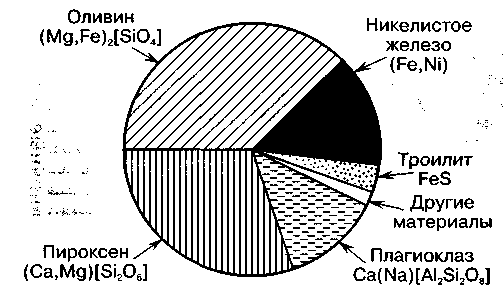Asteroids comets meteors. Asteroids. Meteorites. Meteors. Geograph is a near-Earth asteroid that is either a double object or has a very irregular shape. This follows from the dependence of its brightness on the phase of rotation around its own axis, and that
Minor planets – asteroids (Greek asteroedeis - star-like) have nothing in common with stars, and are named so only because they are visible through a telescope as point objects. The history of the discovery of small planets is interesting. By the end of the 18th century. the empirical law of planetary distances was known (the so-called Titius-Bode rule), according to which there should have been another unknown planet between Mars and Jupiter. The search for it led the astronomer Piazzi to the discovery in 1801 of the planet Ceres with a diameter of 1003 km. The discovery of three more planets: Pallas - 608 km, Juno - 180 km and Vesta - 538 km - was unexpected. In recent years, asteroids up to 1 km in diameter have been discovered, and their total number reaches several thousand. Since asteroids move, during long photographic exposures they appear as bright white lines against a black background of the starry sky.
Finally, asteroids should be mentioned. In this case we talk about larger words because they are much larger than rocks: they are usually irregular in shape, but those that have reached a spherical shape can even be considered minor planets, like Pluto. Some of them come from education solar system, and others - from shocks and others. In short, asteroids pose a threat to the Earth and the reef for cataclysmic Hollywood movies.
Did you understand him?
What then fell on Tunguska? Since there were no remains, it is believed that the comet: the ice has melted. The answer is waiting in the background. Bodies discovered in the first year of the Neovis mission are approaching our planet. The space mission has described 439 nearby organs since the mission was relaunched in December. Of these, 72 were new discoveries.
Observations have shown that asteroids have an irregular polyhedral shape and move in orbits of various shapes - from circles to highly elongated ellipses; the vast majority of them (98%) are contained between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter (“the main asteroid belt”), but the asteroid Icarus approaches the Sun closer than Mercury, and some move away as far as Saturn. The orbits of most asteroids are concentrated near the ecliptic plane; their circulation periods range from 3.5 to 6 years; they are assumed to rotate around their axes (based on the periodic change in apparent brightness). Based on their material composition, asteroids are divided into stony, carbonaceous and metallic asteroids.
A meteorite is flying to Earth: can it be prevented?
Objects located near the Earth are comets and asteroids, which are pushed by the gravitational pull of the giant planets of our solar system into orbits that allow them to penetrate into the vicinity of the Earth. Its follow-up is necessary to prevent future impacts, since exposure to the atmosphere of, say, a rock "only" ten meters deep could result in an explosion equivalent to three atomic bombs.
A meteorite is a solid body of cosmic origin that fell to the surface of the Earth. Most meteorites found weigh between a few grams and several kilograms. A crater may form at the site of a meteorite impact
A new video based on the data collected shows the asteroids and comets observed so far by the probe. Comets and shooting stars. Every year in mid-August we are treated to a celestial spectacle: the Perseids. The Perseids are actually a shower of shooting stars, like the fifteen or so that repeat every year. A shooting star is always a unique moment, mysterious to many, intriguing to others.
The total mass of all asteroids is estimated at 0.01 Earth masses. Their common attraction does not cause noticeable disturbances in the movement of Mars and other planets.
The orbits of some asteroids intersect with the orbit of the Earth, but the probability of the Earth and an asteroid simultaneously being at the same point and colliding is extremely small. It is believed that 65 million years ago, a celestial body such as an asteroid fell to Earth in the area of the Yucatan Peninsula and its fall caused clouding of the atmosphere and a sharp decrease in the average annual air temperature, which affected the Earth's ecosystem.
Today this cloud is known as the Oort cloud, although it has not been observed as such, it is based on accumulated statistics and its existence is assumed. A comet plunges into the sun if its orbital conditions and attractive disturbances allow it, gaining speed and brilliance as it approaches the Sun. Occasionally, it may cross Earth's orbit, and fragments of the dust tail will produce a shower of shooting stars.
Thus, shooting stars are dust particles comparable to grains of sand that enter our atmosphere. This speed depends mainly on two factors, the direction of impact with the Earth and the proper speed of the comet, which obviously depends on its orbit or origin. There are basically two categories of shooting stars, those belonging to comets or solar system and those belonging to galactic system. Most of the shooting stars we see come from a comet. The following table shows the main characteristics of falling star showers.
Currently, astronomers are concerned about the unusual “invasion” of large celestial bodies in the vicinity of the planets of the solar system. So, in May 1996, two asteroids flew at a short distance from the Earth. Many experts suggest that the solar system fell into a kind of trail of large celestial bodies formed outside our system, and therefore believe that, along with the nuclear threat, the number one danger for our planet has become the danger posed by asteroids. A new important problem has arisen - the creation of space protection of the Earth from asteroids, which should include both ground-based and space-based assets, including those located in deep space. The creation of such a system should be carried out on an international basis.
The intersection of a comet with its orbit and the Earth is very rare given the size of the solar system. If a shooting star hits the ground, it is called a meteorite. There are two main types of meteorites, rocky and iron. The table opposite gives the percentage of elements present in meteorites.
Some meteorites or shooting stars are more spectacular than others, they are called fireballs or fireballs, cars are actually large pebbles and a cracking loud sound or a hissing sound can be heard. This sound is heard a few minutes after the car passes.
On the other hand, the increase in the number of visible asteroids can be explained by the increase in the volume of astronomical information in recent years, after observations were transferred from the Earth's surface to near space.
On the issue of the origin of asteroids, two directly opposing points of view have been expressed. According to one hypothesis, asteroids are fragments of a large planet (it was called Phaethon), located between Mars and Jupiter at the site of the main asteroid belt and split apart as a result of a cosmic catastrophe due to the powerful gravitational influence of Jupiter. According to another hypothesis, asteroids are protoplanetary bodies that arose due to the thickening of the dust environment, which could not unite into a planet due to the disturbing action of Jupiter. In both cases, the “culprit” turns out to be Jupiter.
Notes: Comets are made of loose materials, resulting in the comet's remnants never generating a meteorite, the last of the asteroids that scattered debris upon impact. The most famous of the comets is probably Halley, which returned to this comet, crossed the Earth's orbit and gave us two rains. These two comets were the most beautiful of the last 20 years, but did not intersect Earth's orbit, so they did not generate showers of shooting stars.
Oort cloud comets have long, elongated orbits that last millions of years, but those that return after a relatively short period of time, such as Halley's Comet, which returns every 76 years, are called periodic. Famous shooting stars are caused by comets in elliptical orbits. In the case of parabolic and hyperbolic comets, comets are only one step away; a comet in a hyperbolic orbit indicates that it is extrasolar.
Comets (Greek cometes - long-haired) - small bodies of the Solar System, moving in highly elongated elliptical or even parabolic orbits. Some comets have perihelia near the Sun and aphelion outside Pluto. The movement of comets in orbits can be either forward or backward. The planes of their orbits lie in different directions from the Sun. The orbital periods of comets vary greatly: from several years to many thousands of years. A tenth of the known comets (about 40) have appeared more than once; they are called periodic.
Calculation and observation tell us that most comets have elliptical orbits, parabolic and hyperbolic less than 1%, and designing the orbits of comets or planets is quite a difficult task. The basic principles were established more than 300 years ago by Newton and Kepler. To determine the orbit we need 6 parameters.
Orbital eccentricity.
- The inclination of the orbital plane relative to the Earth.
- Longitude of the ascending node.
- Perihelion latitude argument.
- The moment of transition to perihelion.
- Semi-minor axis of the orbit.
Comets have a head and a tail. The head consists of a hard core and coma. The core is an ice conglomerate of frozen gases (water vapor, carbon dioxide, methane, ammonia, etc.) with an admixture of refractory silicates, carbon dioxide and metal particles - iron, manganese, nickel, sodium, magnesium, calcium, etc. It is assumed that the core contains organic molecules. Comet nuclei are small, their diameter ranges from several hundred meters to several (50 – 70) kilometers. Coma is a gas-dust environment (hydrogen, oxygen, etc.), glowing when approaching the Sun. Near perihelion, from the comet’s nucleus, under the influence of solar heat and corpuscular flows, “evaporation” (sublimation) of frozen gases occurs and a luminous tail of the comet is formed, sometimes more than one. It consists of rarefied gases and small solid particles and is directed in the direction opposite to the Sun. The length of the tails reaches hundreds of millions of kilometers. The Earth has fallen into the tails of comets more than once, for example in 1910. This then caused great concern among people, although falling into comet tails does not pose any danger to the Earth: they are so rarefied that the admixture of poisonous gases contained in the composition comet tails(methane, cyanogen), imperceptible in the atmosphere.
Shooting Stars: Grains of dust that burn in our atmosphere, leaving behind a glowing trail. Most of them come from comets. Fireball: A shooting star brighter than magnitude -8, also called a fireball. Cars usually cause pieces of iron or rock from asteroids. If the fragments survive entry into the atmosphere, they are called meteorites.
Meteorite: The remains of a solid object that has survived entry into the atmosphere and remains on the ground. A huge dirty snowball, which can have a diameter of about 60 km, consisting of various solid gases mixed with solid dust. As a comet approaches the Sun, it heats the surface so that gases and dust escape into space and the tail can be observed.
Among periodic comets, the most interesting is Halley's comet, named after the English astronomer who discovered it in 1682 and calculated its orbital period (about 76 years). It was in its tail that the Earth found itself in 1910. It last appeared in the sky in April 1986, passing at a distance of 62 million km from Earth. Careful studies of the comet using spacecraft showed that the icy core of the comet is a monolithic body of irregular shape measuring about 15x7 km, around which a giant hydrogen corona with a diameter of 10 million km was discovered.
Meteorites are...
Asteroids: an asteroid is a small planet that usually gravitates between the orbit of Mars and Jupiter, the largest is Ceres with a diameter of 770 km, only a few dozen have more than 100 km, thousands of others are within a few meters of about ten kilometers. We have not determined the minimum diameter for an asteroid, nor for a planet from other locations. Unlike comets, asteroids are made of rocks and iron and do not produce tails.
The energy that such a moving body possesses is truly amazing, and the comet is actually integrated into the upper atmosphere of Jupiter. The resulting 2 km diameter crater is known as the Arizona Meteor Crater. If such a collision were to occur again, we may ask what would be the consequences? The energy of a moving body is proportional to its mass and the square of its speed, meaning that if you double the speed of an object, you quadruple its energy.
Comets are short-lived celestial bodies, since as they approach the Sun they gradually “melt” due to the intense outflow of gases or break up into a swarm of meteors. The meteoric material is subsequently more or less evenly distributed throughout the entire orbit of the parent comet. In this regard, the history of the periodic (about 7 years) comet Bijela, discovered in 1826, is interesting. Twice after its discovery, astronomers observed its appearance, and the third time, in 1846, they managed to record its division into two parts, which, on subsequent returns They were moving further and further away from each other. Then the meteoric substance of the comet stretched across the entire orbit, during which the Earth crossed an abundant “rain” of meteors.
These systems photograph entire regions of the sky, and computer programs can detect asteroids or comets that might collide with Earth. Left picture: Comet and shooting stars! In the right photo we see Leonid. This time the camera was on a telescope guide to compensate for the rotational motion of the Earth.
On the right is a view of space from a shower of shooting stars on Earth. The direction of arrival indicates the radiance. On the left is an image of the aurora visible from Earth. If the shooting star does not appear to be coming from a known radiant, it is called sporadic. Each of the shooting star showers is not identical. The age of the comet, the size of the comet, the speed and eccentricity of the orbit make the series the same year after year. The two most beautiful rains are the Perseids and Leonids.
There is no precise evidence that the Earth has ever collided with a comet nucleus. No more than five comets penetrate into Earth's orbit each year. However, there is a version that the famous Tunguska “meteorite”, which fell in 1908 in the basin of the Podkamennaya Tunguska River, near the village of Vanavara, is a small (about 30 m) fragment of the nucleus of comet Encke, which exploded as a result of thermal heating in the atmosphere, and the “ice” " and solid impurities "evaporated". At the same time explosive air wave forest was felled over an area within a radius of 30 km.
The Leonidov case is more interesting. Every 33 years, the comet returns and produces thousands of meteors per hour, shooting stars moving at very high speeds, reaching 70 kilometers per second, so they quickly burn in a flash of blue light, often very impressive.
To watch showers of shooting stars, you need to follow some basic rules. 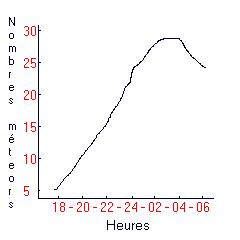
Observations tell us what is most best time to see shooting stars, early in the morning in general. The Earth in its revolution motion around the Sun and its direction of rotation allows us to see more meteors at this moment because we are colliding with the apex. Once again, this is the same principle as snow falling heavily on the windshield of a moving car. There are more flakes in front than behind. The following chart shows the optimal viewing hours, between 2 and 4 am.
In 1994, scientists observed the fall of Comet Shoemaker-Levy onto Jupiter. At the same time, it broke up into dozens of fragments 3–4 km in diameter, which flew one after another at an enormous speed - about 70 km/s, exploded in the atmosphere and evaporated. The explosions created a gigantic hot cloud 20 thousand km in size and with a temperature of 30,000 °C. The fall of such a comet to Earth would end in a cosmic catastrophe.
This association keeps statistics on rainfall, as well as on meteors or cars. Observation reports can be submitted to this association, which will then be compiled and stored. Photos and illustrations: Luc BellavanceNew Crater of Quebec photo: Government of QuebecRevision: Damien Lemay. Comets, asteroids and meteorites.
Asteroids, meteorites and comets are phenomena that regularly make scientific news headlines, especially when they are visible or at risk of impacting Earth. Let's pick up these different celestial bodies, the object of many fantasies. They are irregularly shaped, kilometer-sized conglomerates of ice, dust and rock, orbiting the Sun in a highly elliptical orbit. As the comet approaches the sun, the ice heats up and sublimates, creating for distant observers the famous hair still stretching out in reverse direction to the sun.
It is believed that the “comet cloud” surrounding the Sun formed along with the Solar System. Therefore, by studying the material of comets, scientists obtain information about the primary material from which planets and satellites were formed. In addition, assumptions have emerged about the “participation” of comets in the origin of life on Earth, since radio spectroscopic methods have proven the presence of complex organic compounds (formaldehyde, cyanoacetylene, etc.) in comets and meteorites.
Comets were formed in front of the planets of the solar system about 4.5 billion years ago. The most famous comet Halley, visiting the Earth every 76 years. Asteroids are celestial bodies formed from rocks or metals orbiting the Sun. They are usually irregular in shape and do not exceed several hundred kilometers.
Most likely, they will approach or cross, for some of them, the Earth's orbit around the Sun. Asteroids or comet nuclei viewed during or after impact on a planet, including Earth. Meteorites found on Earth are divided into three families: stones, irons, and mixed. Not to be confused with meteor light, which is caused by a meteorite crossing the Earth's atmosphere. A meteorite viewed before its return to Earth's atmosphere is sometimes called a meteoroid.
Meteors, usually called “shooting stars”, are tiny (mg) solid particles that fly into the atmosphere at speeds of up to 50 - 60 km/s, heat up due to friction with the air to several thousand degrees Celsius, ionize gas molecules, causing them to emit light, and evaporate at an altitude of 80–100 km above the earth’s surface. Sometimes a large and exceptionally bright fireball appears in the sky, which can break apart and even explode during flight. Such a meteor is called fireball. A similar fireball exploded on September 25, 2002 in Irkutsk region, between the villages of Mama and Bodaibo. In the sky, both individual meteors appearing randomly in the sky, and groups of meteors in the form of meteor showers, within which particles move parallel to each other, although in perspective it seems that they are scattering from one point in the sky, called radiant. Meteor showers are named by the constellations in which their radiants are located. The Earth crosses the orbit of the Perseids around August 12, the Orionids - October 20, the Leonids - November 18, etc. Meteor showers move along the orbits of those asteroids or comets, as a result of the disintegration of which they are formed. Orbits meteor showers are carefully studied for the safety of spacecraft and devices.
Meteorites(from Greek meteora - celestial phenomena) are called large meteoroids that fall to Earth. Every year on earth's surface About two thousand meteorites fall with a total mass of about 20 tons. They are fragments of a rounded angular shape, usually covered with a thin black melting crust with numerous cells from the drilling action of air jets. According to their structure, they are of three classes: iron, consisting mainly of nickel iron, stone, which contain predominantly silicate minerals, and iron-stone, consisting of a mixture of these substances. Among the stony ones, there are two groups: chondrites (granular meteorites) and achondrites (earthy meteorites). Stony meteorites predominate (Fig. 3). Physico-chemical analysis of meteorites indicates that they consist of chemical elements and their isotopes known on Earth, which confirms the unity of matter in the Universe.
|
|
Rice. 3. a – relative frequency of meteorite falls different classes(according to J. Bud); b – mineral composition of a typical chondrite (according to V. E. Khain)
The largest Goba meteorite, measuring 2.75x2.43 m and weighing 59 tons, was found in southwest Africa; it is iron. The Sikhote-Alin meteorite (fell in 1947) split into thousands of pieces in the air and fell to Earth as “iron rain.” The total weight of the collected fragments is about 23 tons, they created 24 impact craters ranging from 8 to 26 m in diameter. The Kaaba meteorite (“Black Stone”) is kept in the Mecca mosque in Saudi Arabia and serves as an object of worship for Muslims. Many meteorites have been discovered in Antarctica, and they are also found in the sediments of the floor of the World Ocean.
At the dawn of the Earth's existence, when there was still a lot of unused material in the solar system, and the Earth's atmosphere - protection from meteorites - was still very thin, the number of meteorites bombarding the Earth was enormous and its surface resembled the face of the Moon. With time most of craters were destroyed by tectonic and exogenous processes, but many of them were still preserved in the form of ring-shaped geological structures called astroblemes(“star scars”). They are especially visible from space. They reach tens of kilometers in diameter. The study of meteorites allows us to judge the structure and properties of celestial bodies and supplements our information about the internal structure of the Earth.

A meteorite that fell on Friday, February 15, 2013 in Chelyabinsk led to many questions.
According to the data, a meteorite with a diameter of about 15 meters and weighing 7,000 tons entered the atmosphere at an angle of about 20 degrees at a speed of 65,000 km per hour. It passed through the atmosphere for 30 seconds before breaking apart. This resulted in an explosion approximately 20 km above the ground, producing a shock wave of 300 kilotons. As a result, more than 1000 people were injured.
Meteorite fragments were recently found near Lake Chebarkul.
Events such as the fall of a meteorite once again remind us of the potential danger that exists in outer space. What are a meteorite, an asteroid and a comet? How often do such events occur and can they be prevented?
Meteor falling
Meteor, meteorite, meteoroid - what's the difference?
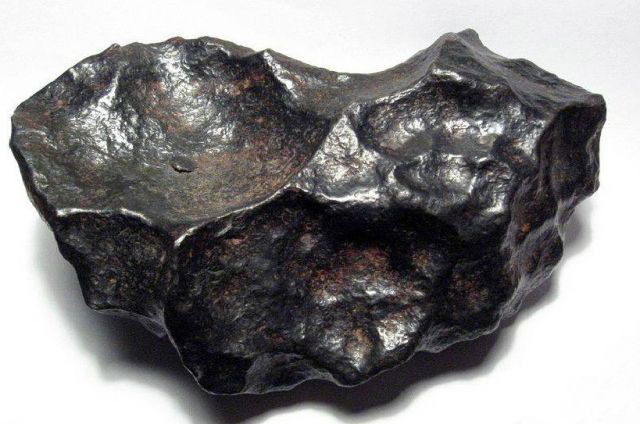

A meteor is the scientific name for a "shooting star" and is the glowing trail of space debris that ends up in the Earth's atmosphere. They can be small as a grain of sand and large meteoroids up to 10-30 meters in size. As a rule, they burn up in the atmosphere, and those that fall to Earth are called meteorites.
How often does a meteorite fall to Earth?
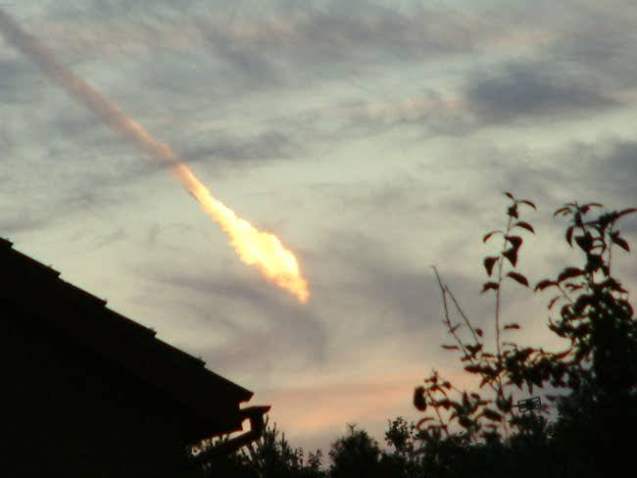

Small drops happen every few months, but we don't see them. The thing is that two-thirds of the Earth is oceans, so we often miss these events. Such large objects as the one that exploded in Chelyabinsk occur much less frequently, approximately every five years. So in 2008, a similar event was observed in Sudan, but no one was hurt.
A meteorite is flying to Earth: can it be prevented?

Typically, such meteor bodies go unnoticed, since most telescopes are aimed at identifying huge, potentially dangerous asteroids. There is no weapon yet that can prevent the fall of a meteorite or asteroid.
Asteroid impact
The Chelyabinsk meteorite was the largest after Tunguska meteorite 1908 in Siberia, which was caused by an object approximately the size of asteroid 2012 DA14, which safely flew within a minimum distance of 27,000 km from Earth on February 15, 2013.
Asteroid Passage: What is an asteroid?

An asteroid is a celestial body that orbits the Sun, usually between Mars and Jupiter. Asteroids are also called space debris or fragments left behind when the solar system was formed.
Because of the collisions, some asteroids are ejected from the main belt, and they end up on a trajectory that intersects the Earth's orbit.
Large asteroids are called planetoids, and objects smaller than 30 meters are called meteoroids.
Asteroid sizes: how big can they be?
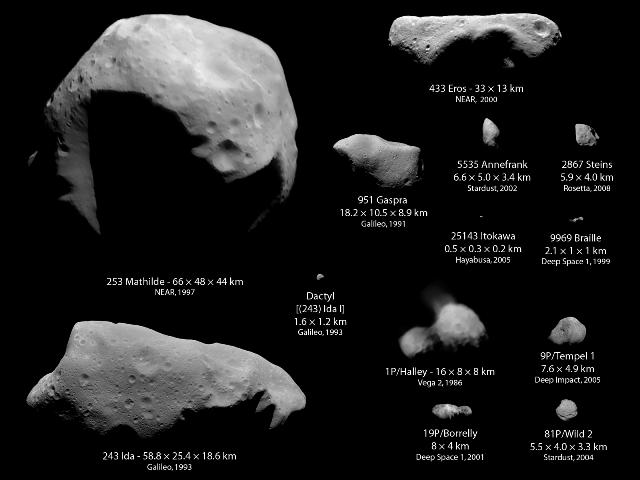

Asteroid 2012 DA14, which flew by on Friday, was about 45 meters in diameter and weighed about 130,000 tons. Scientists believe there are about 500,000 asteroids the size of asteroid 2012 DA14. However, less than one percent of asteroids have been discovered so far.
The supposed asteroid that killed the dinosaurs 65 million years ago is believed to have been around 10-15 km in diameter. If an asteroid of this magnitude were to fall today, it would wipe out all modern civilization.

Statistically, asteroids larger than 50 meters fall to Earth once a century. Asteroids larger than 1 km in diameter can collide every 100 thousand years.
Comet crash
2013 can be called the year of comets, as we will be able to observe two of the brightest comets in history at once.
What is a comet?
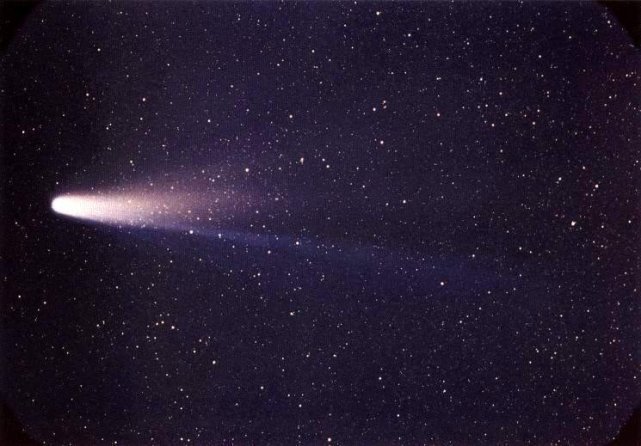

Comets are celestial bodies our solar system, consisting of ice, dust and gas. Most of them are located in the Oort Cloud, a mysterious region of the outer edge of the solar system. Periodically they pass close to the Sun and begin to evaporate. The solar wind turns this steam into a huge tail.
Most comets are too far from the Sun and Earth to be seen with the naked eye. Bright comets appear every few years, and it is even rarer for two comets to appear in one year.
Comet 2013
Comet PANSTARRS
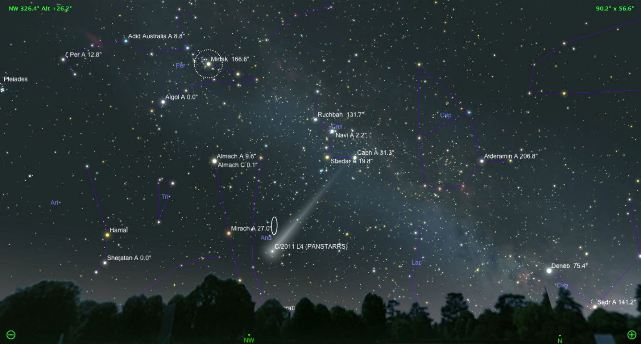
Comet PANSTARRS or C/2011 L4 was discovered in June 2011 using the Pan-STARRS 1 telescope located on the summit of Haleakala in Hawaii. In March 2013, the comet will be closest to the Sun (45,000 km) and the Earth (164 million km).
Although comet PANSTARRS was a dim and distant object at the time of its discovery, it has steadily become brighter since then.
Comet ISON, discovered in 2012
When can you watch? Mid November – December 2013
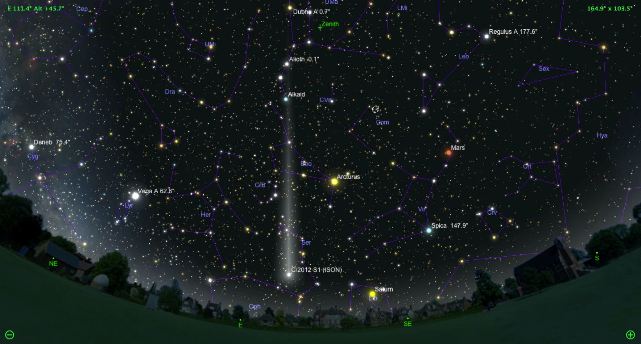
Comet ISON or C/2012 S1 was discovered on September 21, 2012 by two astronomers Vitaly Nevsky and Artem Novichonok using a telescope International Scientific Optical Network(ISON).
Orbital calculations showed that comet ISON will make its closest approach to the Sun at a distance of 1.2 million km. The comet will be bright enough to be visible in the sky at its closest approach to the Sun in the first weeks of November.
It is believed that this comet will be brighter than the full Moon and will be visible even during the day.
Comet Impact 
Could a comet collide with Earth? It is known from history that the comet Shoemaker-Levi 9 collided with Jupiter in July 1994, and it became the first comet collision observed by scientists. Considering that this happened on an uninhabited planet, the event became more likely interesting example destructive forces of the Universe. However, if this had happened on Earth, history would have taken a completely different turn.
Comets and asteroids
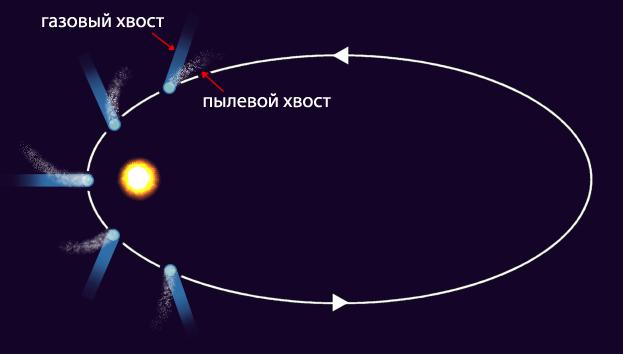
Comets differ from asteroids in that they have an unusually elongated elliptical orbit, meaning they move very large distances from the Sun. On the contrary, asteroids remain within the asteroid belt.
Fortunately, it takes many years to pass the comet's orbit. A comet approaches Earth once every 200,000 years. To date, there are no known comets that pose a threat to our planet in the near future.
Comets with an orbital period greater than 200,000 years have a less predictable orbit and, although there is little chance of colliding with Earth, they should not be forgotten.