worthy figure. The transfer of the center of gravity of the body for one leg allowed Agelead and other masters of this school to achieve free naturalness of the posture and gesture of a human figure. The consistent development of the Argossky-Sykion masters of a well-thought-out system of proportions that reveal the real beauty of the perfect human body was also very important.
The ionic direction in the same desire to master the vital persuasion of the image of a person went its own way, according to its old traditions. The wizard of the ionic direction especially paid a lot of attention to the image of the human body in motion.
However, the difference between these two directions in the classical period was not essential. Advanced masters of both directions, although they went different ways, but the goal had a common one - the creation of a realistic image of a perfect person. Already in 6 c. BC. Attic school synthesized the best sides of both directions: by mid 5 c. BC. It most consistently approved the basic principles of an advanced realistic art associated with the flourishing of Athens, and acquired the importance of the Governing General of Art. The main city of Attica is Athens - by mid 5 c. BC. collected and united the best artistic forces of Eldlaces to create monuments and architectural structures, praising the dignity and beauty of Athenian, and with him and all the Greek people (or rather, free citizens greek policies).
An important feature of the Greek sculpture of the classics period was its inextricable connection with a social life, which was affected both in the nature of the image and in its place on the city square.
Greek sculpture The classics period had a social character, she was the property of the whole team of free citizens. Naturally, therefore, that the development of the public-educational role of art, the disclosure of a new aesthetic ideal in it has affected the most fully in monumental sculptural works related to architecture or stood in the squares. But at the same time, it was precisely in such works with a special visibility that the deep breakdown of the entire structure of the artistic principles was reflected, which was accompanied by the transition from archaic to the classics. The new public ideas of the victorious democracy came to a sharp clash with the conventionalness and distraction of the archaic sculpture.
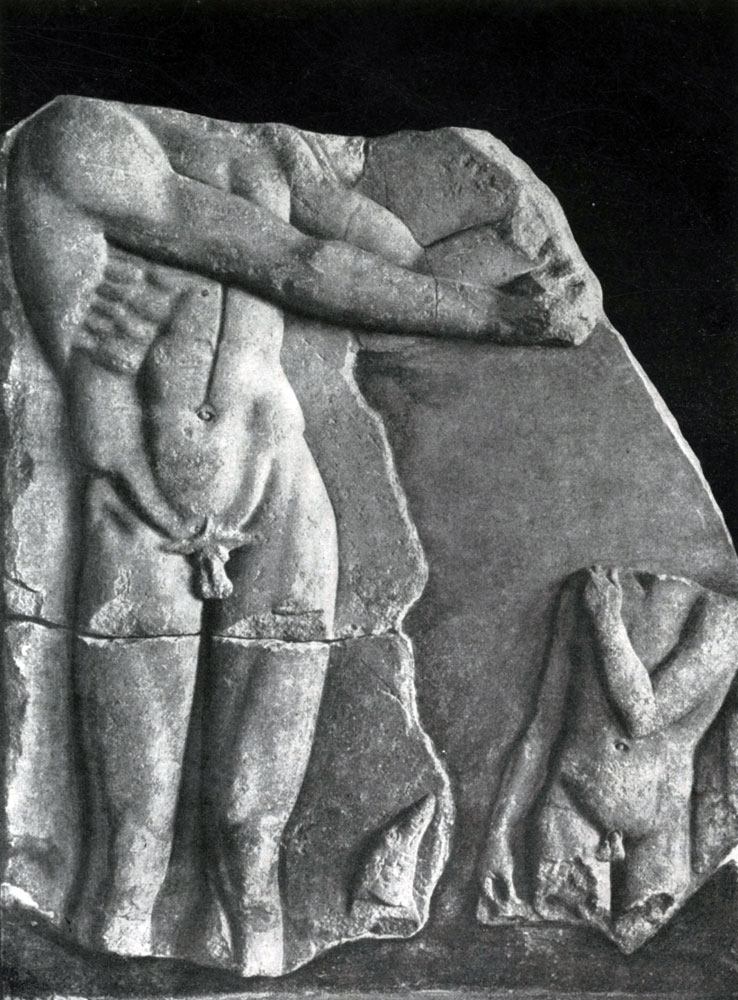
Contribusive, transitional nature of some sculptural works of the beginning of 5 V. BC. Disposable in the front-distance groups of the Afai Athens Temple on the island of Eger (about 490 BC).
Fronton sculptures of the Eginsky Temple were found at the beginning of the 19th century. In a strongly destroyed form and at the same time, the famous Danish sculptor Torvaldsen is restored. One of the most likely options for the reconstruction of the Fronton composition was proposed by the Russian scientist V. Malmbarg. The composition of both frontoths was built on the basis of strict mirror symmetry, which to some extent attached to the painted sculptural groups speaking on the colored background of the frontones, the features of ornamentality.
In Western Fronton, the struggle of the Greeks and Trojans per body of the Patrole was depicted. In the center there was still standing, strictly frontal, as if deployed on the plane of the front figure of Athens, impassively calm and, as if invisibly present in the midst of battles. Her participation in the resulting struggle is shown only by the fact that its shield is facing the outside to the Trojans and the legs of the legs are turned into the same side. Only on these symbolic hints can be guessed that Athena acts as a defender of Ellin. If you do not count the figures of Paris in a high curved helmet and with a bow in your hands, it was impossible to distinguish the Greeks from their enemies, so much figures are mirrored on the left and on the right half of the front.
Yet in the figures of warriors no longer there is no archaic frontal, their movements are more correct, the anatomical structure is more correct than usually in the art of archaic. Although all the movement is deployed strictly on the plane of the fronton, it is quite vital in each individual figure specifically. But on the faces of battle warriors and even the wounded, the same conditional "archaic smile" is given - a clear sign of connectedness and conventions, poorly compatible with the image of stressful structures of heroes.
In the Eginsky fronton, there was still a reproaching cosmy of old archaic canons. Composite unity was achieved by external, decorative methods, the most principle of the connection of architecture and sculpture was here, in essence, still archaic.
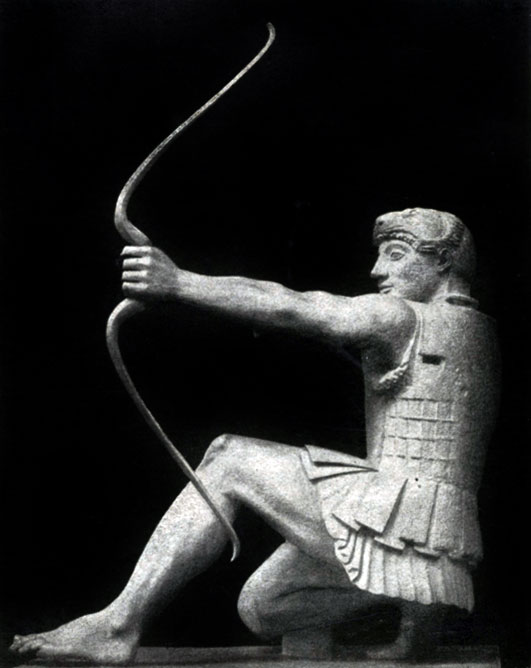

True, already in the Eastern Frontone of the Eginsky Temple (which remained much worse than the Western), the undoubted step forward was made. Comparison of Hercules's figures from East Frontone and Paris - from Western clearly shows great freedom and truthfulness in the image of a person from the Master of East Fronton. The movements of the figures here are less subordinated to the plane of the architectural background, more natural and free. Especially instructive comparing the statues of the wounded warriors on both frontions. The master of Eastern Frontone has already seen the inconsistency of the "archaic smile" of the condition in which the warrior is located.
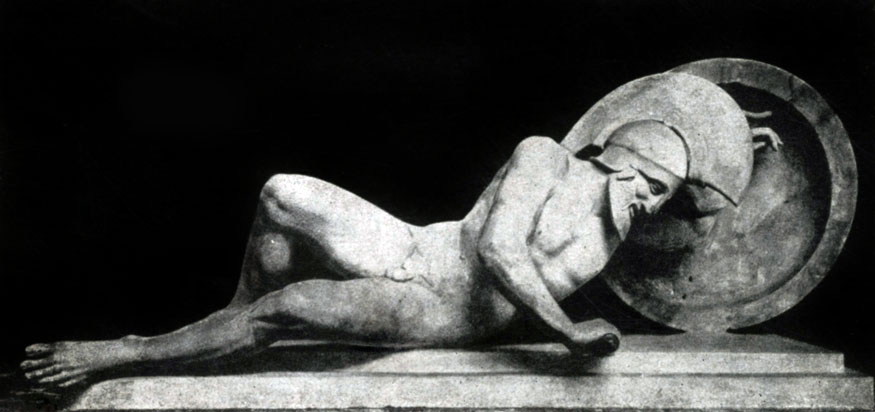


The motive movement of the wounded warrior is recreated in strict accordance with the vital truth. To some extent, the sculptor mastered here not only the transfer of external signs of movement, but also by the image through this movement of the inner state of a person: the vitality forces slowly leave the athletically folded body of the wounded warrior, a hand with a sword, which rests the semi-chase warrior, slowly bends, legs slide on the ground without giving more reliable body support, powerful torso gradually falls out. The rhythm of the cloneware body is emphasized in contrast by a vertically delivered shield.
Mastering the complex and contradictory wealth of the movements of the human body, directly transmitting not only the physical, but also the mental state of a person - one of the most important tasks classic sculpture. The statue of the wounded warrior from the Eastern Frontone of the Eginsky Temple was one of the first attempts to solve this task.
To destroy the syllants of the archaic art, the appearance of sculptural works devoted to specific historical events, visualizing the public and moral ideals of the victorious slave-owned democracy, was extremely important. With their relative smallness, they were a particularly bright sign of the growth of socio-educational, civil content of art, its realistic orientation.
The mythological topic and the plot continued to dominate Greek art, but the cult and fantastically fabulous side of the myth went to the second Alan, almost disappeared. The ethical side of the myth, disclosure in the mythological images of the strength and beauty of the ethical and aesthetic ideal of modern Greek society, figuratively embodied in mythological images of the strength and beauty of the ethical and aesthetic ideal of modern Greek society. A realistic rethinking of mythological images, which made modern ideas in them, was carried out by the Greek artists of the classics period as well as the Great Greek tragedies of the 5th century. BC. - Eschil and Sophocl.
Under these conditions, the appearance of individual works of art, directly addressed to the facts of real history, although sometimes the mythological tint has been deeply natural. So, Eschil created the tragedy of "Persians" dedicated to the heroic struggle of the Greeks for freedom.
Sculptors of critical and neutot created at the beginning of the 470s BC. The bronze group of Tiranoubyz is a harmony and aristogiton, - in exchange of the archaic sculpture taken by the Persians, portraying the same heroes. For the Greeks of the 5th century. BC. Images of harmony and aristogiton killed in 514 BC. Athena Tirana Hippark and at the same time the dead were an example of the dedicated validity of citizens, ready to give life to protect civil liberties and the laws of the native city ( In fact, the Garmody and Aristiton were guided by the interests of not a democratic, but the Aristocratic Party of Athens 6 V. BC, but in this case, it is important to us, as the 5th century. BC.). The composition of the group unreverited to the present day can be restored in ancient Roman marble copies.
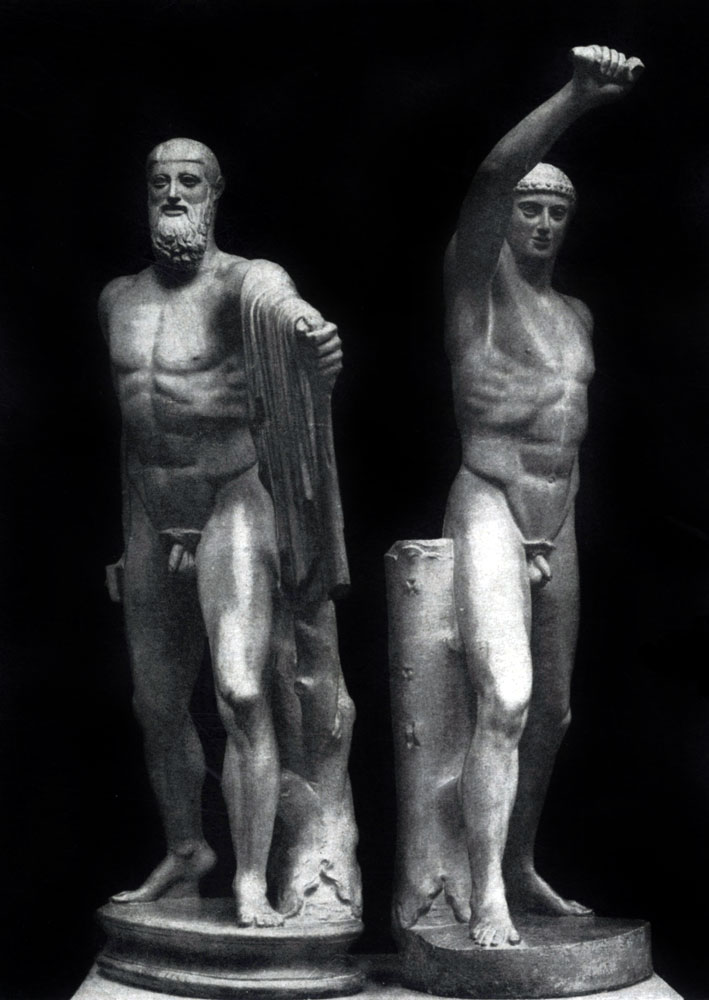

In the "Garmody and Aristogiton" for the first time in the history of the monumental sculpture, the task of constructing a sculptural group, united by a single action, a single plot was delivered. Indeed, for example, the Archaic sculpture of "Kleobis and the Biton" of the Argossky polymer can be considered only conditionally as a single group - essentially it's just two stories of the statues of kuros, where the relationships of the heroes were not shown. The harmony and aristogon are united by a common action - they strike the enemy. The movement of the figures made separately and delivered at each corner to each other in which an imaginary opponent stands. The unified direction of movement and gestures of the figures (in particular, the harmony's hand is created) creates the necessary impression of the artic wholeness of the group, its compositional and plot completeness, although it should be emphasized that the movement is interpreted in general, very schematically. Lisured expressions were the faces of the heroes.
According to those who have come down to us in the ancient Greek sources, leading masters who have determined the decisive turn of sculpture of the 70s - 60s. 5 V. BC. To realism, there were Agelad, Pythagoras Register, Kalaside. The idea of \u200b\u200btheir work to some extent can be compiled in Roman copies from the Greek statues of this time, and most importantly, for a number of preserved genuine Greek statues of the second quarter of 5 V. BC, made by unknown masters. The overall picture of the development of Greek sculpture until the middle of 5 V. BC. You can imagine with sufficient clarity.
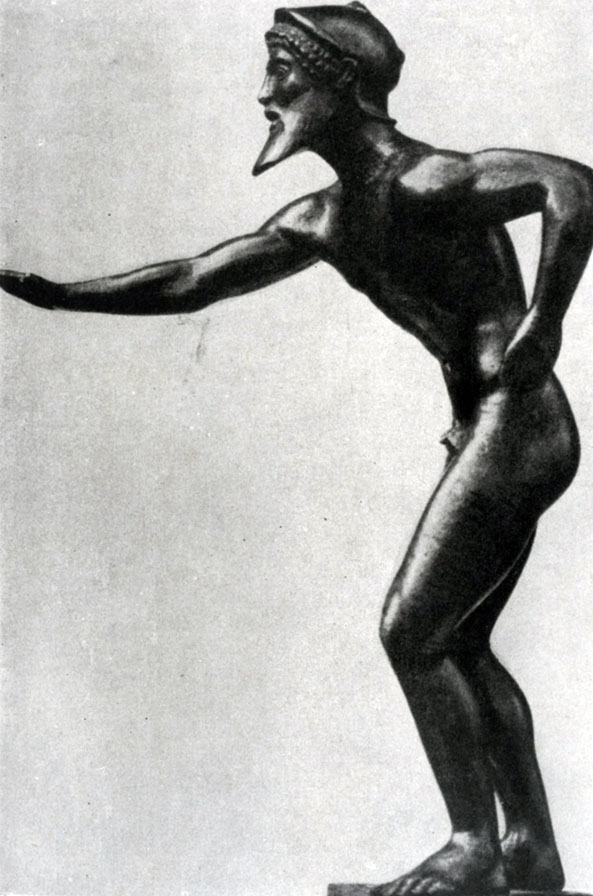

The concept of Greek art 70 - 60s. 5 V. BC. Also give small bronze statuettes that have come down to our time. Their meaning is particularly great because the bronze Greek originals, with rare exceptions, are lost and judged about them are far from accurate and dry Roman marble copies. Meanwhile, it is for the 5th century. BC. The wide use of bronze as a material for monumental sculptures is characteristic.
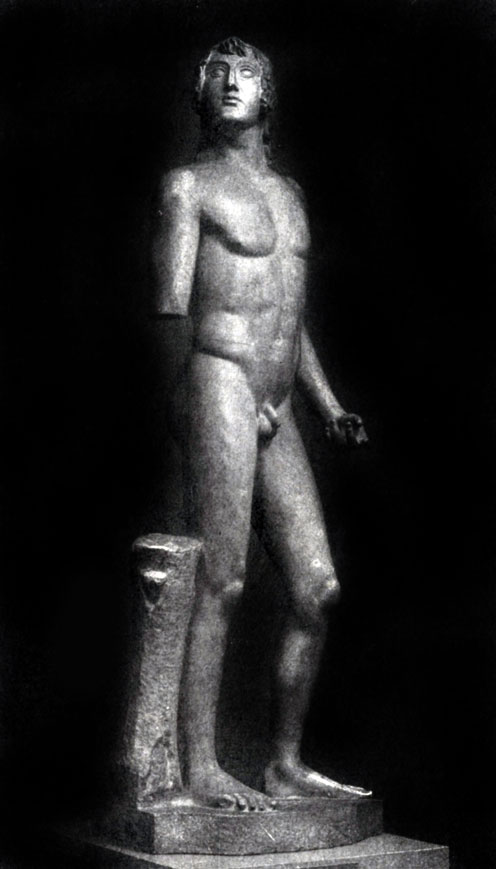

One of the most consecutive, innovators of the initial period of early classics was, an obeyable, Pythagoras Regisis. The main goal of his creativity was a realistic image of a person in natural life movement. Thus, according to the description of the ancients, his statue "wounded Philoktt" is known, striking contemporaries to the truthful transmission of human movements. Pythagora Zapysky statue "Hyacinth" or (as it was called before) "Eota Sorano" (State Hermitage, Roman Copy). The master depicted a young man at the moment when he follows the flight of the disk abandoned by Apollo; He raised his head, the severity of the body was transferred to one leg. The image of a person in a holistic and single movement is the main artistic task that the artist put in front of him, strongly discarded the archaic principles of a strictly frontal and stationary statue, consistently and deeply developed the features of realism accumulated in the art of Late Archaic. At the same time, the movement of "Hyacinth" is still a few cutting and angular; Some stylistic features, for example, in the interpretation of hair, are directly adjacent to archaic traditions. In this statue, new artistic tasks are boldly and sharply, but not fully created by these tasks is a slim and consistent system of the new artistic language.
Realistic vitality, inseparable merging of philosophical and aesthetic principle in an artistic form, the heroic typing of a real person's image is the main features of the folding art of classics. The socio-educational value of the art of early classics was inextricably and naturally merged with its artistic charm, it was deprived of any elements of deliberate moralization. A new understanding of the tasks of art has also affected the new understanding of the image of a person, in a new beauty criteria.
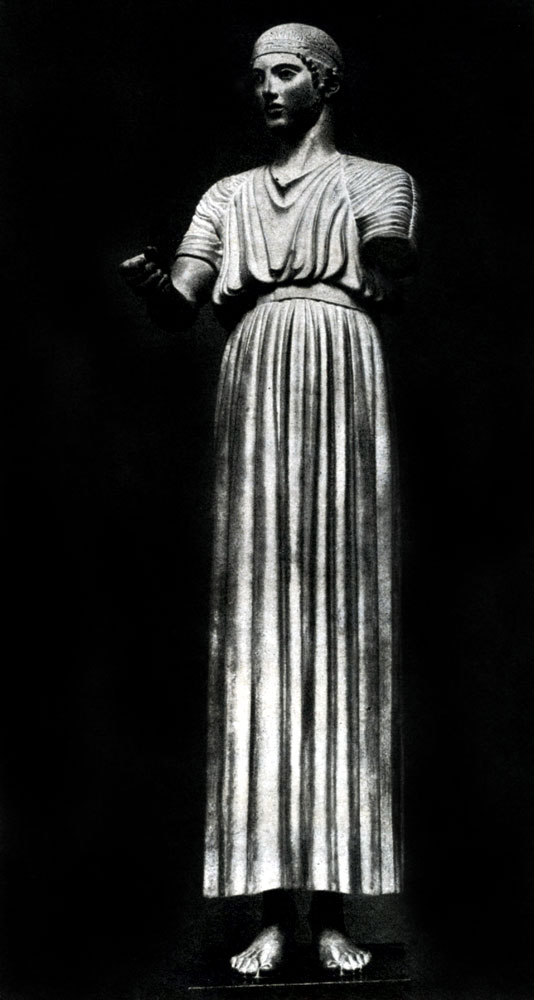

The birth of a new aesthetic ideal is particularly clearly revealed in the image of the "Delphian edition" (the second quarter of the 5th century BC). "Delphic cat" is one of the few of the authentic ancient Greek bronze statues to us. She was part of a large sculptural group, created by the Peloponnesian Master, close to Pytagora Village. The harsh simplicity, the calm greatness of the Spirit is spilled in the entire figure of the eager, dressed in long clothes and standing in strictly fixed and at the same time natural and vibrant pose. The realism of this statue is primarily a sense of significance and beauty of a person who is permeated with the whole figure. The image of the winner on competitions is generalized and simple, and although individual details are made with great care, they are subordinated to the general strict and clear line of statues. In the "Delphica" was already expressed already in a sufficiently determined form characteristic of the classics, the idea of \u200b\u200bsculpture, as a harmonious and vital image of the typical features of the perfect person, shown in such what should be every free innocence.
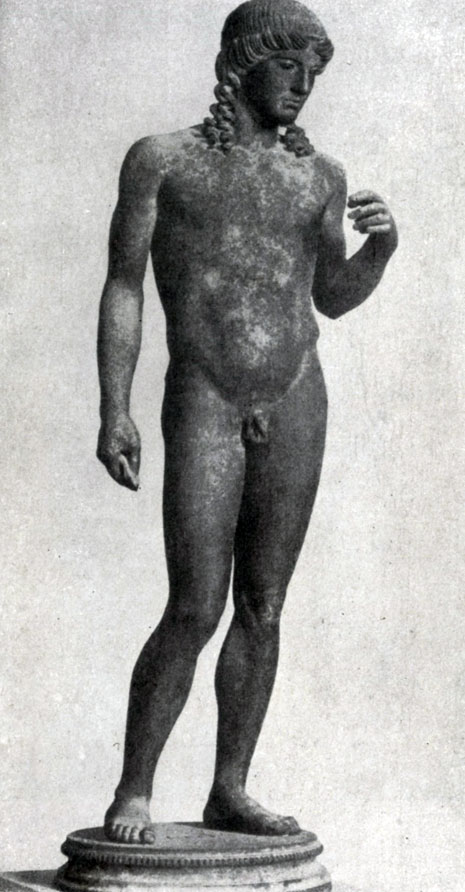
The same realistic typification of a person's image was fully transferred by masters of early classics and on the images of the gods. "Apollo from Pompeii", which is a Roman replica of Greek (North-Route) statues of the second quarter of 5 V. BC, differs from archaic "Apollonov" not only incomparably more realistic modeling of body forms, but also by a completely different principle of composite decision of the figure. All the severity of the body is transferred here to one left foot, the right leg is slightly moved away to the side and forward, it is easy to turn the shoulders in relation to the thighs, slightly inclined on the side of the head; The hands of a beautiful young man, how the god of sun and poetry is depicted here, are given in a free and relaxed movement. At first glance, these seemingly small changes in that period of accumulation of realistic funds were actually extremely important: each change in artistic techniques, who focused on the archaic, was not just technical innovation, but an expression of new features in the worldview.
In such statues, the conditional frontal composition was completely overcome and the conditioned stiffness of the archaic statues was completely overlooked. Although at the end of the 6th and most early 5th century. BC. A number of masters and tried to process the scheme of the Archaic Statue of the Kuros in this direction, still successfully solve the task of an image of a natural, organically holistic movement, artists managed only after deep changes in all artized worldview - in the years after the victory in Greco-Persian wars.
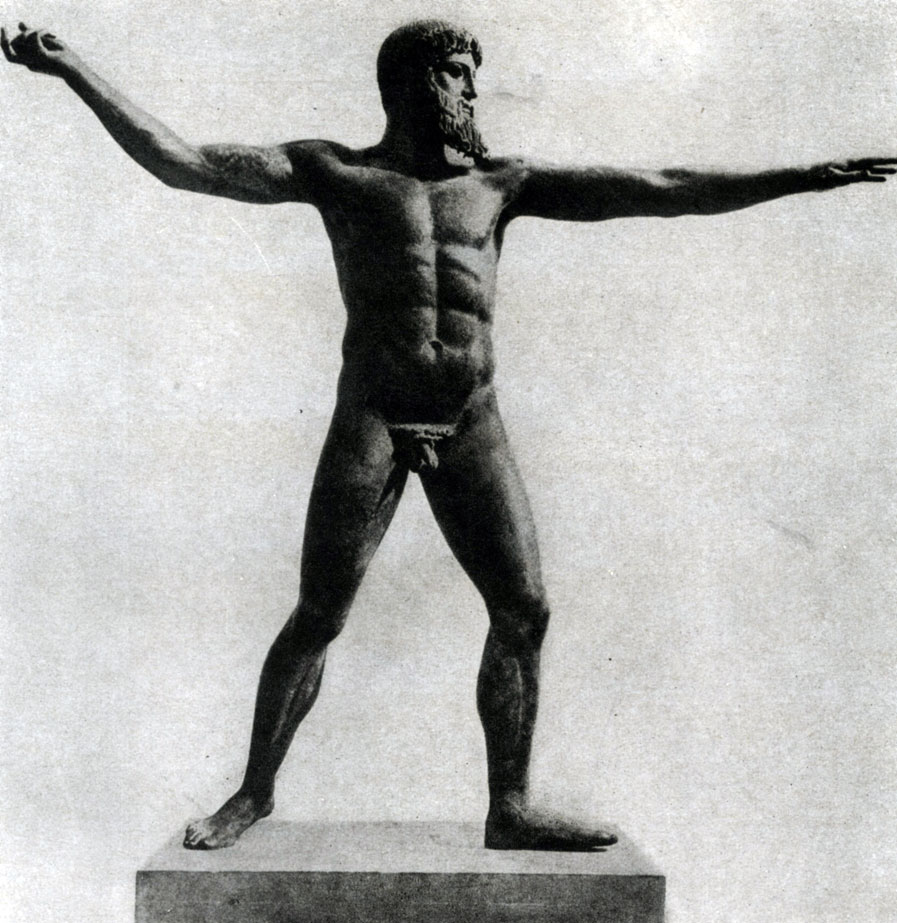

The heroic character of the aesthetic ideals of the early classics received its perfect embodiment in the bronze statue of Zeus Studacity, found in 1928 at the Sea Day off the coast of Evbei Island. This large statue (more than 2 m high) along with the "Delphian Call" yes, we have a clear idea of \u200b\u200bthe wonderful skill of the early classics. Zeus Thunderzzts compared to the "Wind" differs even more realism in the modeling of body forms, greater freedom in movement. Wide apart, slightly bent legs give elasticity to the rapid step of the figure. Undoubtedly, the full of the majestic power of a wide sweep of the hands of Zeus was gorgeous (even in the wreckage), far brought back his right hand with a zipper chosen in it, which he raises an enemy in an invisible enemy, in whose side his spiritualized face was drawn. Muscles of mighty torso are tense. The game of light glare on dark bronze, undoubtedly, even more emphasized the strong modeling of forms. In the statue of Zeus, the Rulerizz was well solved by the task of expression in the sculpture of the general mental state of the hero. This bronze statue of Zeus may be close in its character's creativity of Agelada, the master who created a number of statues known in the ancient times, in which he (judging by the descriptions of the ancients) made the most important step towards improving the realistic transfer of the human body in motion or alone, full of restrained revival.
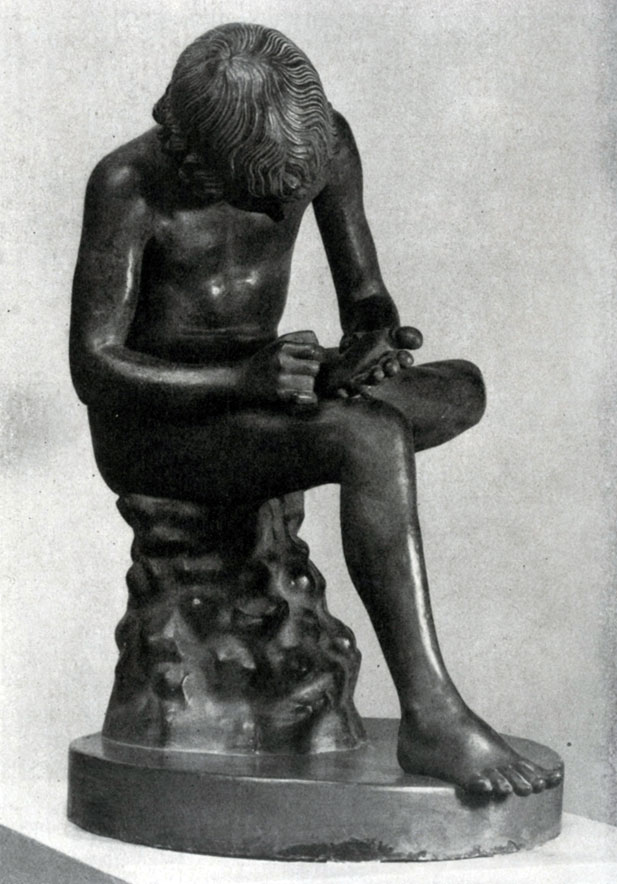

On the development of the sculpture of the early classics in the direction of the "Boy, takes out the ubanist", which came to us in the marble Roman copy from the Bronze Original of the second quarter of the 5th century. BC. A boy figurine is distinguished by the naturalness of angular poses, realistic transmission of the body forms of a teenager. Only hair, as if not subject to the strength of gravity, are given somewhat conditionally. Life observation reminds here the full realism of the scene on the vase drawings of this time. However, this is not just a genre sculpture. The statue talks about a teenager that glorified by his valor during the competition in Run. A sharp spike stood in his leg, but the boy continued running and first reached the goal.
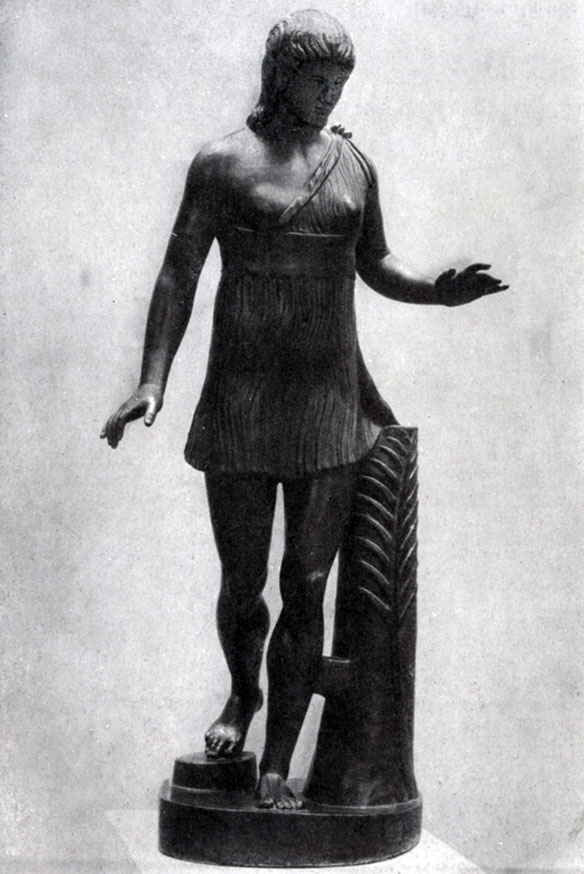

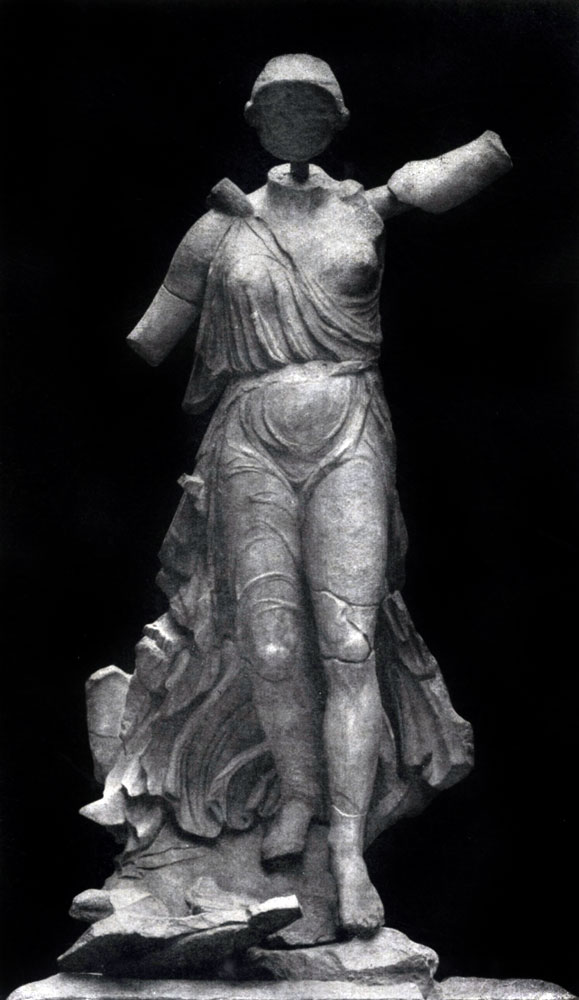
A great success in the image of a real movement and at the same time in the creation of a realistic truthful and typical image was the emergence of such statues as the "winner in running". At the change of angular sharpness of "hyacinth" and other early classical statues, a strict harmonic unity came, transmitting the impression of naturalness and freedom. Dressed in short chiton, with an open right breast, the girl is depicted at the end of the run. The impression of a slowing run has been achieved by a slight movement of slim legs, a slightly catchy turn of the shoulders, settled on the sides. The statue was made of bronze; Roman copist, repeating it in marble, added a gross backup.
Artists of the second quarter of the 5th century. BC. did not know complex internal characteristics. But, by depicting the real appearance of a person and his actions, they invariably transferred the whole system of his spiritual life and character.
So, despite some sharpness and angularity of the movement, deployed in the same plane, undoubted drama is distinguished by a wonderful statue of "wounded Niobida", stored in the Museum of Term in Rome. This statue may have entered the front-distance group that did not reach us.
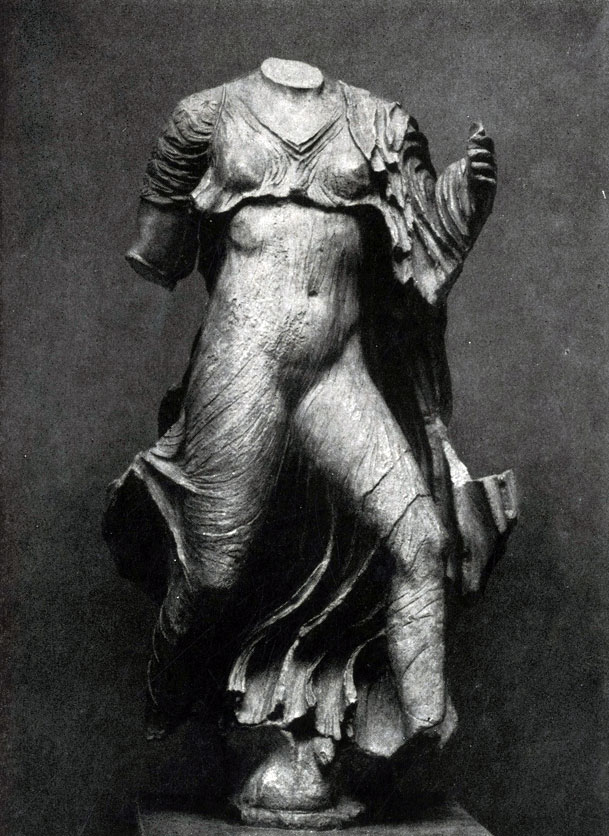
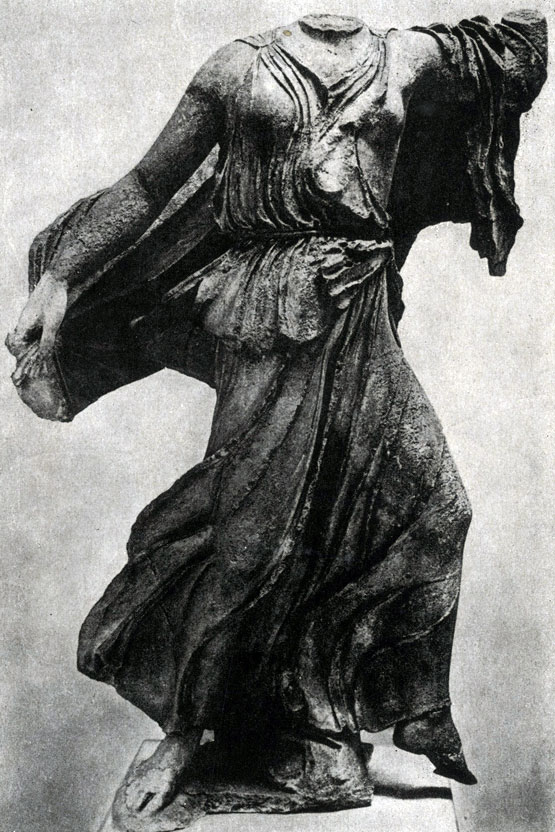



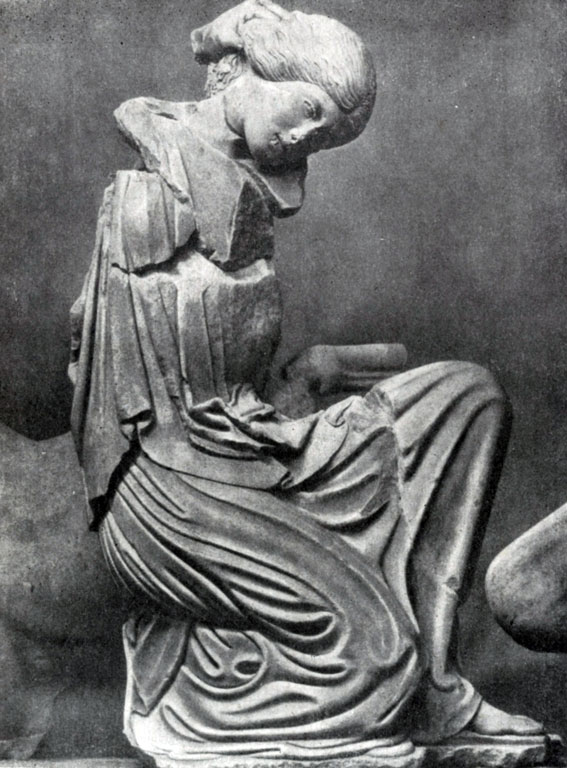
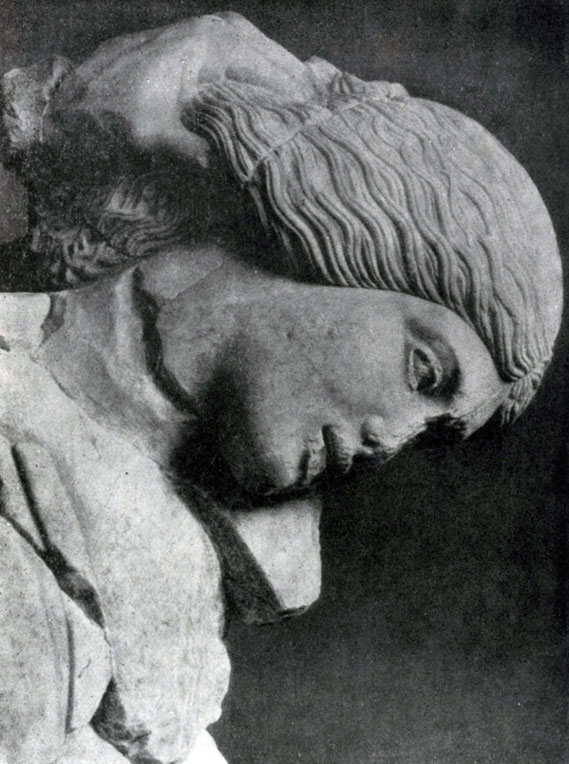
The task of the image of the human body in all its life naturalness was also put in the statues of "Nereid from Xanf", performed by the Ionian master near the middle of 5 V. BC. "Nereides" decorated "Monument Neremid" in Malaya Asia. The extensions of the archaic scheme of the "knee-free run" are still noticeable in the interpretation of these figures (legs, data in the profile, do not quite correspond to the position of the upper part of the body). However, "Nered" is distinguished by the unusually vibrant body modeling, which contributes to the elegance of thin, as if the flowing folds of their clothes.
A vivid example of rethinking the usual mythological plots during the years of radical breakdown of the traditions of the archaic and the formation of art classics is a wonderful relief, fulfilled, probably also by the Ionian master of the second quarter of the 5th century. BC. and the birth of aphrodite from the marine foam (the so-called "Trone of Louds"); On the side of this marble "throne" or, rather, a nude girl playing on the flute, and dressed in long clothes. Woman in front of a smokehouse is depicted. Clear and simple harmony, the calm naturalness of the movements of the figures and the realistic vitality of their grouping sharply distinguish these works from archaic reliefs.
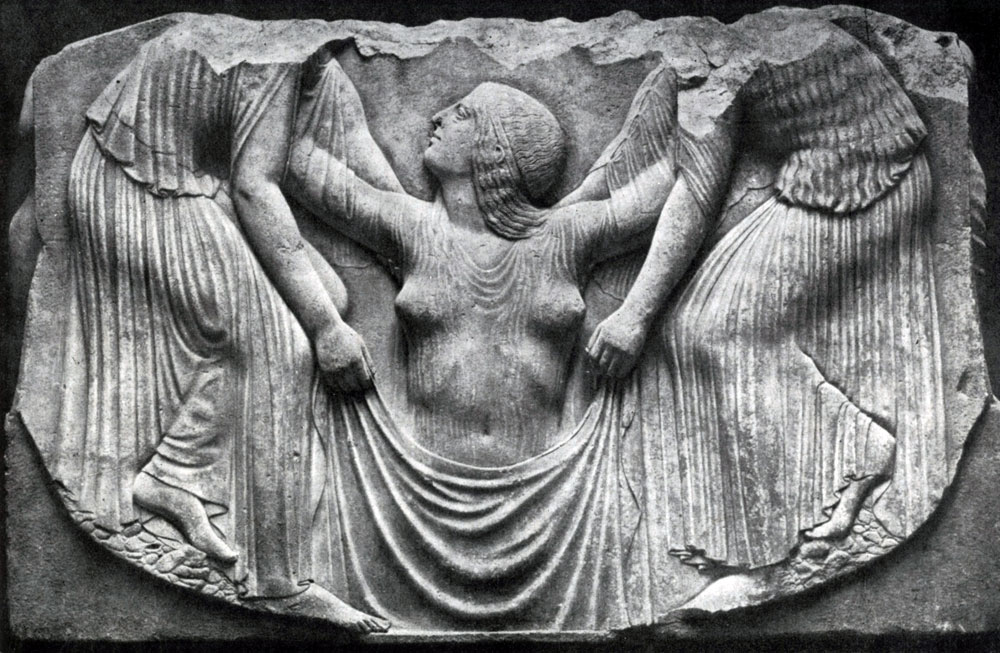
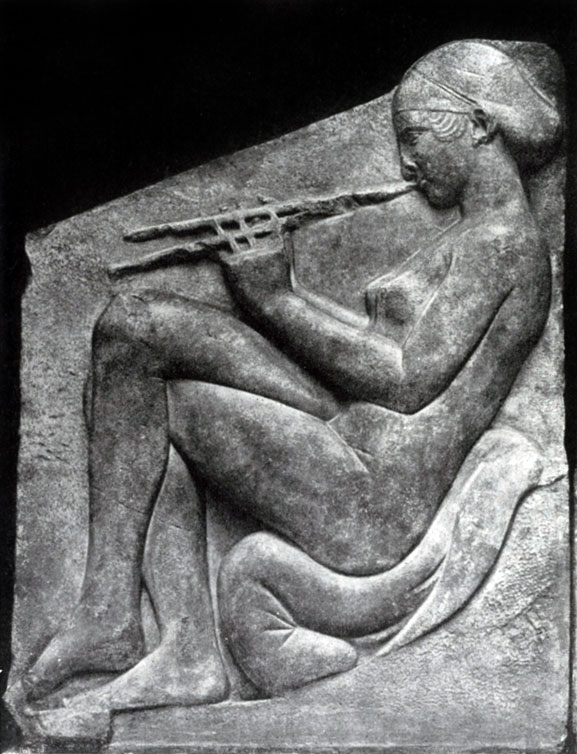



On the central of the three sides of the "TRONE LUDUDIZI" - two nymphs, bending, maintain the emerging from waves Aphrodite; The calm rhythm of the movements of the raising Aphrodites and straightening the nymph corresponds to the rhythm of the thin folds of their clothes. The focal body Aphrodite wet peplos covers it with a thin network of wavy lines, similar to water jets. Sea pebbles, on which the nymph fellows, speaks about the place of action. Although in the strict symmetry of the composition and there are echoes of archaic art - they can no longer disrupt the realistic vitality of this relief.
The nagging girl pictures are depicted on the sides of the central group, and a woman, wrapped in a raincoat and the delight of the gods, compositionally almost identical to each other. However, the entire group is far from the purely decorative ornamental symmetry of the archaic composition. Figures Volta and three-dimensional, they are given in natural and free poses. The sitting girl at ease leaned back. One leg is thrown on another, the real spatiality of the relief is especially emphasized. Her figure is full of grace. Fingers easily and quickly slide on flute. The pose of a sitting young woman - wife and mother, the keeper of a homemade hearth - stricter, still, the movement of hands is calm and measured. Both of these figures, in their difference, embodying different sides of beauty and love, as far as Aphrodites are combined, under whose power they are equal to different directions of the ministry of which they are both embodied. From the mechanical combination of figures that had abstract-symbolic nature, art turned to a holistic, organic and living artistic image, in which the main ethical and aesthetic ideas were embodied.
Thus, the Greek sculpture of the early classics to the 50th gg. 5 V. BC. Passed an extremely big way of development. The next important step to the high classics was the frontal groups and the methops of the temple of Zeus in Olympia (50s. 5 V. BC).


The general style of Olympic sculptures is already approaching the style of Mirone sculptures. PAsani attributes the authorship of the sculptures of the frontones of the temple of Zeus Penilation from Mende and Alcamen senior, but there was no confirmation yet. In any case, the authors of these sculptures were first-class artists.
East Fronton is dedicated to the myth of the Pellops contest and Enonaya, which put the founding of the Olympic Games, the West - the Battle of Lapiphs with Centaurs. Both fronton differ sharply from the frontones of the Eginsky temple with their decorative conditional composition. The masters of the Olympic Fronton understood the sculptural group first as an image of a real event. The location of the figures is determined primarily by the meaning of the event, in the participation in the event, which is characteristic of each shape. The equilibious composition in this case contributed to the strict clarity and integrity of the story. Statues of the Olympic Temple are remarkable with genuine realism. Not accidentally open in the 70s. 19th century Sculptures of Olympia caused a well-known disappointment in the archaeologists and art historians of the time representing the art of 5 c. BC. As a certain "ideal" and "harmonious" art and "shocked" harsh strength of realism and the "coherent" images of these wonderful monuments, adequately completing the period of realistic search for early classics.

Refusing the complete submission of the sculpture image to the tasks of the decoration of architectural forms, the sculptors of the Olympic frontons established other and deeper links between the architectural and sculptural images, which led to their equality and their mutual enrichment and the most consistent expression found a quarter of a century in the fidium built under the leadership of Fidiya Parfenone.
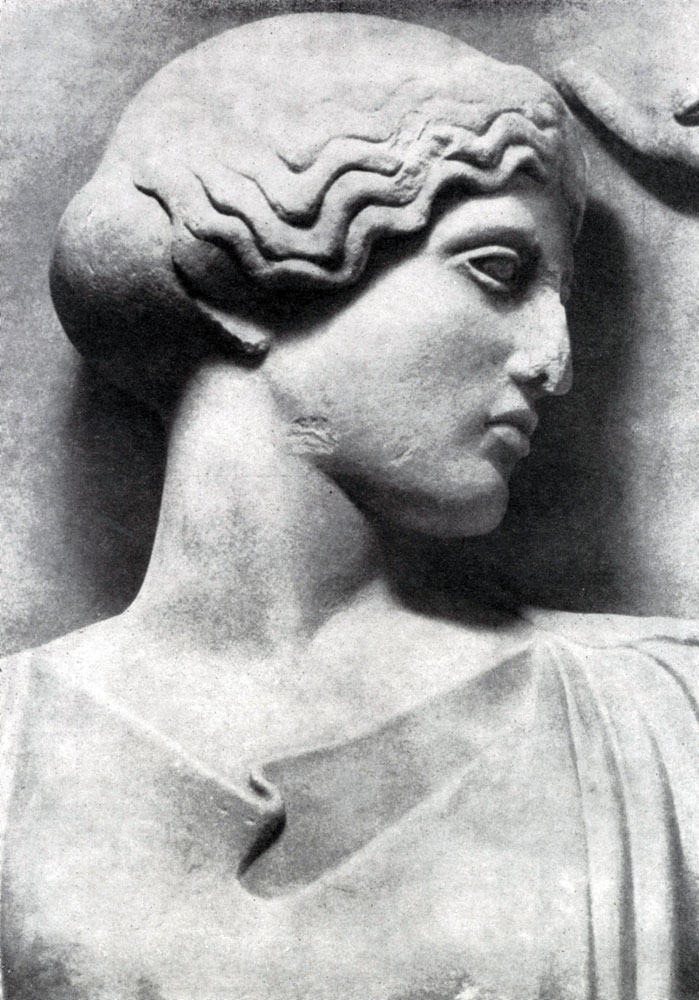
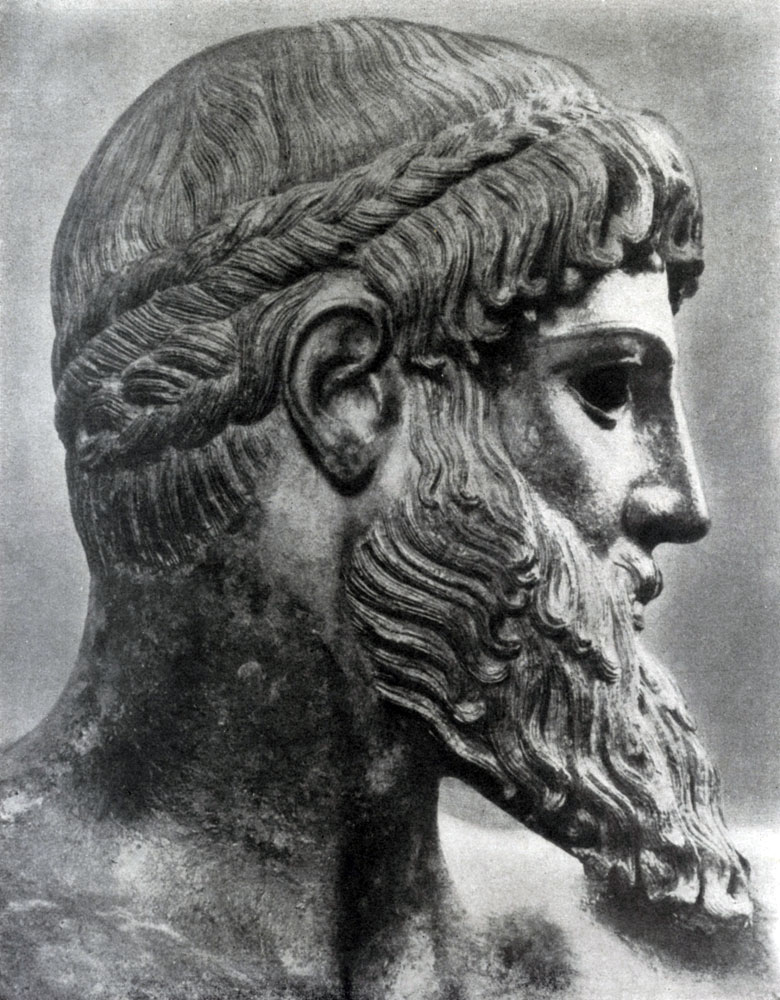
The myth to which the East Fronton of the temple of Zeus is devoted to the next. The king Enonoy was predicted that he would die of her husband's hand of Hippodami. To avoid this fate, Enonai, who had fabulously fast horses, announced that his daughter's hand would receive the one who would win him in a contest on chariot. The defeated had to part with life, and many grooms were killed by cruel and insidious Enonoma. Finally, Pelops, with the help of tricks, managed to defeat Enonaya: the arcing enzyme enhancing the check from the chariot axis and replaced it made from wax. Enomai crashed to death during the competition. The East Fronton of the Temple of Zeus depicts heroes before starting the contest. The majestic figure of Zeus in the center of the fronton, solemn rest, covering all participants in the events, gives the fronton that strict and at the same time, which corresponds to the composition located above the main entrance to the temple. The absence of sharp movements, almost symmetric location of figures at all, however, do not lead to frosts and immobility. This one is apparent, he is full of internal tension.
Although the statues of the Eastern Frontone reached our days in a highly destroyed state and their location is also completely not yet established, yet the overall nature of their poses and gestures can be represented with sufficient reliability. In any case, five central figures - Zeus, Enomai, his wife Sterrup, Pelopes and Hippodami, - standing in calm poses, as if answering the strict rhythm of the columns over which they are tested, with the symmetry of their arrangement, are very different and individual in their appearance and gestures. .

One of the greatest conquests of classical art was that it managed, unlike the art of the Ancient East, to show the role and significance of each person in its relationship with other people, to give it not as an impersonal particle dissolving in general, often ornamental strictly - by a multifigure composition, namely, as a person, as a conscious participant in a common action, which occupies a clear and certain place in it. In the Olympic frontones, many important parties to this conquest of classical art were found for the first time.
Parties from the central group on the Eastern Fronton were placed chariots with horses, servants, viewers, in the corners of the fronton - lying figures, personifying local rivers. Some of these statues differ particularly sharply underlined realistic truthfulness - so, for example, a thoroughly transmitted dyeing body of a sitting old man or a rude gesture of the boy pulling off the city. You can even think that the master who created this fronton consciously sought to emphasize his gap with the old principles of archaic conventionality, showing that in his figurative thinking he comes from life, and not from the conditional scheme.
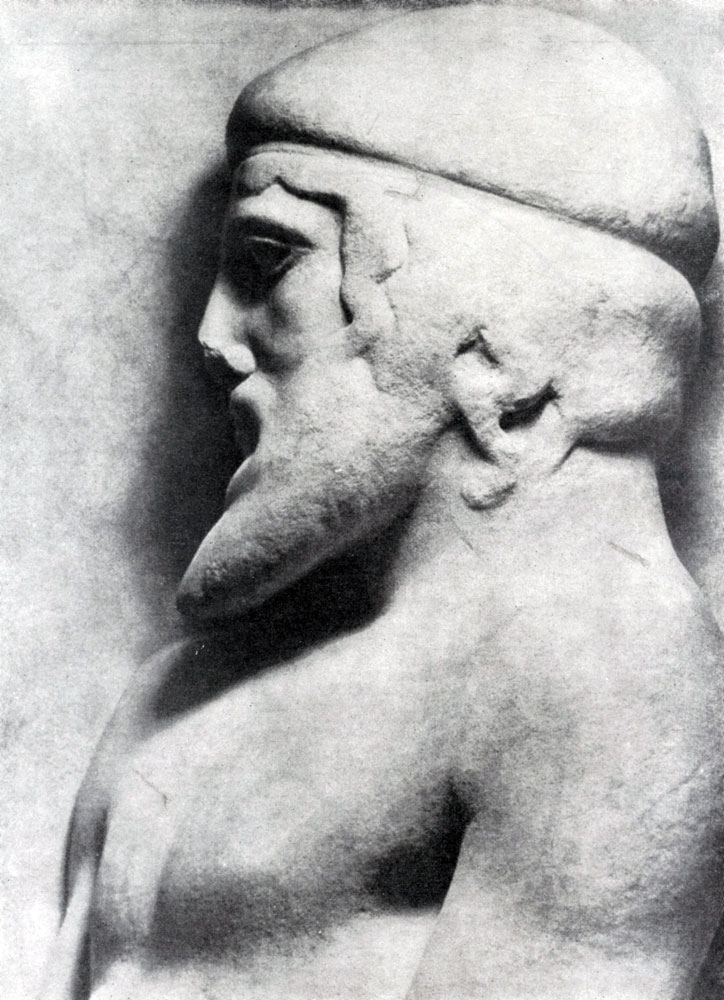
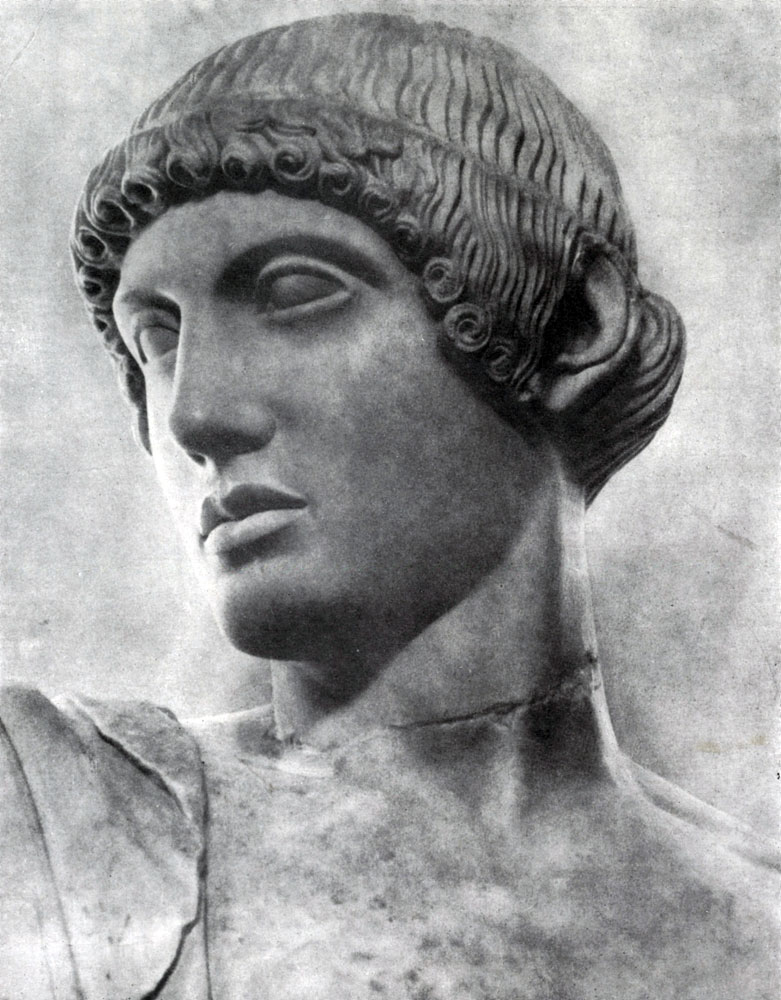
The realistic principles of the sculptors of the temple of Zeus in Olympia were particularly clearly revealed in the composition of the Western Frontone, depicting the battle of lapiphs with centaurs. This Fronton reached a relatively less damaged form and caused less disagreement relative to its reconstruction. Particularly valuable is that many of the heads of statues have been preserved here, highly committed in their execution. For Western Fronton, as well as for the Eastern, characteristic of the general compositional equilibrium of both half of the frontonone is characteristic of strict symmetry. This fronton with a large statue of Apollo in the center consists of a number of separate groups of battle and fighting people and centaurs; The groups are regularly backed by the total mass and intensity of the movement, without repeating at all one different. Fights fighting exactly inscribed into a gentle triangle of the fronton, and the voltage and sharpness of movements increase to the corners of the fronton - as they remove from the calm figure of Apollo. Its strict and clear face and the domineering, the guide gesture, which he indicates Lapipham, how to overcome wild and violent centaurs, serve as a kind of psychological and dramatic center of all this complex and at the same time easily foreseeable composition.
Central standing figures - Apollo, Tezay and Perifa - Again, as I am in Eastern Fronton, to some extent repeat the measured rhythm of the colonnade, thereby seemingly emphasizing the calm power and the confidence that they contribute into the battle tension. In action, in the heroic struggle with hostile person, the spirit of masculinity and unity, which is embodied in the architecture of the temple of Zeus.

In the myth shown in the front-distance group, it tells how those invited to the wedding of the king lapiphs of the Periphoy Centaur, the semi-semi-semoreties, personifying the lower natural forces of nature, rushed to abduct Lapife women. We led by theses and the periphy and inspired by the support of Apollo, the lapiphs destroyed the centaurs. Although the Battle of Fronton is shown in full swing, the victory of people is clearly predetermined. Created by an unknown artist's images of Apollo, the bride of Periphoy - Deidamy or women captured by a centaur for hair belong to the number of the most perfect and most attractive creatures of the early Greek classics. The struggle of human will and mind with an outbreak of natural and unbridled forces is that complete humanity is a heroic idea that this wonderful sculptural group is penetrated. However, the difference in lapiphs and centavrov is given here within the common aesthetic norms; The laws of beauty act in the image of ugly centaurs, traded without any naturalistic underlining.



Images on the Metops of the temple of Zeus, dedicated to the exploits of Hercules, close in their spirit of the frontal compositions. Metop reliefs are distinguished by the laconic simplicity and clarity of images, bright expressiveness. The location of the figures on the Metops, the nature of their movement is closely related to the architecture, without disturbing the borders allocated to the relief architectural design. So in a metope depicting a herakla supporting the Heavenly Code with Athens, and the atlas carrying apples hesperd ( According to myth, Hercules was supposed to get gold apples from the Garden Heper on the edge of the light. Hercules turned to the atlas supporting the Heavenly Code, with a request to get these apples to him. Atlas agreed on the condition that Hercules will exercise heavenly arch for him.), All the figures with their verticals repeat the vertical of the columns and framing triglyphs. At the same time, the horizontal of a heavy cornice lying on the frieze is used to transmit the sensation of the severity that herakli carries; His hands raised above their heads, as they support the design of the cornice.
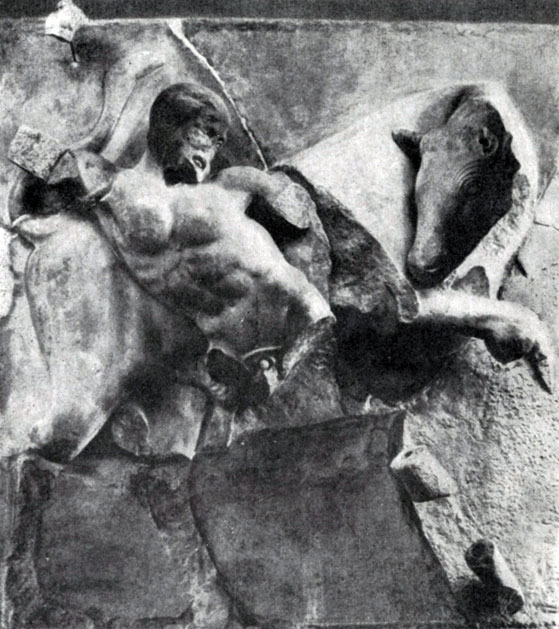


Very expressive Metope dedicated to the fight of Hercules with Cretan Bull. Crossing the different directed movements of the herakla and bull create a stable composition included in the square methopas; The movements of these figures coincide with the diagonals of the square and thereby include in the overall system of geometric relations and proportions characteristic of the architectural structure. At the same time, strictly equilibrium of the composition did not prevent the sculptor to approve the victory of a man: the free and bold movement of Hercules is full of energy and rapidness, the strength and will of the hero are triumphant over the power of the bull.
The effective and morally significant image of the Hercule's National Hero did not accidentally appear on the frieze of the Olympic Temple of Zeus, as well as the battle with Centaurs on his frontonone. For the art of Greek classics, a real person is his alive feelings and heroic feats became the main topic.
The image of a citizen and warrior, a person harmoniously developed their physical and moral qualities, became central in the art of classics. However, human labor, the conditions of his life, the connection with the environment relatively little and was rarely depicted in the Greek monumental art of the classical period. The image of a person has revealed specifically, but social life is only indirectly. For Greek classics there was a natural expression of public conflicts and behavior standards in the images of fabulous and mythological.
Realism of the classics 5 V. BC. Visited his own, only his characteristic means of expression. Thus, the proportions of the body and diverse forms of movement already in early classics became the most important means of characteristics of the overall state of the spirit, which corresponded to this movement. This feature of the art of the classics has developed during the second quarter of the 5th century. BC, having achieved complete disclosure in the sculptures of the Olympic Temple. The disclosure of realistic meaning and artistic expressiveness of the gesture was one of the biggest conquests of the Greek classics, which carried the path to a truly realistic image of a person in all the vital truth and the integrity of his being.


Slower and with great difficulty, but also a person's face in a classic sculpture was freed from the psychological frost and distracted imperference, which was characteristic of archaic Greek sculpture. Indeed, the face of the "Delphian edition" is imbued with a clear seriousness, the look "Zeus Thunder" Surov and Grozen, the faces of the battle of Centaurs on the Western Frontone of the Olympic Temple are distorted by rage, the face of Apollo, Iri all his strict generalness, expresses the domineering gust, anger, who is a volitional voltage. But nowhere here typical generalization is combined with the individualization of the image. The personal peculiarity of a person, a unique warehouse of his character far from a complete measure included in the circle of interests of artists of Greek classics. This side of the realistic disclosure of a person's image was able to turn around in advanced art only after a fracture from the Middle Ages to a new time - in the Renaissance Epoch, in 17 or 19 V.

The creation of a true and deeply significant typical image of a person as a rule and sample for each person-citizen had a greater importance for Greek classics than the disclosure of an individual human character. This was a huge force and at the same time the border of the realism of the Greek classics. Therefore, in the Olympic sculptures, quite real and various mental states are generalized, there are no complex and psychologically in-depth experiences.
The following feature of the Greek sculpture is connected with this and generally the Greek Fine Art of Early and High Classics: the person of man has not yet taken against the human body of the preemptive or exclusive right to transfer mental life. She is equally expressed in the whole body, in all his movements, including the facial expressions of the face.
This feature has largely determined the peculiar nature of the development of a portrait in Greek classics. Initially, the most common type of portrait (in its intended purpose) of the sculpture was the statue of the winner at the Olympic competitions. But the winner, from the point of view of the ancient Greeks, was honored with the statue for the fact that his victory argued the fame of his native city, for playing as a courageous and exemplary citizen, becoming a model for others. The statue of the winner was ordered by the city-state to glorp the winner, but at the same time for the glorification of the city, whose representative was the winner on competitions. Naturally, it was in such a plan that he was portrayed by an artist. The valiant spirit in a harmoniously developed body was considered the most valuable in man. But these properties are the Greek young man, the participant of the Olympic Games, really and possessed. Therefore, probably the community and the winner itself quite satisfied that his name stood on the pedestal, on which the typical-generalized beautiful statue was treated.
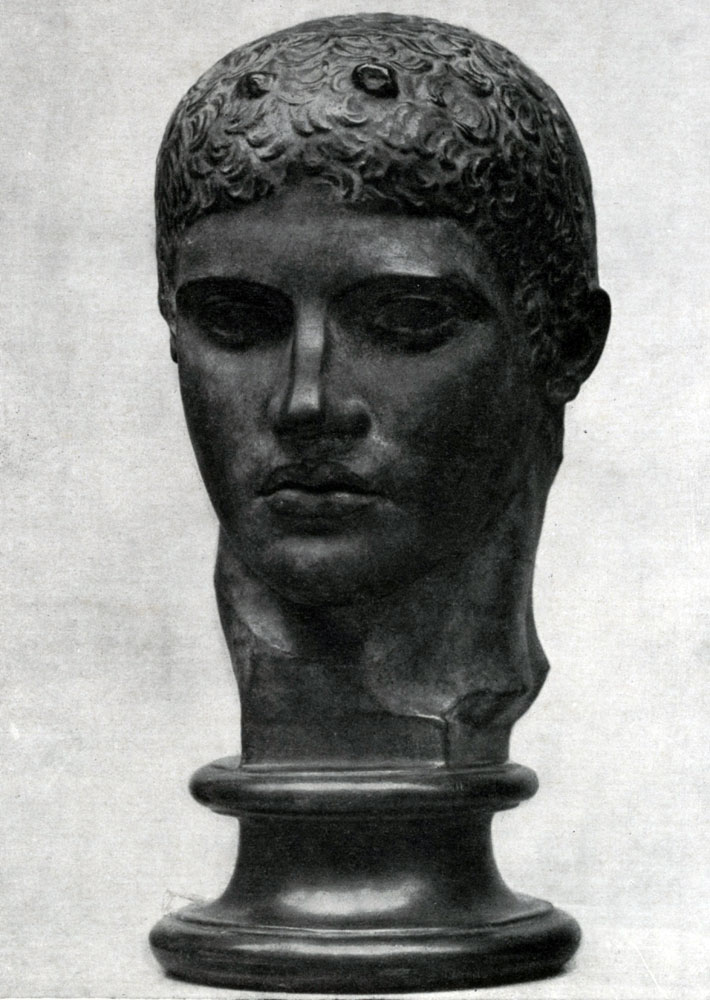
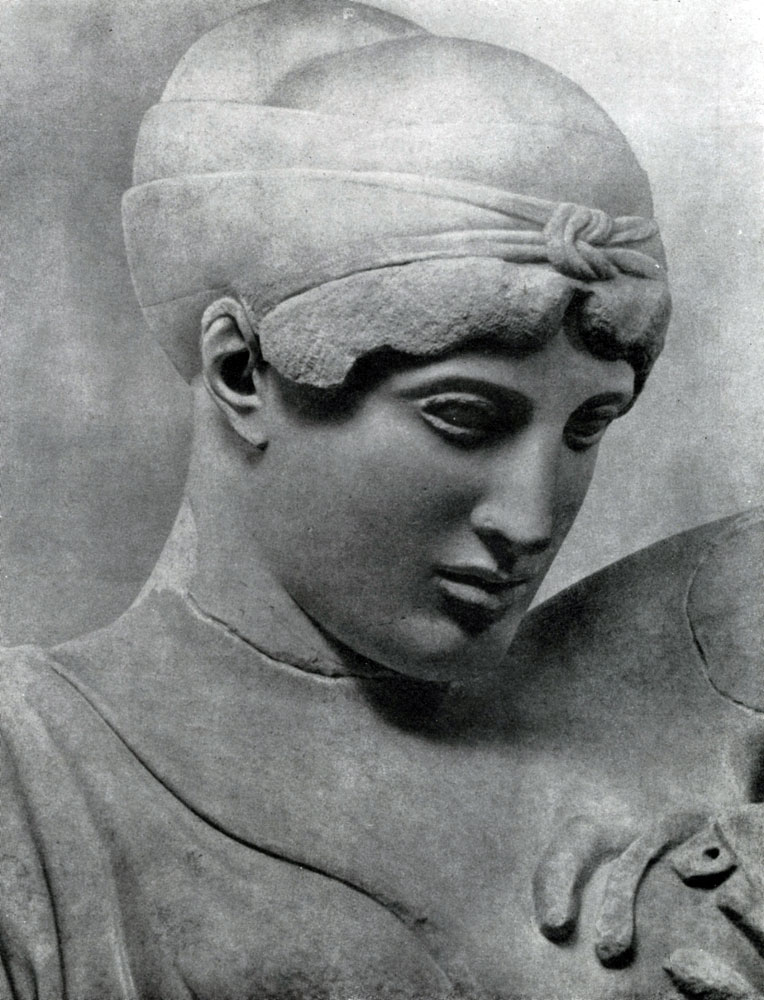
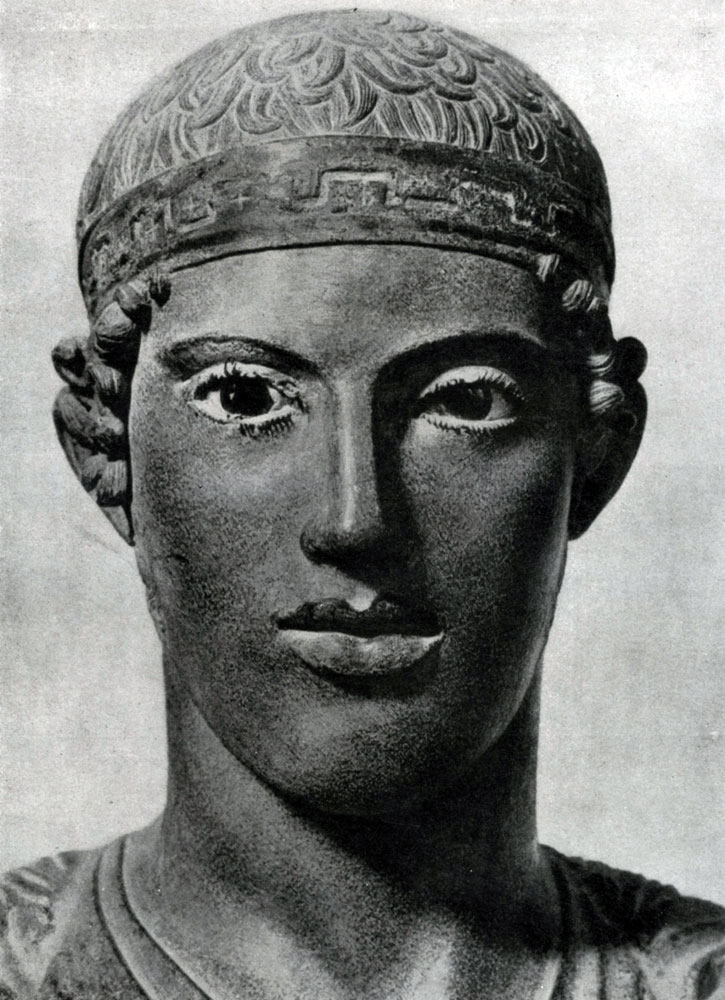
The first portraits in their own sense of the word who were honored by citizens outstanding with their merits before the policy and elected to one of the most honorable and responsible public posts, were also deprived of a sharply pronounced individual characteristic. Portrait of a strategist (in Munich Gillotek) gives us an idea of \u200b\u200bthe portrait of this period: Face forms are transferred very generally and simply, with harsh expressiveness. The artist created an image of a statesman, calm and decisive, but this image does not convey unique features of the character of this person. Yes, and signs of pronounced external similarities are unlikely to occupied the sculptor.
With the greatest strength of creative quest for early classics, her search for heroic, typical generalized images was expressed in the activities of the great Greek sculptor of Miron from Eleutzer. Miron worked in Athens at the end of the second and at the beginning of the third quarter of the 5th century. BC. Genuine works of Mirone to us did not reach us. They have to be judged by marble Roman copies.
In an effort to unity of harmoniously beautiful and directly-life, Miron was freed from the last extensions of the archaic convention, from angular sharpness of movements and at the same time from a sharp underlining of the details, to which the masters of the second quarter of the 5th are sometimes resorted to. BC, who wanted to give a special truthfulness and naturalness to their statues. It is in the work of this attic master that ionic and doric artistic traditions are finally merged. Miron became a master that synthesized in his work the main qualities of the realistic art of early classics.
With the greatest force, the features of the art of Mirone are expressed in the "discobole", described in the following expressions Lucian: "Do you not say about the disk thrower, which leaned in the movement of throwing, turned his head, looking at his hand holding the disk, and slightly bent one leg, As if preparing to straighten up simultaneously with the blow. " "Antique poets about art", M., 1938, p. 60.). It came to us somewhat not always accurate, and sometimes not fully preserved Roman copies of the famous statue of Mirone. Of great interest is the bronze statuette 5 V. BC, depicting a dyscompetutor, apparently, a modern statue of Mirone. The image of the picture reproduces the cast, which is synthesizing on the basis of the description of Lucian's best Roman copies.
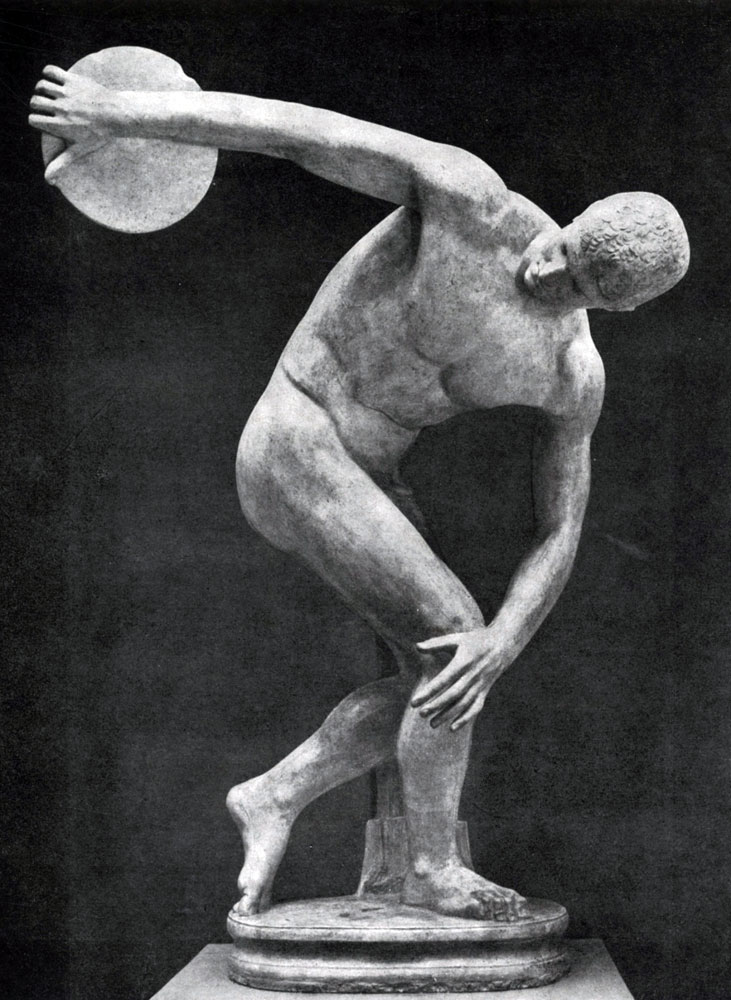

"Discobol", like many other statues of this type, is raised in honor of a certain person. The artist's focus was the task of an image of a strong and beautiful spirit and human body, which is in a tense and rapid motion. Miron depicted a disc thrower at the moment when he puts all his strength into a disc. Despite the tension that permeates the figure, the statue produces the impression of stability. This is determined by the choice of moment of movement: a moment of transition of one movement to another, the culmination point in the development of motion was taken.
Elastic bent bent and tightly resting his foot in the ground, the young man threw back his hand with a disc. Another moment, and the body, as a spring, rapidly straighten, the hand with force will throw off the disk into space. The moment of rest attaches monumental resistance to the image, but in this moment the completed movement and the comprehension of the entire subsequent movement are combined, the action of the hero is covered in its entire finished completeness, in its entirety. The specific viability of the movement of the merge with clear finishes, the integrity of the image, which was so close to the Greek aesthetic consciousness, who considered beautiful only what was clearly expressed by the basic essence of the phenomenon. The composition of the statue reduces the complex and controversial motive of the movement to a few clear and vital convincing gestures, which gives a feeling of concentrated, concentrated force. Despite the complexity of the movement, in the statue of the "discobol", as in general in the sculpture of the classics, a single point of view is preserved, which allows you to immediately see all the figurative wealth of the statue.
Quiet self -lation, domination over their feelings is a characteristic feature of the Greek classical worldview, determining the measure of the ethical value of a person. Images of Mirone, as well as the idea of \u200b\u200bthe Western Olympic Fronton, grow on the same soil, which is still 6 in. BC. gave rise to two-stop:
Also in trouble do not burn and do not rejoice too, with happiness. That and the other must be worn in the heart
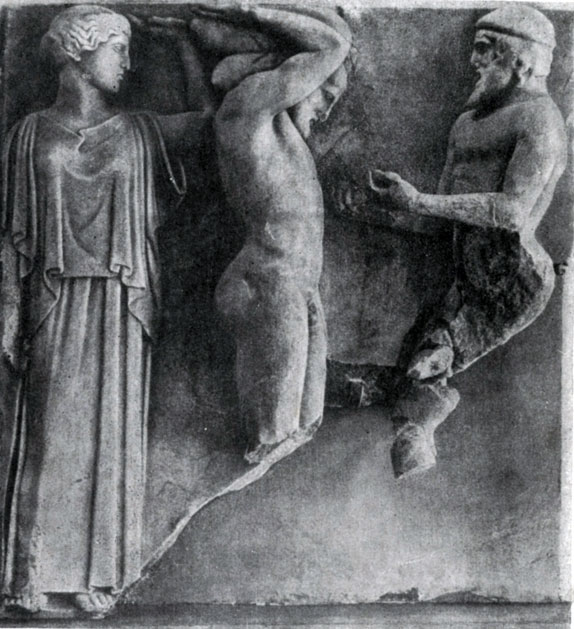
The approval of the beauty of a reasonable will, holding back the power of the passion and a decent person who gives it to the expression, found its particularly clear expression in the sculptural group "Athena and Mariji" created by the Miron and Miron.
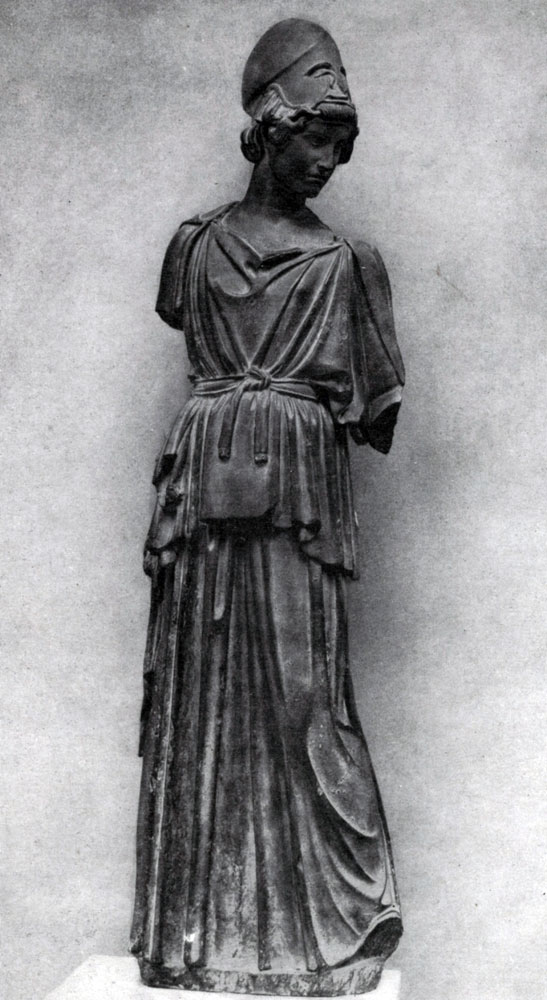

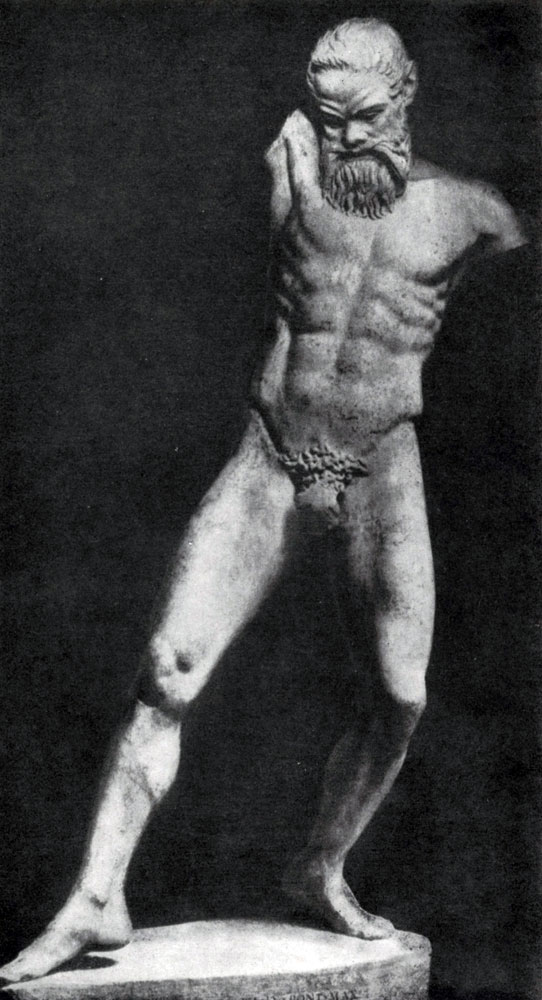
According to the myths, Athena, among the most directed to the benefit of the invention, created a double flute. But when she played on her, he heard the laughter of other goddesses. Being bending over the source, she saw in his reflection, as during the game her cheeks were ugly. Athena threw the flute and cursed the tool disturbing the beautiful harmony of the human face. Silen Mariji, who neglected the Curse of Athens, rushed to pick a flute. Miron depicted a moment when Athena, leaving, was angry with a breath, and Marsiy pulled back in fright.
Again, as in the "discobole", a brief moment is taken, in which the highest voltage of action is concluded, and again in the selected situation contains a complete disclosure of the entire event. At the same time, here for the first time in the history of sculpture, and in the history of art in general, the clash of different characters is shown.
This conflict clearly reveals both the true characters characteristics and the creature of their relationship. As in the grain, the whole plant is contained and in this mythological sculptural group the possibility of all further ways to develop a realistic plot composition showing the relationship of characters associated with a common action, a single life event.
Athena and Mariji are like antipodes. These are the characters are directly opposite to each other. Movement rapidly leaning back and waving his hands roughly and sharply; His strong body is devoid of harmony. The powerful and angry, but restrained motion of Athena is full of natural and strict nobility. The face of Marcia is rude: the convex forehead, the animal ears, the reptile nose make it to some extent the typical generalization of the deformity. The face of an angry goddess gives anger only contemptuously semi-handed lips, the severity of the view. The anger should die holding the power of norms and laws, following which determines the dignity of a public person. At the same time, Athens's head is a vivid example of a perfect merger in the sculptural form of the physical and spiritual beauty of a person. Strict proportion proportion, clear, open look, the naturalness of the expression - everything merges into a single, full of life and harmony image.
In general, the Mironovskaya group "Athena and Mariji", like the Olympic Fronton, figuratively approves the idea of \u200b\u200bthe superiority of the mind, the human start over opposing them by the natural, instinctive forces. At the same time, this composition is the apology of Athens, the patroness of the city of Athens, figuratively embodying the idea of \u200b\u200bthe Athenian state.
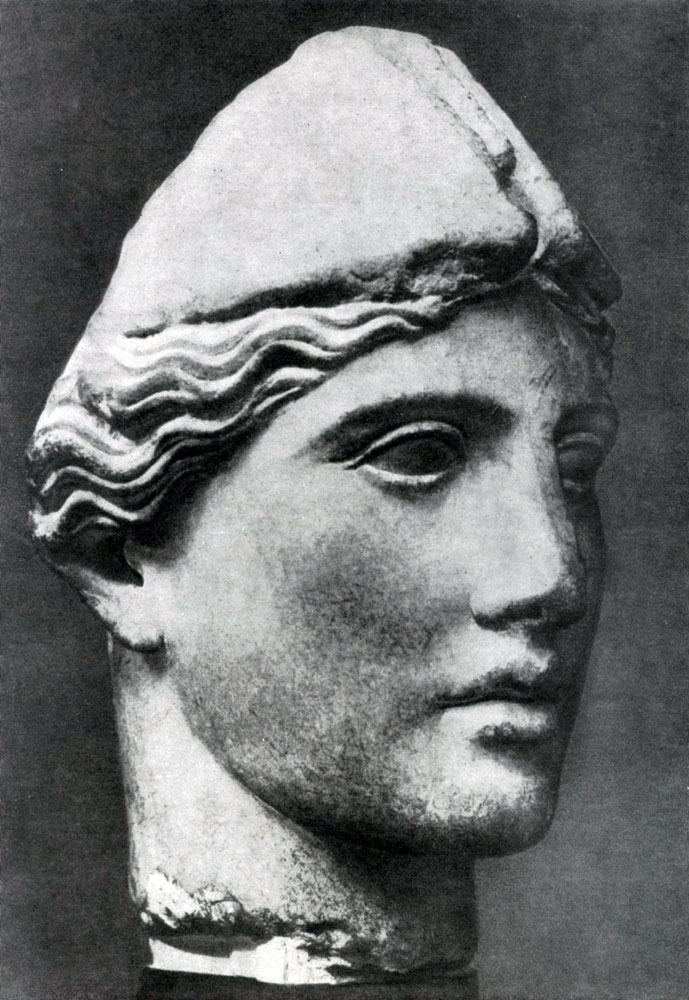

It is possible that this group was placed on the Acropolis also because Marshi, revered in hostile Athens Boeotia, was exhibited here in the offensive light. Of course, the Athenians did not see the basic artistic value of the group. However, the fact that political passions naturally and naturally embodied in a figurabical form are also very characteristic of the art of that time.
About the works of Mirone, who did not even reach us even in copies, can be judged by the reviews of the ancient writers.
It is known that he portrayed the famous Argos Runner of Lada, who achieved victory in the competition at the cost of his own life (he died of a heartbroken, rejoicing to the goal). About this statue can be judged by the epigram of an unknown poet that reached us:
Polon Hope Runner: On the tips of the lips, only the breath. It can be seen: drawn by inside, the hollow beer. Bronze tends to ahead behind the wreath; Do not hold down her stone. Wind fastest runner, miracle he Mirone hands.
From literary sources it is known that Miron made a giant statue of a sitting Hercules, as well as an image of a cow, admiring contemporaries near nature.
For works, related to the art of Mirone and forming the transition from the frontones of Olympia to the art of high classics, refers to the relief of the attic master depicting Athena based on a spear (about 460 BC.
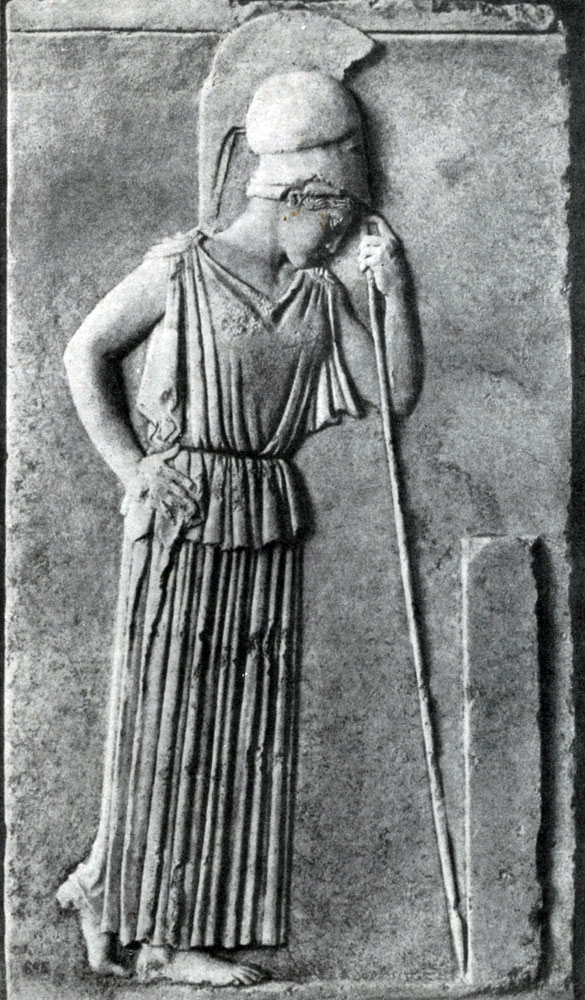


In this relief, the condition of the clear and bright Duma is well transferred, which is immersed by Athena. The rhythm rhythm of the folds of Peplos Athens shall select the free and natural grace of its movement. Easy slope Figure forward enhances the feeling of relaxed rest and has just ended the movement.
Close to the circle of creative tasks of the art of Mirone and a wonderful statue of the Winged Niki-Victory, the work of the Ionian sculptor PEONIY from Mende (3rd quarter of 5 century BC). Established in honor of the victory overwhelmed Messinians, "Olympia architectural ensemble decorated.

The statue depicting the goddess of Victory was placed on a high nine-meter triangular pedestal. The winged Nick, descending from the sky on the prostrate wings, barely touched the legs of the flying eagle. The masterfully passed the feeling of a soaring flight, resembling the planning descent of a large bird. Although the motive of a flying female figure and fantastic, characteristic of the realism of the Greek classics, the feeling of organic integrity and vitality of the image gave the statue of the nickname. The poetic image of the winged and wonderful victory found its truthful and visual incarnation. A strongly damaged statue of Pedonia Nicky reached us in a marble script, according to which one can judge the mastery of textured and black and black and black-free processing of the surface of the marble.
The time of activity of Miron and Pedia probably belongs to the adorable figure of Athens, producing from the outstretched HOWE (British Museum). A small bronze statuette is characterized by monumental severity and simplicity. Although folding the folds somewhat resembles the earlier art of the second quarter of the 5th century. BC, - the noble naturalness and harmony of movement and body proportions bring this statuette to the works of high classics. Just like in the "Athena" of Mirone, in this small figure of a barefoot girl handed over a clear and light state of the spirit, in a relaxed grace of her movements - charm of purity and youth.
Greek sculpture of the classics period
The fifth century in the history of the sculpture of Greece of the classic period can be called''shag forward. Sculpture development Ancient Greece In this period, it is associated with the names of such famous masters, like Miron, Polyclin and Fidi. In their creations, images become more realistic, in case it can be said, even a dealing schematics, which has been characteristic of archaic sculpture. But the mains''geroami'''''''''''s people remain the main thing.
Miron, who lived in Senin 5 V. BC Uh, known to us in drawings and Roman copies. This brilliant master was perfectly owned by plastic and anatomy, clearly passed the freedom of movement in his works (''Discobol''''''s). It also knows his work "Athena and Mariji", ĸᴏᴛᴏᴩᴏᴇ Created on the basis of the myth about these two characters. According to Legend, Athena invented the flute, but during the game he noticed how ugly changed the expression of her face, in anger she throws a tool and curses everyone who will play on it. After all the time, the Forest Deity of Mariji was observed, ĸᴏᴛᴏᴩᴏᴇ the curse was frightened. Sculptor tried to show the struggle of two opposites: calm in the face of Athens and wildness in the face of Marcia. Modern art connoisseurs are still admired by his creativity, its sculptures of animals. For example, about 20 epigrams on a bronze statue from Athens are preserved.
The polyclet that was creating in Argosœe, in the second half of the 5th century. BC U, is a bright representative of the Peloponess School. Sculpture of the classic period rich in his masterpieces. He was a master of bronze sculpture and an excellent theorist of art. The polyclet preferred to depict athletes, in which ordinary people at all saw the ideal. Among his works are known for the statues of Dorifora and Diadumen. First work - ϶ᴛᴏ Strong warrior with a spear, the embodiment of calm dignity. The second is a slim young man, with a bandage of a winner in competitions on the head.
FIDIA is another bright representative of the creator of the sculpture of the classic period. His name briefly sounded during the heyday of Greek classical art. The most famous sculptures were the colossal statues of Athena Parfenos and Zeus in the Olympic temple from a tree, gold and ivory, and Athens Prosakhos made from bronze and located on the square Athenian Acropolis. These art masterpieces are irretrievably lost. Only descriptions and reduced Roman copies give us a weak idea of \u200b\u200bthe magnificence of these monumental sculptures.
Athena Parfenos is a bright sculpture of the classic period, was built in the Temple of Parfenon. It was a 12-meter wooden foundation, the body of the goddess covered the plates from the ivory, and the clothes and weapons were improved from gold. The approximate weight of the sculpture is two thousand kilograms. Surprisingly, the gold parts took off every four years and weighed anew, as they were the Gold Foundation of the State. Fidi decorated the shield and pedestal reliefs, which showed himself and pericla in the battle with Amazons. For that, he was accused of conflict and sent it in conclusion, he died there.
Zeus statue Another masterpiece of the sculpture of the classic period. Her height is fourteen meters. The statue depicts the Supreme Greek Deity Sitting with the goddess of the nickname. The statue of Zeus, according to many art historians, is the greatest creation Fidiy. It was built using the same technique as in the creation of the statue of Athena Parfenos. The figure was made of wood, depicted naked on the belt and coated with ivory plates, and the clothes were covered with gold sheets. Zeus renounced the throne and held the figure of the Goddess of Victory Niki in his right hand, and in the left was the rod, which was a symbol of power. The statue of Zeus ancient Greeks perceived as another miracle of the world.
Athena Prosakhos (approximately 460 BC), the 9-meter bronze sculpture of ancient Greece was built right among the ruins, after the Persians destroyed the Acropolis. FIDIA 'Rajes''''l Other Athena - in the form of a warrior, an important and strict protector of your city. In her right hand she has a powerful spear, in the left shield, and on the head helmet. Athena in this image was the military power of Athens. This sculpture of ancient Greece as if prevailed over the city, and everyone who traveled around the sea along the shores could contemplate sparkling in the rays of the sun, covered with gold the top of a spear and a crest of a statue helmet. In addition to the sculptures of Zeus and Athens, Fidium creates images from the bronze of other gods in Christhelenefactory technique, takes part in contests of sculptors. He was also managed by large construction work, for example, the construction of the Acropolis.
Greek sculpture of the classics period is a concept and species. Classification and features of the category "Greek sculpture of the classics period" 2014, 2015.
Works-Representants of the sculpture of the period late classic
Characteristics of the sculpture of ancient Greece of the period of late classics (IV century BC)
Works-Representants of the Sculpture of the High Classic Period
The originality of the sculpture of ancient Greece of a high classic period (450-410 BC)
Characteristics of the ancient Greek sculpture of the early classic period (490-450 BC)
The purpose of creating statues in the period of early classics is still an image of a typical image, art infection of archaic images gradually loses, losing sensual contact with the audience. The picture of the world is changing, causing the formation of a new image and expressiveness, which entails the search for a artistic and statue model that would imitate the naturalness of the human figure. In the era of early classics, four-fasciance disappears, turning into multiphasadity, the sculpture becomes round. Ranneclassical statues require more expanses than archaic. The decorative beauty of archaic statues in early classical time is changing towards the natural, life beauty of the figures, requiring greater integrity of the movements, all individual movements are subordinate to the overall movement. Stresses calm, increased calm, restrained character power. This is a typically generalized construction of a hero man in all perfection of his physical and moral beauty, education of the idea of \u200b\u200bwhat a person should be. The sculptural images are characterized by severe simplicity, calm greatness of the spirit, a sense of significance and beauty of man.
All more clothing turns into an echo of the body.
The desire to solve the problem of revitalizing a calm figure. Achieving free natural poses and gesture of a human figure.
Much attention is paid to images of the human body in motion. Mastering the complex and controversial wealth of movements of the human body, directly transmitting not only the physical, but also the mental state of a person is the most important task.
Mythological topics and plots continue to dominate art, but the ethical side of the myth is put forward to the fore.
Sculptural groups of early occupational frontones showed the role and significance of each person in its relationship with other people. A person is represented not as an impersonal particle, dissolved in a general composition of the composition, but as a person who occupies its clear and certain place in the composition.
The most important means of characteristics of the overall state of the spirit become the proportions of the body and its dynamic position (movement). Constability and artistic expressiveness of the gesture appears.
In this case, the typical generalization is not combined with the individualization of the image. The purpose of the sculpture of early classics was to create a typical image of a significant person as a norm and sample for each person- citizen. Various mental states opened by sculpture are generalized.
The person's face does not have in relation to the rest of the flesh of his preferential or exclusive right to the transfer of mental life, which is equally expressed in the whole body, in all his movements, including facial.
The main material for the wizards of the sculpture of the early classics becomes bronze.
2. Works-Representants of the sculpture of the period of early classics
Tiranoubytsy Garmody and Aristiton (approx. 470 G.DU N.E., sculptors of critical and nevot) - In this statuational composition, the task was for the first time to create a unified sculptural group united by one action and the plot. The opponent-tyrant itself, who killed heroes is not depicted, but it can be presented as a speculative point, which is intended to hit heroes.
Poseidon (Ok.460 G.D. N.E., Bronze), according to another version, this is the Statue of Zeus-Sturry. The statue was found at the bottom of the sea, nearby. EVBEY in 1928, its height is approx. 2m All movements are subordinated to a single impulse, but on the head all the hair is in absolute rest, decoratively arranged. It is believed that the statue belongs to the School of Agellad, which attached a number of ingenious masters, incl. Miron, policlet, fidium. The whole School of Agellada was engaged in the image of the movement, with inner peace or tension.
Calling (approx. 470 g. BC, Bronze), part of the sculptural group created by Pytagora Egian School of Pythagora's Peloponess Masters. The image of the winner of the Olympic Games in the chariot competition is presented. Everything seemingly should be in motion, but the image presented by the masters is calm, is immobile, resembles a column with folds - flutes. In sculpture, many naturalistic elements. The statue was visible only from behind from a long distance, but there are carefully worked eyelashes, a youthful beard has been preserved, unevenly trimmed nails, there are swollen blood vessels on the legs.
Statue of Neread from Xanf (Ser. V C. BC, Marble) Ionian sculpture, monument in Malaya Asia. The statue shows the traditional scheme of the knee-free run - depicted nonreide, flying over the surface of the water with which it connects the duck. The means of sculpture creates a sense of real flight over the water, which was part of the monument. Clothing statues paint flesh, become echoing body.
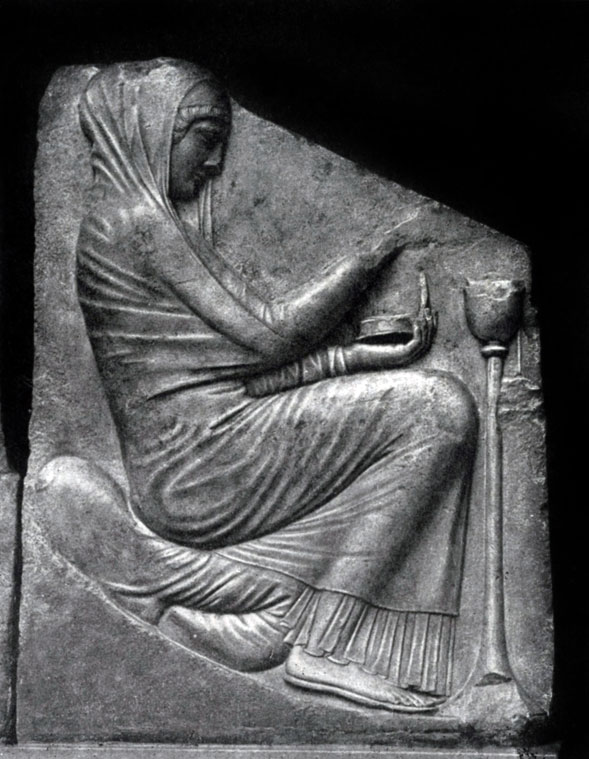
Trone Lududisi (OK.470 G.D. N.E., Marble) was actually a fence of the altar. Previously, it was a construction of three walls covered with reliefs, an altar himself was located inside. On the walls in the central part, the birth of Aphrodites from sea foam is depicted. Nereides cover the mysterious moment of birth. In the lower part, pebbles are shown, above - the matter is still empty, and only Aphrodite appears in the upper part. Aphrodite clothes are wet, fill her flesh. The movement is emphasized by the folds of clothing - from the bottom up, the figure slowly rises, together with our glance, Aphrodite is born.
On the side walls there are two figures - a hetero playing on flutes in the front clothes (nude), singing the song of carnal love, and a fully draped figure of a female mother who personifies family love. The altar was, apparently female, representing two types of love, on the one hand, love like a carnal pleasure, on the other - the creation of a family hearth.
Athena, based on a spear (OK.460 G.D. N.E., Marble,) Relief from the Acropolis Museum. Athena is presented a strict, thoughtful goddess, a symbol of wisdom. The lower part of the goddess body is like a column with flutes, gradually at the top of the Athens's figure with an emphasisment of female elements unfail. The flesh is felt under the clothes.
In the period of high classics, the leading role in the crystallization of artistic norms belonged to Athens. It was the attic of the time of the pericla that gave rise to a sculpture as the synthesis of all the most significant, which was previously worked out by the masters of the Ionical, Doric and Attic Schools of Plastics.
For monumental art of a period of high classics, the principle is characterized as if involuntary, freely emerging harmony of architecture with sculpture, which, fully carrying out its shaft tasks, did not destroy the architectural integer.
In the era of high classics, the human problem is considered, its place in the center of the Universe. Statues and reliefs of this time are distinguished by naturalness, ease of location in the artistic space, simplicity of gestures. It is precisely those movements and positions of the body through which and with the help of which human essence is highlighted. Highlights, peace, deep humanity statues were born with the help of a harmonic composition, thought out to the smallests of the mass distribution, uniformity of lighting and relief.
An even more difficult problem solved in high classics is the problem of modeling a person as space. The knowledge of themselves and doing themselves according to a certain pattern, the desire for this sample was noted earlier in geometric and archaic time, and in classical time it continues to be present. But now a person becomes in the center of the Universe and is simulated not only and not so much a person as the Universe is simulated through a person, the essence of the universe is understood through a person.
Recognizing a man by the main value measure of the wisely arranged world, on the theoretical and philosophical foundation were mathematically calculated by the reference dimensions of all parts of the human body and their exemplary ratio with each other. This was expressed in the theoretical work of the School of Agellad's School "Canon", where the reference proportions of the human figure were proposed: the human growth was taken for a unit of measurement, the head should have been one seventh part, the face and brush - one tenth, the feet - one sixth, etc. . The masters were confident that such proportions embodied in sculpture are able to create perfect works-statues. Created by a policlet, the work "Doryina" serves as an example of such perfect proportions, demonstrates how a person should be to embody the essence of the cosmos, the integrity of a person, the hero, God together in the bullion, in unity in integrated form. Touching such a perfect thing, as Ellina believed, the person inevitably improves.
Discombol ("Sculptor Miron; Ok. 450 BC; Roman Copy; Bronze ^). The statue depicts the disk thrower, the winner of the Olympics, was completed by order of one of the low-depth cities. Discobol is presented at the last moment of making (shubles) and the first time of the throw (MAX). Miron puts his statue in such a posture, in which it is longer than a moment, a person cannot. This intermediate position of the shuffle is just infecting the viewer, makes it possible to speculately build a sequence of events to this moment and design an event number after the image of the moment. Miron masterfully depicts such intermediate positions, changing states that flow one to another. Unlike most of the statues of high classics, which suggest several points of view, all the main elements of the discolobol movement are focused on the front surface of the sculpture, which In any case, the viewer leads (where does it have been an overview) to consider discobol only from one point - Front.
"Athens and Mariji" (sculptor Miron; the second quarter of V c. BC; Roman copy; marble). Miron speaks in this sculptural group on motion overflows, overflowing the state. Unlike the sculptures of the early classics here, on the one hand, there is no staticness, there is no clarity, although, on the other hand, everything is extremely clear. This contradiction is amazing for high classics. In each person, this or that condition is not held long, it is constantly changing, flows into the opposite state. It is not by chance that the saying of the heraklite "can not enter twice in the same river." The plot is the myth of the invention of the flute. Athena invented flutes, she came with them to the gods, played and the gods laughed. Those flutes that were invented by Athena had a funny look, they were attached to the head with belts, passing along the face and attached to the back of the head. When Athena played on such flutes, her cheeks and her nose blushed, the eyes got saddled, the gods laughed at her. She threw these flutes in anger, Mission decided to raise them, and, leaving, Athena turned around - she was sorry for flutes. This moment is overflowing one state to another and captured Miron. A person constantly passes through such states - leaves, looking around, wants to raise, but stop. Fixing the posture in which the body can only be a moment. It goes, throwing flutes, but the Athena turns around. Wishes to raise, but marksius is excited.
"Nika" (Middle Master; Middle V c. BC; marble) The statue was found during excavations in the Olympia, in the dedication lettering it says that the statue of Niki is dedicated to Messinians and Zeus's Baspaktyans. The statue was at a high (9 m) trigger pedestal. Nick is depicted next to an eagle (zeus symbol) flying. Flight is presented through an almost complete absence of support for the statue of Nicky. The goddess is connected to the pedestal by means of a heavy mass falling behind her clothes and only slightly touches the tip of the left leg of the pedestal. Nicky wispped by the wind created the illusion of the flight. Increased the impression of a high pedestal. Nika has been read against the background of the sky and moving clouds in the fluttering clothes that make the flesh with the help of real wind. There is an inclusion in the artistic space of real wind and fluttering clouds.
Dorinaphor (sculptor Peloponnese polyclet; Middle V c. BC.; Roman copy; marble). Presented a monumental typed image of a citizen athlete. Dorifina is a sculpture in which everything is measured and calculated to the smallest details (what size should be in the thumb, which should be palm in relation to the finger, what should be hand in relation to the finger, shoulder belt, etc.) The statue is created as an embodiment of the theoretical treatise of the Canon Policlet. All the severity of the body of the spear on his right leg; The left foot is referred to and concerns the pedestal only with his fingers. The foot is assessed, but it is impossible to say it comes or standing. The left thigh is omitted, right raised. The left shoulder is raised, the right is omitted. A cross-combination of lowered and raised parts of the shoulders and thighs is obtained (the S-shaped line passes through the body of the Doryifora). Much later, in the XVIII century. William Hoggart in his work "Beauty Analysis" will display a S-shaped curve as a better, perfect curve.
"Wounded Amazon" (master polyclet; marble copy). The statue ranked first at the competition announced by the Euzyans about 440 BC. The body of the Amazon is characterized by athletic forms. In the image of it prevails calm strictness and masculinity.
"Diadumen" (Master Polyclet; Ok. 420 BC; Roman Copy) A young man who turns himself with a victorious bandage. The same formulation of the figure as Doryifora. Body shapes are more elongated, slender and lungs, outlines are softer and elegant. This is caused by the influence on the polyclet of the attic school of sculpture.
"Pericles" (Master Chair; OK.420 G.D. N.E.; Roman Copy). Possesses like others greek statues, simultaneously, portrait and typical. We can say that we are in front of us, but if you remove the helmet and make a beard of massive, then we can say that we are in front of us. And removing the beard and mustache, you can find apollo in it, etc. The Greeks depict the type of person, a certain universal structure, which, if desired, can be turned into anything. Therefore, it is quite difficult to speak about portrait. Greeks are more worried about human than private. In this case, the political figure is considered and there are not so many individual portrait qualities of the pericles, how many individual qualities of the statesman.
In the period of late classics, the monumental severity and the heroic direction of images are softened in the sculpture. Individualistic trends are developing, the psychology of the works of sculpture is growing. Appear different imagesIn one case, complete paters, through ecstasy, on the other hand, contemplation, lyricism, hedonism, works saturated with the spirit of peace, sweet rest, lazy island. Artistic forms are complicated, the powerful effects of lighting, boring a feeling of the destruction of forms, the inability to cover with gaze.
Often, Matera decide their works so as to cause the need from the viewer in a circular circumpassment to get a holistic idea of \u200b\u200bthe artistic and ideological components. The spectrum of views on the sculpture is built as a fan relative to the independent aspects of a complex plastic image.
A new canon proportions are produced. Plastic forms are strongly pulled, the heads of the statues become equal to one eighth part of the height of the body.
There is keen interest in emotionality, to the disclosure of human feelings in the art monument. The beauty of an open new world in art is in the development of drama, intertwining of complex feelings, outbreaks of human passions. In the sculpture, this is expressed in the complication of the composition, increasing dynamism and gustiness, in contrast of lighting.
When creating women's images, the problem of the ratio of clothing and body receives a new interpretation. A sharp comparison of the fabric and figure violates the usual classical harmony, the dress is perceived as a hindrance of the flesh, trying to break out of the tubes. For the first time, the masters show the nudity of a harmoniously folded woman, glorifying the perfect beauty. The first image of the naked goddess in Greek art appears.
The era of late classics was the heyday of portrait art, due to increased interest in the world of human experiences, thoughts, feelings. On the squares of cities, the statues of statesmen, commander, famous speakers, philosophers and poets are erected, the masters set themselves the task of achieving external similarity and at the same time emphasize the characteristic features that turn a portrait in a typical image.
Menada (Master Skas; Ser. IV century. BC; Roman copy; marble). Attempts to create pathetic art made in the second half of V c. BC. In the relief of the temple of Apollo in the Bass, they found their completion in the work of the Skopas, the masters of individualism in art. Menada Skopas is saturated with pathos, transmission of strong emotions, stormy spiritual experiences, full passion, struggle and speakers. All this has been made to extreme pointedness. Consigned by flavored frenzard, Menada is depicted in a sharp movement, with his head trapped back, with a person on which violent emotions are fixed. Circular bypass statue allows you to highlight the beginning, flourishing and dance finals. Menad dance is a swollen dance, in which the carnival is breaking from the soul, where the soul is striving for spirit, uniting with him in a rush.
"Amazonacia". Fries Galicarnas Mausoleum (scales scales, Timofey, Brixis, Jleoxap; Ok. 350 BC. BC; marble). Friez is executed in high relief. If in the period of high classics (in the Friesofore of Parfenon), the artistic space in the relief was allegedly stated between the two conditional planes (front surface and the background), then in the reliefs of the Fries of Galicarnas Mausoleum, the total dynamics of the figures of fighting Ellinov and Amazons are often moving, as it were, As if flowing deep into the relief or leaving the depths of it, cutting the conditional front surface of the relief, arguing in an artistic attitude, the space that is concluded between the relief and the audience. The relief figures are mostly deployed on diagonally in order to freely enter the artistic space.
"Hermes with the baby Dionysis" (sculptor Praxitel; Ser. IV. BC.; Paros marble). Praxitel was a junior contemporary Spropasia occurred from the kind of breeders. In his work, Prapkitel developed a hedonistic direction in art (work for pleasure). The statue was perceived in this case as a matter of luxury, sophisticated comfort.
The statue shows a myth on how Gesznik Hermes were instructed to attribute the infant of God Dionysus to raise the nymphs. The episode of Hermes stop is depicted on the way, where one God entertains the other with the help of a grape vine (not survived). The work of Praxitel is saturated with the spirit of peace, sweet rest, lazy ister. Rounded forms of the statues of Praxitel are characterized by soft transitions and the finest modeling of the body surface. Well used light and transparency of marble. A hint of the genre is noticeable in the sculpture, the chamber mood of the characters, the idea of \u200b\u200bthe masculinity of the flesh is happening. The body of Hermes is deprived of the former masculinity, which was so distinguished by the bodies of the gods of the first half and the middle of the V c. BC. Forms become flowable, smooth. Solving baby body, Praxitel deliberately leaves the problem to convey the proportion of the child's body.
Apollo Saurokton (Master Praxitel; Third quarter of IV century BC; Roman Copy; Marble). Statue of resting satire, eliminated on a woody trunk. The motive of the support was very successful (first was introduced by a policlet in the "wounded Amazon"). The contours of the statue smooth and flowable. The pose of the body repeats the bending of the lizard cruising on the trunk. Sculpture is devoid of equilibrium. Satir is depicted precisely based on the trunk of a tree.
"Apoxiomen" (master Lisipp; Third quarter of IV century BC; Marble Roman Copy; Original - Bronze). For art, lisippa is characterized by artistic images, full vigor, nervous tension, active and active start. Young athlete depicts after the struggle, which is shifting through a sand scrub with grated body oil. The situation depicted in sculpture is very common - playing in the mind of the past struggle, the experience of her again. Athletic figure is extremely ease and sophistication. The proportions of the body are strongly elongated, the head is equal to one eighth part of the body height. There is no peace of mind in the statue and sustainable equilibrium. Apoxiomen is not worth directly - the full nervous voltage of his body is strongly tilted forward, he as if balancing or crosses from foot to the leg. The dynamism of the statue is emphasized with his hands forward, creating the impression of the depth and claiming the space surrounding the figure. Apoxiomen's hand breaks through the artistic space, as a result of which the space surrounding the sculpture, and the space surrounding the viewer becomes one.
"Hercules fighting with Lvom" (master Lisipp; Roman copy; marble). LisiPU has repeatedly depicted Hercules, the image of which gave the greatest opportunities for the embodiment of an active, active start and heroic. A group of Hercules with Neamed Lvom is presented. The full vitality of the mighty body of the hero is given in a spectacular opposition of the body of the beast. The statue is quite developed, full dynamics Group: both components of its figures cannot be separated from one another. The figures of Hercules and Leo are associated with close interaction recorded at a certain point in time. The helplessness of a lion, whose head is clamped under the arm of Hercules, is handed over to the verge of Grotesque, but still the battle comes with a worthy opponent. Lisipp suggests that there is a human reasonable principle, the will of a person and there is an animal beginning. They are inherent in each person. No matter how the mind restrained, the animal began to require his own, but the human mind is able to curb him, suppress.
Apollo Belvedhersky (Sculptor Leochar from Attica; Ok. 340 BC.; Marble Roman Copy; Original - Bronze). Statue of Apollo Academic. Apollo Leohara has a light sliding gait, the body is distinguished by elegant proportions, the formulation of the figure is full of paradity and several theatrical. God, who struck out of his famous Luka evil in the appearance of the pithhone, feels like a view of the viewer looking at him and is similar to the actor speaking on the scene. Apollo Leohara does not work, but depicts action.
The sculpture of Hellenism (end of the IV-I centuries. BC) includes in its composition art schools of mainland Greece with the islands of the Aegean Archipelago, Malaya Asia (mainly the Pergamm kingdom), Islands of Rhodes, Syria (Western part of Seleucidov) and Egypt . These are those and states in the art of which Greek traditions, having gained partly the national color, had the prevailing value.
Among the individual sculpture genres, monumental plastic was obtained at the time of Hellenism, which was the necessary element of architectural ensembles. In addition to the colossal statues, multifigure statuational groups and huge embossed compositions were cultivated here, created as not mythological and historical plots.
I received great distribution sculptural portrait. Keeping the principle of typing, which is peculiar to Greek artists, the Master of the Hellenistic portrait could transmit not only the appearance features, but also various shades of the mental state of the model.
The sculpture of genre character was popular with a tendency to naturalization.
A new type of plastic was a garden decorative sculpture, widely used for decorating gardens and parks.
Hellenistic masters, expanding the arsenal of artistic sculptures, opened the capabilities of a particular transmission of nature, found techniques of showing various emotions, developed new composite techniques of demonstration of movement in its complex and diverse forms, continued the search for the three-dimensionality of the sculpture and the construction of the statue, taking into account the multiplicity of points of view.
Victory over the powerful Persian Empire in V c. BC e. The Greek policies were rallied and gave the strongest impetus to the development of all industries, starting from the economy and ending with creativity. It seems that the Greek masters of that time have suffered some sacral secrets of being, they have obtained such impressive creations. Characterizes works of visual art of that era as sensual, natural, immediate, rational. This was especially brightly expressed in sculpture.
Today, the sculpture is associated with museum expositions, but at that time the heroes of the myths and legends from marble and bronze decorated the streets of Greek policies, temples, parks and squares. It was a natural embodiment of beauty, accessible to everyone to humilion. Probably, that is why the original ancient Greek sculptures They found mainly in the form of fragments and fragments - the Greeks could not imagine that the creations of their sublime consciousness need to be hidden and protected from the consciousness of the barbaric.
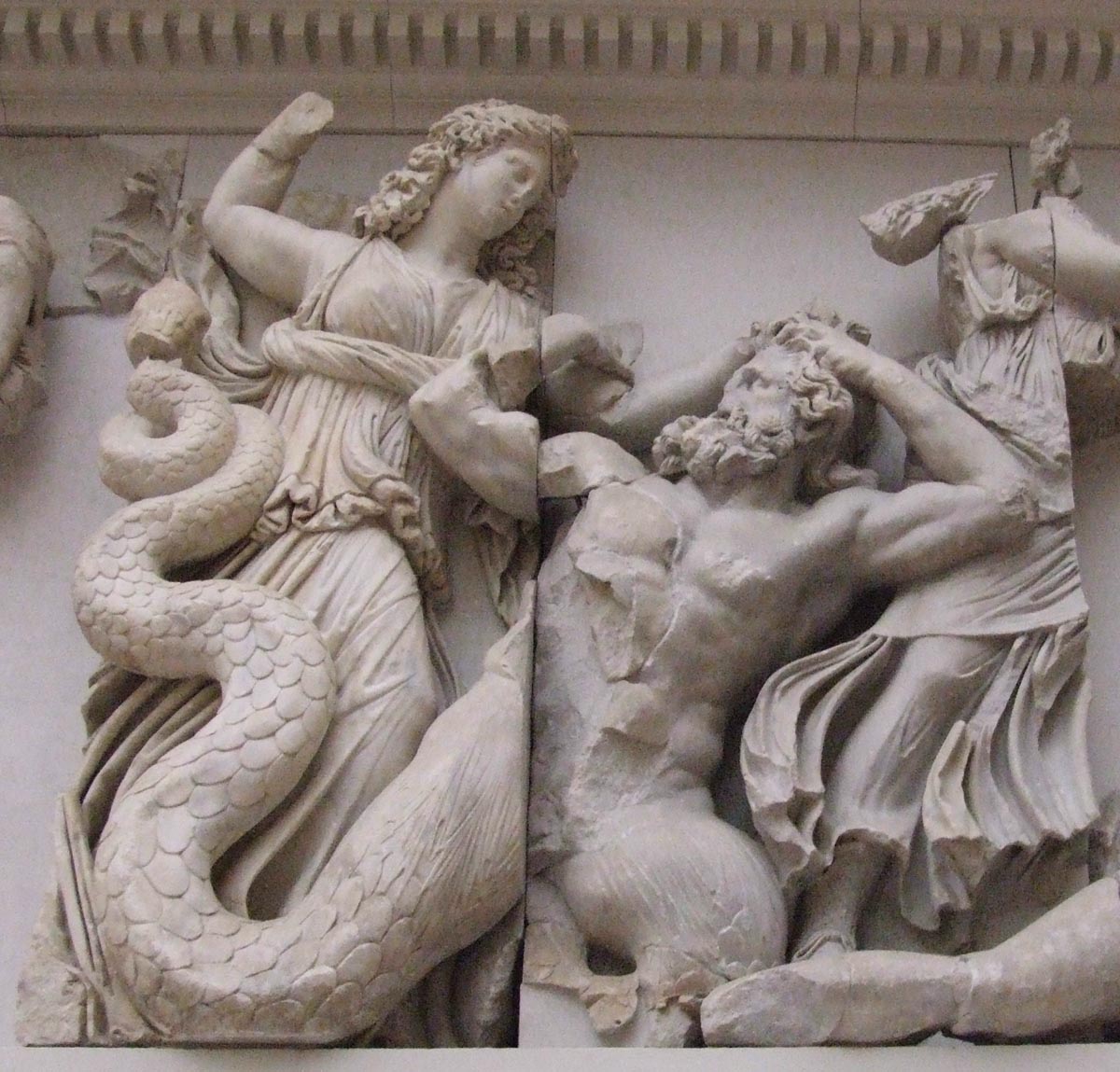

Many classic statues are known to us thanks to Roman copies. Rome generally was the successor of Greek culture, but the copies often simply could not convey the beauty of the originals, passing only the plot. The difference was felt not so much in the absence of mastery of imitators, as in the spirit of the era itself. So, Greek statues were from another marble - yellowish, filled with light and warm tones. This was achieved thanks to the witch marble.
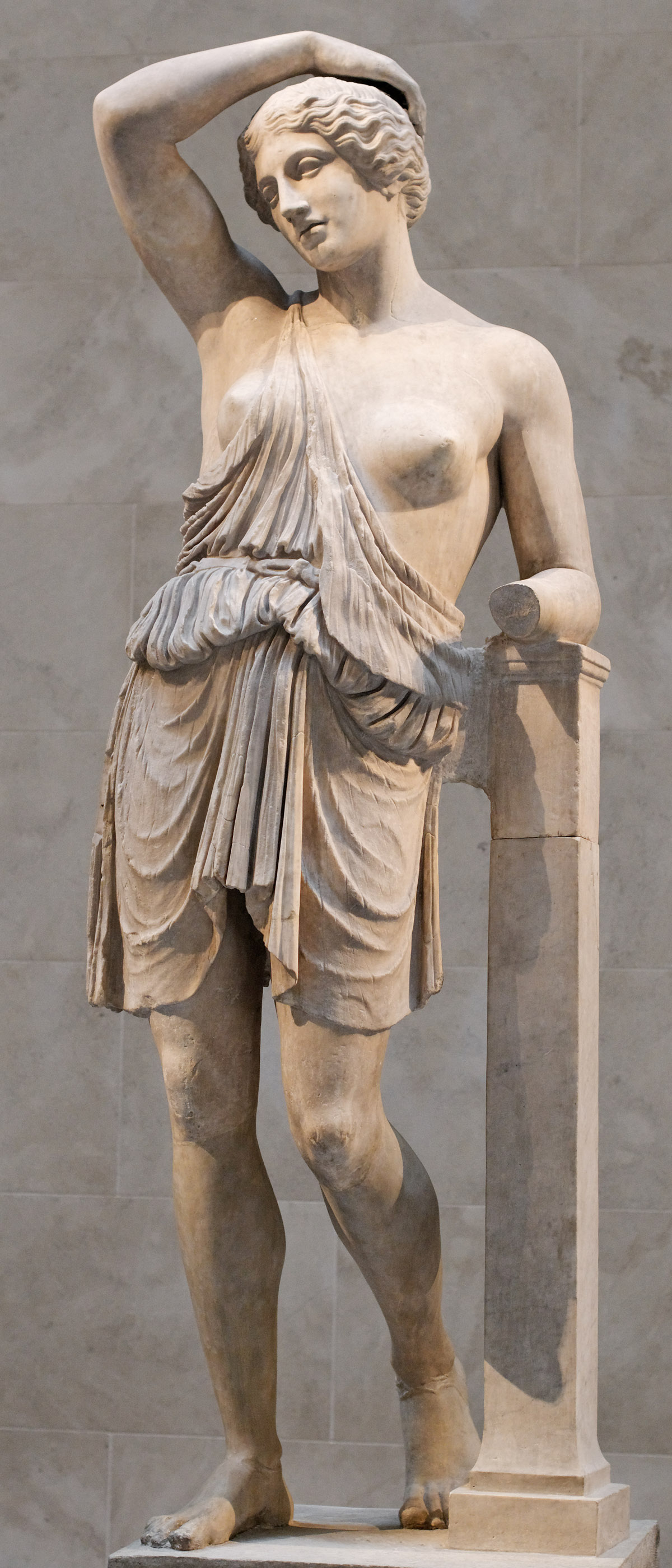

Loved motifs ancient Greek sculptors - The accomplishments of mythical heroes, the battle of the Olympic gods with titans, sports competitions. Thanks to the specifics of scratched greek sculptors He learned how to recreate the human body in motion, depicting complex poses.
An innovator is the attic sculptor Miron and his "discobol". The athlete waves, getting ready to run the disk, it is tilted and tense, even a moment - the throw will be perfect and the athlete will relax members. But Miron captured this second, when the athlete froze in the position seemingly unstable but, at the same time, in equilibrium.
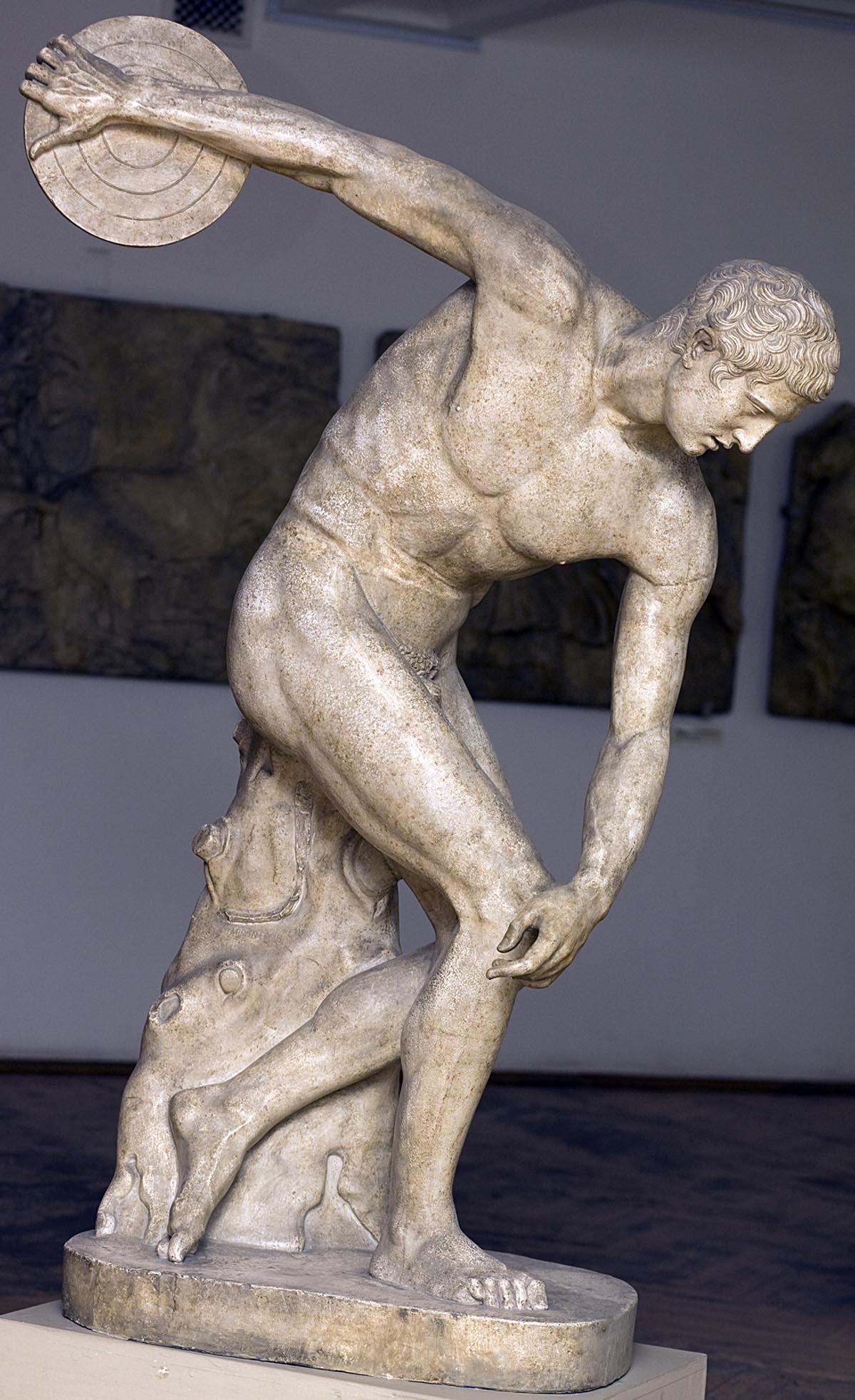

The Greek original of an unknown author, presumably Sotades, preserved relatively good - the bronze statue of the "cat", found in delphes. Specialists belong to the period of strict style (approx. 470 g. BC. Er). Look at this young man. He controls the four horses, but at the same time absolutely calm. It costs without shoes, the flute of doric columns is measured in the folds of his Hiton, and the hair is pulled on the foreheads of the silver dress. Peer in his eyes - they are like alive, full of energy. What is characteristic of all outstanding sculptures, "WIND", when looking from different angles, "opens up" various facets to the contemplator. One of this bronze figure, its strong, cast plastic, allows you to feel - what exactly the ancient Greeks understood under human dignity.

Ellity bowed before the beauty and wisdom of the living body device. They understood the body language - as the language of the soul. As a result, the Greek masters mastered the art of the transmission of "typical" psychology, expressing the richest gamut of spiritual experiences through generalized human types. For the same reason, the art of the portrait in ancient Greece was developed relatively weak - the whole body was expressed by the mood and essence of the hero depicted.

In the period from the end of the VI to IIV centuries. BC er, the creators sought to express spiritual power and the vigor of the Spirit, but over time, the accents shifted to excessive pathos, dramaticness and lyrical contemplation. Sculptors attracted the charms of childhood, the power of maturity, old age with her wisdom and femininity - her charm, temptation and chastity. Skas, Praxitel and Lisipp - the greatest Greek sculptors of the Late classic era. They had such an impact on the development of ancient art, which is comparable to significance with the sculptures of Parfenon.

The peak of the classical sculpture of ancient Greece, as a general opinion, is "Apollo Belvedere", the authorship of Leohara. This statue is synonymous for aesthetic perfection. "Apollo Belvedere" really amazes with his plastic advantages: in the figure and switches, the Lord MUCs are combined with force and grace, energy and ease; Stepping on the ground, he boot over the ground. To achieve such an effect, the exclusive skill of the brewer was required - the trouble is only that the calculation on the effect is too obvious.

The ancient Greeks left behind the great cultural heritage, which can be considered a decent landmark for the creators of today, newly emerging from the barbaric state.
An attribute image is still the most common subject of sculpture. The perfect human beauty is that they strive to embody the Greeks in the images of athletes. The figure of the Delphian edition of the composition created by about 476 BC. e. An unknown master. The figure is cast in bronze, which has become a favorite material from that time.
Not only anonymous works V c are known. BC e. At this time, the sculptures of FIDI, Miron and a policlet worked in Athens. Many statues have reached us only in Roman marble copies of I-II century. n. e. The most famous among the works of Mirone from the Eleuter "Discobol" (about 460-450 BC), depicting an athlete at the time of the highest voltage before throwing the disc. Mirona first managed to convey the liveliness of movement in static art, the inner voltage of the figure. In another work - "Athena and Mariji", performed for the Athenian Acropolis, the Forest Forest of Mariji chooses a musical instrument among scattered at his feet, stands next to him with anger of Athena. Both figures are combined by action. It is interesting to note that, although Marsii acts here as a creature, expressing modern tongue, negative, only in his improper face emphasizes the absence of perfection, the body is perfectly perfect.
The policlet from Argos worked already in the period of high classics, in the middle and second half of the V c. BC e. He created the generalized artistic image of an athlete, which became the norm and sample. He was written theoretical treatise "Canon" (measure, rule), where the sculptor accurately calculated the size of the parts of the body on the basis of human growth as a unit of measurement (for example, a head - 1/7 to growth, face and brush hands - 1/10, feet - 1/6, etc.). He expressed his ideal in the restrained-powerful, calm-majestic images of Dorimfora (spear; 450-440. BC. Er), "Diadumen" (Athlete, who grows his head by a victorious bandage, about 420 BC. er) and "wounded Amazon", intended for the famous temple of Artemis in Ephesus. The polyclet embodied in his statures, above all, the image of an ideal free-born citizen of the policy, the city-state of Athens.
The third greatest sculptor V c. BC e. There was already mentioned Athenian Fidium. In 480-479 Persians captured and plundered Athens and the main sanctuations on the Acropolis. Among the ruins of the sacred church of Fidi, the seventener bronze statue of Athena Warper, Athens-Prosakhos, with a spear and a shield in hand, as a symbol of the revival of the city, its power and irreconcilities to enemies. Like all the subsequent works of Fidia, the statue died (she was destroyed by crusaders in Constantinople in the XIII century).
About 448 BC. FIDI performed the 13-meter Statue of Zeus for the temple of Zeus in Olympia. The face, hands and body of God were laid out by plates of ivory on a wooden basis, eyes from precious stones, raincoat, sandals, olive branches on the head, hair, beard - from gold (the so-called Christhelefactory technique). Zeus recresented on the throne, holding a scepter in his hands and the figure of the Victory Goddess. The sculpture was enjoying great fame, but she died in V c. n. e.
From 449. G. BC. e. The reconstruction of the Athenian Acropolis and FIDI began to be an embodiment of pericla's plan, supported by all Athenians.
In the sculpture to replace the masses and the severity of the strict classics, interest in the spiritual world of man comes, and in plastic, a more complex and less rectilineaceous characteristic is reflected. So, in the only sculptor reached the sculptor of the marble statue of Hermes (about 330 G. BC), the master portrayed an excellent young man, carelessly calm on the stump, in a state of rest and serenity. Thoughtfully and gently he looks at the baby Dionysus, who keeps on his hands. To change the courageous beauty of the athlete V c. BC e. Beauty comes a somewhat feminine, elegant, but also more spiritualized. On the statue of Hermes, traces of ancient coloring are preserved: red-brown hair, silver bandage. Another sculpture of Prakkitel was used by special glory - the statue of the Aphrodite of the Book. It was the first image of a naked female figure in Greek art. The statue stood on the banks of the Peninsula of Books, and the contemporaries wrote about real pilgrimages here to admire the beauty of the goddess, who was preparing to enter the water and dropping the clothes to the Vaza standing nearby. The original statue of the Aphrodite Book, unfortunately, has not been preserved. The heroes of Praxitel are not alien to the lyrical feeling, distinctly expressed, for example, in his "resting satire". Such traits developed even earlier, in the plastic of students of the Fidiye school, it is enough to indicate "Aphrodite in the gardens" of Alkamena, the reliefs of balustrade church of the Nick Aptereros or the tombstone of Gegezo unknown masters.
Skas, a native of the island of Paros, was a modern manner of Prapkitel. He participated in the creation of a relief frieze for Galicarnas Mausoleum in conjunction with Timothy, Leohhar and Brixis. Unlike Praxitel, Skasa continued the tradition of high classics, creating images of monumental-heroic. But from the images V c. They are distinguished by the dramatic tension of all spiritual forces.
In the state of ecstasy, in a stormy impulse of passion is shred to Menada. The satellite of God Dionisa is shown in the rapid dance, her head is trapped, the hair fell on the shoulders, the body is curved, represented in a difficult perspective, the folds of a short chiton emphasize the rapid movement. Lighting game enhances the dynamics of the image.
Unlike sculpture V in. Menada Schopasa is already calculated on all sides.
Lisipp - the third great sculptor IV century. BC e. (370-300 Gg. BC. E.). He worked in bronze and, if you believe the ancient writers, left after myself 1,500 bronze statues, which did not reach us in the script. Lisypes used already known plots and images, but it sought them to make them more vitality, not perfectly perfect, but characteristic of expressive. So, he showed athletes at the time of the highest voltage of the forces, but, as a rule, at the time of their recession, after the competition. This is how his apoxy is presented to the sand after sports battle. He has a tired face licking his hair. Plenitive Hermes, always fast and alive, is also represented by the Lisipp, as it were, in a state of extreme fatigue, briefly fastened to a stone and ready to run on their winged sandals at the next second. Tired from the features depicts Lisipp and Hercules ("Recreation Hercules"). Lisipp created his canon proportions of the human body, according to which his figures are higher and slimmer than at the polyclet (the size of the head is 1/9 of the figure).
Lisipp was a multifaceted artist. The court sculptor Alexander Macedonsky, he made gigantic multi-digurized compositions, such as the battle of 25 shapes of riders, statues of the gods, portraits (more than once he depicted Alexander Macedonian, the best portraits of the famous commander carries the features of almost tragic rejection).
For the art of late classics it was characterized by the introduction of new genres, which were further developed at the next stage - in Ellinism.
