Information about interesting celestial bodies - comets. Asteroids. Comets. meteoric substance
To small bodies solar system include asteroids, meteoroids, comets, and Kuiper belt bodies. Asteroids are less than a thousand kilometers in size. More small bodies, than asteroids, are called "meteoroids" or meteoroid bodies, they can be on the order of several meters or even smaller.
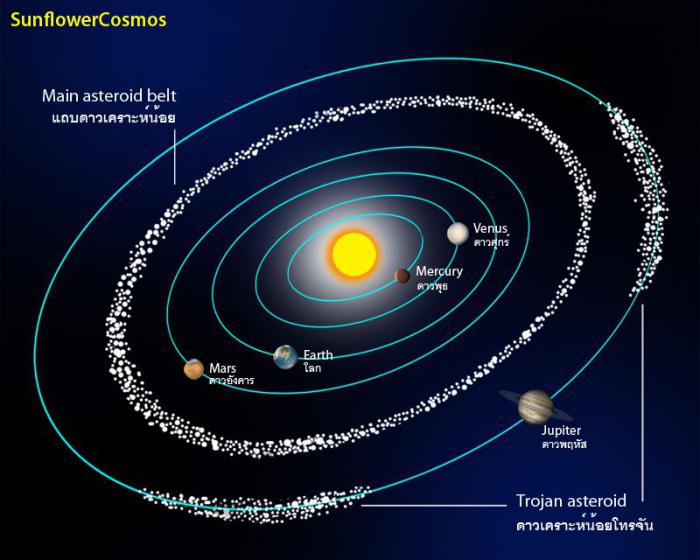
Asteroid- a small planet-like body in the solar system, ranging in size from several meters to thousands of kilometers, asteroids are often called minor planets(but not dwarf planets!) Most asteroid orbits are concentrated in the main asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
History of the discovery of asteroids.
On January 1, 1801, Italian astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi accidentally discovered a star whose declination changed noticeably over the course of 24 hours of observation; this object was located between Mars and Jupiter. This object was named Ceres after the ancient Roman goddess of fertility. Thus, astronomers discovered a new type of objects in the solar system, later called asteroids. Observing the movement of Ceres, the German physician Heinrich Wilhelm Olbers discovered a new asteroid in 1802, which was named Pallas in honor of the ancient Greek goddess Pallas Athena. Juno was discovered in 1804, Vesta in 1807. Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel proposed calling small planets asteroids. Asteroid means "star-shaped" in Greek.
In 1804, Olbers expressed the famous hypothesis about the rupture of the hypothetical planet Phaeton between Mars and Jupiter and the formation of asteroids - its fragments. Since 2006, the first asteroid found, Ceres, has been classified as a dwarf planet. Asteroids near the Earth and their danger to the planet
Hazardous space objects, such as asteroids whose orbits intersect the Earth’s orbit, represent serious threat the existence of human civilization during a collision between the Earth and an asteroid. The number of asteroids crossing the Earth's orbit and having a diameter of more than 1 km is approximately 500.
Behind last years large asteroids passed by repeatedly, causing fear and anxiety. In 1936, the Adonis asteroid flew 2 million km from the Earth; in 1937, the Hermes asteroid flew at a distance of 800 thousand km from the Earth. In 1996, the Tautatis asteroid flew at a distance of 450 thousand km from Earth
A significant part of the main belt asteroids move along stable, stable orbits, which have changed little over the past 4.5 billion years, so collisions with such asteroids are practically unlikely.
But the orbits of asteroids can change when approaching giant planets or when colliding with other asteroids and comets, so the orbits of asteroids can change.
The American astronomer R. Binzel developed a high-quality a scale for assessing the risk of collisions with the Earth by asteroids and comets, similar to the Richter scale, used to gradate earthquake hazards. In 1999, the scale was approved by the International Astronomical Union. (show table on presentation slide). According to various estimates, there is a high probability of an asteroid with a diameter of about 1 km falling to Earth once every 100 thousand years. But the greatest probability is that the Earth will encounter smaller celestial objects.
Several double asteroids have been discovered.
In 1993, the American spacecraft Galileo, heading towards Jupiter, crossed the main asteroid belt. It turned out that the asteroid Ida has a small satellite called Dactyl.
Asteroid Eros revolves around the Sun with a period of 1.8 Earth years. Its dimensions are 40 x 14 x 14 km. In 2000, the robotic NEAR-Shoemaker spacecraft took many photographs of the asteroid. Studies of the asteroid have shown that Eros is a monolithic solid, that its chemical composition is approximately homogeneous, and that it was formed in the “young years” of the Solar System. In 2001, the device landed on the surface of an asteroid.
Asteroid 216 Cleopatra consists mainly of metals such as nickel and iron, as shown by radar studies.
Asteroid 951 Gaspra has dimensions of 19x12x11 km and orbits in an almost circular orbit within the main asteroid belt. Gaspra consists of a mixture rocks and metal-containing minerals.
Asteroids beyond the orbit of Jupiter.
Other asteroids were discovered beyond the orbit of Jupiter at the end of the 20th century. The second asteroid belt is called the Kuiper belt.
The Kuiper Belt is a disk-shaped region beyond the orbit of Neptune, at a distance of 30 AU. up to 100 a.u. from the Sun, populated by asteroids and comet nuclei.
It is assumed that Kuiper belt objects are ice with small admixtures of organic substances, that is, they are close in composition to cometary matter. The mass of all Kuiper belt objects exceeds the mass of all asteroids in the main asteroid belt. But it is assumed that the mass of Orth cloud objects exceeds the mass of Kuiper belt objects.
Comets- the most numerous, most extensive and most amazing celestial bodies of the Solar System. The word “comet” translated from Greek means “hairy”, “long-haired”. As the comet approaches the Sun, it takes on a spectacular appearance, heating up under the influence of the sun's heat so that gas and dust fly away from the surface, forming a bright tail.
According to scientists, on the distant outskirts of the solar system, in the so-called Oort cloud - a giant spherical accumulation of cometary matter - there are about 10 12 -10 13 comets orbiting the Sun. As the comet approaches the Sun, the ice of the comet's nucleus begins to evaporate, and streams of gas and dust begin to be released into space.
- Comet structure
Each comet has several different parts:
- Core: Relatively solid and stable, consisting mainly of ice and gas with minor additions of dust and other solids.
- Head (coma): a luminous gas shell arising under the influence of electromagnetic and corpuscular radiation from the Sun. A dense cloud of water vapor, carbon dioxide and other neutral gases sublimating from the core.
- Dust tail: consists of very small dust particles carried away from the core by a gas flow. This part of the comet is best visible to the naked eye.
- Plasma (ion) tail: consists of plasma (ionized gases), interacts intensely with the solar wind.
The structure of comets and the features of comet tails are best illustrated using the “Comets” and “Comets: structure” models.
Meteor bodies
There is no clear distinction between meteoroids (meteor bodies) and asteroids. Usually meteoroids are bodies measuring less than a hundred meters, and larger ones by asteroids. The collection of meteoroids forming around the Sun forms meteoric material in interplanetary space. A certain proportion of meteoroids are the remnants of the substance from which the Solar System was once formed, some are the remnants of the constant destruction of comets, and fragments of asteroids.
meteor body or meteoroid- a solid interplanetary body that, when entering the atmosphere of a planet, causes a phenomenon meteor and sometimes ends with a fall to the surface of the planet meteorite.
What usually happens when a meteoroid reaches the Earth's surface? Usually nothing, since due to their small size, meteoroids burn up in the Earth's atmosphere. Large clusters meteor bodies are called meteor swarm. During the approach of a meteor swarm to the Earth, meteor showers .
- Meteors and fireballs
The phenomenon of combustion of a meteoroid in the atmosphere of a planet is called meteor. A meteor is a short-term flash, the combustion trail disappears after a few seconds.
About 100,000,000 meteoroids burn up in the Earth's atmosphere per day.
If the meteor trails are continued back, they will intersect at one point called meteor shower radiant.
Many meteor showers are periodic, repeating year after year, and are named after the constellations in which their radiants lie. Thus, the meteor shower, observed annually from approximately July 20 to August 20, is called the Perseids because its radiant lies in the constellation Perseus. The Lyrids (mid-April) and Leonids (mid-November) meteor showers respectively get their name from the constellations Lyra and Leo.
It is extremely rare that meteoroid bodies are relatively large in size, in which case they say that they are observing car. Very bright fireballs are visible during the day.
- Meteorites
If the meteor body is large enough and could not completely burn up in the atmosphere during its fall, then it falls onto the surface of the planet. Such meteoroids falling to Earth or another celestial body are called meteorites.
The most massive meteoroids with high speed fall onto the Earth's surface to form crater.
Depending on the chemical composition meteorites are divided into stone (85 %), iron (10%) and iron-stone meteorites (5%).
Stone meteorites consist of silicates with inclusions of nickel iron. Therefore, heavenly stones are usually heavier than earthly ones. The main mineralogical components of the meteorite substance are iron-magnesium silicates and nickel iron. More than 90% of stony meteorites contain round grains - chondrules . Such meteorites are called chondrites.
Iron meteorites almost entirely composed of nickel iron. They have an amazing structure, consisting of four systems of parallel kamacite plates with a low nickel content and interlayers consisting of taenite.
Stone-iron meteorites consist half of silicates, half of metal. They have a unique structure, not found anywhere except meteorites. These meteorites are either metallic or silicate sponges.
One of the largest iron meteorites, the Sikhote-Alin meteorite, which fell on the territory of the USSR in 1947, was found in the form of a scattering of many fragments.
Since ancient times, people have sought to uncover the secrets that the sky holds. Since the first telescope was created, scientists have been gradually collecting grains of knowledge that are hidden in the boundless expanses of space. It's time to find out where the messengers from space - comets and meteorites - came from.
What is a comet?
If we examine the meaning of the word "comet", we come to its ancient Greek equivalent. Literally it means “with long hair.” Thus, the name was given in view of the structure of this Comet, which has a “head” and a long “tail” - a kind of “hair”. The head of a comet consists of a nucleus and perinuclear substances. The loose core may contain water, as well as gases such as methane, ammonia and carbon dioxide. The comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, discovered on October 23, 1969, has the same structure.
How the comet was previously represented
In ancient times, our ancestors revered her and invented various superstitions. Even now there are those who associate the appearance of comets with something ghostly and mysterious. Such people may think that they are wanderers from another world of souls. Where did this come from? Perhaps the whole point is that the appearance of these heavenly creatures ever coincided with some unkind incident.
However, as time passed, the idea of what small and large comets were changed. For example, a scientist like Aristotle, studying their nature, decided that it was a luminous gas. After a while, another philosopher named Seneca, who lived in Rome, suggested that comets are bodies in the sky moving in their orbits. However, real progress in their study was achieved only after the creation of the telescope. When Newton discovered the law of gravity, things took off.
Current ideas about comets
Today, scientists have already established that comets consist of a solid core (from 1 to 20 km in thickness). What does the comet's nucleus consist of? From a mixture of frozen water and cosmic dust. In 1986, photographs of one of the comets were taken. It became clear that its fiery tail is an emission of a stream of gas and dust, which we can observe from earth's surface. For what reason does this “fiery” emission occur? If an asteroid flies very close to the Sun, then its surface heats up, which leads to the release of dust and gas. Solar energy exerts pressure on the solid material that makes up the comet. As a result, a fiery tail of dust is formed. This debris and dust is part of the trail that we see in the sky when we observe the movement of comets.
What determines the shape of a comet's tail?
The post on comets below will help you better understand what comets are and how they work. They come in different varieties, with tails of all sorts of shapes. It's all about the natural composition of the particles that make up this or that tail. Very small particles quickly fly away from the Sun, and larger ones, on the contrary, tend to the star. What is the reason? It turns out that the former move away, pushed by solar energy, while the latter are affected by the gravitational force of the Sun. As a result of these physical laws, we get comets whose tails are curved in different ways. Those tails that are largely composed of gases will be directed away from the star, while corpuscular tails (consisting mainly of dust), on the contrary, will tend to the Sun. What can you say about density? comet tail? Cloud tails can typically measure millions of kilometers, in some cases hundreds of millions. This means that, unlike the body of a comet, its tail consists largely of discharged particles, having practically no density. When an asteroid approaches the Sun, the comet's tail can bifurcate and acquire a complex structure.

The speed of particle movement in a comet's tail
Measuring the speed of movement in a comet's tail is not so easy, since we cannot see individual particles. However, there are cases when the speed of movement of matter in the tail can be determined. Sometimes gas clouds can condense there. From their movement, the approximate speed can be calculated. So, the forces moving the comet are so great that the speed can be 100 times greater than the gravity of the Sun.
How much does a comet weigh?
The entire mass of comets largely depends on the weight of the comet's head, or more precisely, its nucleus. Presumably, the small comet could weigh only a few tons. Whereas, according to forecasts, large asteroids can reach a weight of 1,000,000,000,000 tons.
What are meteors
Sometimes one of the comets passes through the Earth's orbit, leaving a trail of debris in its wake. When our planet passes by the place where the comet was, these debris and cosmic dust remaining from it enter the atmosphere at great speed. This speed reaches more than 70 kilometers per second. When the comet's fragments burn up in the atmosphere, we see a beautiful trail. This phenomenon is called meteors (or meteorites).
Age of comets

Fresh asteroids of enormous size can survive in space for trillions of years. However, comets, like any other one, cannot exist forever. The more often they approach the Sun, the more they lose the solid and gaseous substances that make up their composition. “Young” comets can lose a lot of weight until a kind of protective crust forms on their surface, which prevents further evaporation and burning out. However, the “young” comet ages, and the nucleus becomes decrepit and loses its weight and size. Thus, the surface crust acquires many wrinkles, cracks and breaks. Gas streams, burning, push the body of the comet forward and forward, giving speed to this traveler.
Halley's Comet
Another comet, the structure is the same as the comet Churyumov - Gerasimenko, is an asteroid discovered by Edmund Halley. He realized that comets have long elliptical orbits in which they move at large intervals. He compared comets that were observed from the earth in 1531, 1607 and 1682. It turned out that it was the same comet, which moved along its trajectory after a period of time equal to approximately 75 years. In the end, she was named after the scientist himself.
Comets in the Solar System
We are in the solar system. At least 1000 comets have been found near us. They are divided into two families, and they, in turn, are divided into classes. To classify comets, scientists take into account their characteristics: the time it takes them to travel the entire path in their orbit, as well as the period from orbit. If we take Halley's Comet mentioned earlier as an example, it completes a full revolution around the sun in less than 200 years. It belongs to periodic comets. However, there are those that cover the entire path in much shorter periods of time - the so-called short-period comets. We can be sure that in our solar system there is great amount periodic comets whose orbits around our star. Such celestial bodies can move so far from the center of our system that they leave Uranus, Neptune and Pluto behind. Sometimes they can come very close to planets, causing their orbits to change. An example is Comet Encke.
Comet Information: Long Period
The trajectory of long-period comets is very different from short-period comets. They go around the Sun from all sides. For example, Heyakutake and Hale-Bopp. The latter looked very spectacular when they approached our planet for the last time. Scientists have calculated that the next time they can be seen from Earth will be thousands of years later. A lot of comets with a long period of movement can be found at the edge of our solar system. Back in the mid-20th century, a Dutch astronomer suggested the existence of a cluster of comets. Over time, the existence of a cometary cloud was proven, which is known today as the “Oort Cloud” and was named after the scientist who discovered it. How many comets are there? According to some assumptions, at least a trillion. The period of movement of some of these comets can be several light years. In this case, the comet will cover its entire path in 10,000,000 years!
Fragments of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9
Reports of comets from all over the world help in their research. Astronomers could observe a very interesting and impressive vision in 1994. More than 20 fragments remaining from Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 collided with Jupiter at crazy speed (approximately 200,000 kilometers per hour). Asteroids flew into the planet's atmosphere with flashes and huge explosions. The hot gas caused the formation of very large fire spheres. The temperature to which the chemical elements were heated was several times higher than the temperature recorded on the surface of the Sun. After which a very high column of gas could be seen through telescopes. Its height reached enormous dimensions - 3200 kilometers.
Comet Biela - a double comet
As we have already learned, there is plenty of evidence that comets break up over time. Because of this, they lose their brightness and beauty. There is only one example of such a case that can be considered - Biela's comet. It was first discovered in 1772. However, it was subsequently noticed more than once again in 1815, then in 1826 and in 1832. When it was observed in 1845, it turned out that the comet looked much larger than before. Six months later it turned out that it was not one, but two comets that were walking next to each other. What happened? Astronomers have determined that a year ago the Biela asteroid split in two. This is the last time scientists have recorded the appearance of this miracle comet. One part of it was much brighter than the other. She was never seen again. However, over time, a meteor shower, the orbit of which exactly coincided with the orbit of Comet Biela, caught the eye more than once. This incident proved that comets are capable of disintegrating over time.
What happens during a collision

For our planet, a meeting with these celestial bodies does not bode well. A large piece of comet or meteorite, approximately 100 meters in size, exploded high in the atmosphere in June 1908. As a result of this disaster, many people died reindeer and two thousand kilometers of taiga were destroyed. What would happen if such a block burst over big city such as New York or Moscow? This would cost the lives of millions of people. What would happen if a comet with a diameter of several kilometers hit the Earth? As mentioned above, in mid-July 1994 it was “bombarded” with debris from comet Shoemaker-Levy 9. Millions of scientists watched what was happening. How would such a collision end for our planet?
Comets and the Earth - ideas of scientists
Information about comets known to scientists sows fear in their hearts. Astronomers and analysts paint terrible pictures in their minds with horror - a collision with a comet. When an asteroid flies into the atmosphere, it will cause irreversible destruction processes inside the cosmic body. It will explode with a deafening sound, and on Earth you can see a column of meteorite debris - dust and stones. The sky will be covered in a fiery red glow. There will be no vegetation left on Earth, since all forests, fields and meadows will be destroyed due to the explosion and fragments. Due to the fact that the atmosphere will become impenetrable to sunlight, it will become sharply cold, and plants will not be able to carry out photosynthesis. This will disrupt the nutritional cycles. sea creatures. Being without food for a long time, many of them will die. All of the above events will also affect natural cycles. Widespread acid rain will have a detrimental effect on the ozone layer, making it impossible to breathe on our planet. What happens if the comet will fall to one of the oceans? Then this can lead to disastrous environmental disasters: the formation of tornadoes and tsunamis. The only difference will be that these cataclysms will be on a much larger scale than those that we could experience in several thousand years of human history. Huge waves of hundreds or thousands of meters will sweep away everything in their path. There will be nothing left of towns and cities.
"No need to worry"
Other scientists, on the contrary, say that there is no need to worry about such cataclysms. According to them, if the Earth comes close to celestial asteroid, then this will only lead to illumination of the sky and meteor shower. Should we worry about the future of our planet? Is it likely that we will ever be met by a flying comet?
Comet fall. Should you be afraid?

Can you trust everything that scientists present? Do not forget that all the information about comets recorded above is just theoretical assumptions that cannot be verified. Of course, such fantasies can sow panic in the hearts of people, but the likelihood that something similar will ever happen on Earth is negligible. Scientists who study our solar system are amazed at how well thought out everything is in its design. It is difficult for meteorites and comets to reach our planet because it is protected by a giant shield. The planet Jupiter, due to its size, has enormous gravity. Therefore, it often protects our Earth from passing asteroids and comet remnants. The location of our planet leads many to believe that the entire device was thought out and designed in advance. And if this is so, and you are not a zealous atheist, then you can sleep peacefully, because the Creator will undoubtedly preserve the Earth for the purpose for which he created it.
Names of the most famous
Reports about comets from various scientists from all over the world form a huge database of information about cosmic bodies. Among the particularly well-known are several. For example, comet Churyumov - Gerasimenko. In addition, in this article we could get acquainted with comet Fumeaker-Levy 9 and comets Encke and Halley. In addition to them, comet Sadulayev is known not only to sky researchers, but also to amateurs. In this article, we tried to provide the most complete and verified information about comets, their structure and contact with other celestial bodies. However, just as it is impossible to embrace all the expanses of space, it will not be possible to describe or list all known this moment comets. brief information about the comets of the Solar system is presented in the illustration below.
Sky exploration
The knowledge of scientists, of course, does not stand still. What we know now was not known to us some 100 or even 10 years ago. We can be sure that man's tireless desire to explore the vastness of space will continue to push him to try to understand the structure of celestial bodies: meteorites, comets, asteroids, planets, stars and other more powerful objects. We have now penetrated into such vastness of space that contemplating its immensity and unknowability is awe-inspiring. Many agree that all this could not have appeared on its own and without a purpose. Such a complex design must have an intention. However, many questions related to the structure of space remain unanswered. It seems that the more we learn, the more reasons we have to explore further. In fact, the more information we acquire, the more we understand that we do not know our Solar System, our Galaxy, and even more so the Universe. However, all this does not stop astronomers, and they continue to struggle with the mysteries of existence. Each comet flying nearby is of particular interest to them.
Computer program “Space Engine”
Fortunately, today not only astronomers can explore the Universe, but also ordinary people whose curiosity prompts them to do so. Not long ago, a program for computers called “Space Engine” was released. It is supported by most modern mid-range computers. It can be downloaded and installed completely free of charge using an Internet search. Thanks to this program, information about comets will also be very interesting for children. It presents a model of the entire Universe, including all comets and celestial bodies that are known to modern scientists today. To find a comet that interests us, for example, we can use the oriented search built into the system. For example, you need comet Churyumov - Gerasimenko. In order to find it, you need to enter its serial number 67 R. If you are interested in another object, for example, comet Sadulayev. Then you can try entering its name in Latin or entering its special number. Thanks to this program you can learn more about space comets.
On warm summer nights it is pleasant to walk under the starry sky, look at the wonderful constellations on it, and make wishes at the sight of a falling star. Or was it a comet passing by? Or maybe a meteorite? There are probably more astronomy experts among romantics and lovers than among planetarium visitors.
Mysterious space
Questions that constantly arise during contemplation require answers, and celestial mysteries require solutions and scientific explanations. For example, what is the difference between an asteroid and a meteorite? Not every schoolchild (or even adult) will be able to answer this question right away. But let's start in order.
Asteroids
To understand the difference between an asteroid and a meteorite, you need to define the concept of “asteroid”. This word from ancient Greek is translated as “star-like”, since these celestial bodies, when observed through a telescope, resemble stars rather than planets. Until 2006, asteroids were often called minor planets. Indeed, the movement of asteroids in general is no different from planetary movement, because it also occurs around the Sun. Asteroids differ from ordinary planets in their small size. For example, the largest asteroid, Ceres, is only 770 km across.
Where are these star-like space inhabitants? Most asteroids move along long-studied orbits in the space between Jupiter and Mars. But some small planets still cross the orbit of Mars (such as the asteroid Icarus) and other planets, and sometimes even come closer to the Sun than Mercury.

Meteorites
Unlike asteroids, meteorites are not inhabitants of space, but its messengers. Each earthling can see a meteorite with his own eyes and touch it with his own hands. A large number of them are kept in museums and private collections, but it must be said that meteorites look rather inconspicuous. Most of them are gray or brownish-black pieces of stone and iron.
So, we managed to figure out how an asteroid differs from a meteorite. But what can unite them? Meteorites are believed to be fragments of small asteroids. Stones flying in space collide with each other, and their fragments sometimes reach the surface of the Earth.
The most famous meteorite in Russia is the Tunguska meteorite, which fell in the remote taiga on June 30, 1908. In the recent past, namely in February 2013, attracted everyone's attention Chelyabinsk meteorite, whose numerous fragments were found in the area of Lake Chebarkul in the Chelyabinsk region.
Thanks to meteorites, unique guests from space, scientists, and with them all the inhabitants of the Earth, have an excellent opportunity to learn about the composition of celestial bodies and get an idea of the origin of the universe.
 Meteora
Meteora
The words “meteor” and “meteorite” come from the same Greek root, meaning “heavenly”. We know what a meteorite is, and how it differs from a meteor is not difficult to understand.
A meteor is not a specific celestial object, but an atmospheric phenomenon that looks like It occurs when fragments of comets and asteroids burn up in the Earth's atmosphere.
A meteor is a shooting star. It may appear to observers, fly back into outer space, or burn up in the Earth's atmosphere.
It is also not difficult to understand how meteors differ from asteroids and meteorites. The last two celestial objects are concretely tangible (even if theoretically in the case of an asteroid), and the meteor is a glow resulting from the combustion of cosmic fragments.
Comets
An equally wonderful celestial body that an earthly observer can admire is a comet. How do comets differ from asteroids and meteorites?
The word “comet” is also of ancient Greek origin and is literally translated as “hairy”, “shaggy”. Comets come from the outer solar system, and therefore have a different composition than asteroids that formed near the Sun.
Besides the difference in composition, there is a more obvious difference in the structure of these celestial bodies. When approaching the Sun, a comet, unlike an asteroid, exhibits a hazy coma shell and a tail consisting of gas and dust. As the comet heats up, its volatile substances are actively released and evaporated, turning it into a beautiful luminous celestial object.

In addition, asteroids move in orbits, and their movement in outer space resembles the smooth and measured movement of ordinary planets. Unlike asteroids, a comet is more extreme in its movements. Its orbit is highly elongated. The comet either approaches the Sun closely or moves away from it to a considerable distance.
A comet differs from a meteorite in that it is in motion. A meteorite is the result of a collision of a celestial body with the earth's surface.
Heavenly peace and earthly peace
It must be said that watching the night sky is doubly pleasant when its unearthly inhabitants are well known and understandable to you. What a pleasure it is to tell your interlocutor about the world of stars and unusual events in outer space!
And the point is not even in the question of how an asteroid differs from a meteorite, but in the awareness of the close connection and deep interaction between the earthly and cosmic worlds, which must be established as actively as the relationship between one person and another.
People have looked up at the night sky for centuries and wondered what they see and what lies beyond. Over time, as a result of the development of space exploration and astronomy, scientists gradually began to answer these questions by giving names to various objects in space and even predicting certain astronomical events. For those new to the study of astronomy, these terms can be confusing and difficult to remember. A great example is comets and asteroids, two space objects that are constantly confused. This article takes a closer look at the main difference between comets and asteroids.
What are comets made of?
Comets are somewhat round, astronomical objects that follow an orbit around the Sun. They consist of ice, ammonia, carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, methane, rock, dust and other organic compounds. Because of their composition, comets are often called "dirty snowballs." The materials that form comets arose with the formation of the solar system, which appeared about 4.5 billion years ago.
Comet structure
The structure of a comet is based on the nucleus, which is the frozen center. This core is surrounded by a coma, which is a large cloud of gas, water and dust. A coma forms when a comet comes close to the Sun. The heat from the star causes the ice in the comet to melt and evaporate, and the steam is then pulled away from the core by the solar wind and radiation pressure. The resulting effect is often called a comet's tail, which tends to point toward the Sun. This process means that each time the comet gets closer to the sun, it becomes smaller as a result of the loss of material.
Types of comets
Comets are generally considered to fall into one of two categories: short-period and long-period. Short-period comets, also known as periodic comets, typically take less than 200 years to complete a full orbit. These comets tend to follow the same path as other bodies or travel as far as Jupiter and Neptune. As short-period comets approach these larger planets, they are subject to additional gravitational pull.
Long-period comets complete a full orbit in a period of 200 to 1000 years. Not only do these space objects take longer to travel all the way around the Sun, but they also have an elliptical orbit rather than a circular one. Gravitational attraction is more major planets may cause long-period comets to be forced out of the solar system entirely.
What are asteroids made of?
An asteroid is an irregularly shaped object that orbits the Sun. These bodies are often considered dwarf planets, especially when they are located in the inner solar system. Asteroids are mainly composed of minerals and rocks. Scientists believe that asteroids are remnants of materials that were never large enough to be considered a planet.
Asteroid structure
Most asteroids are very similar in structure, as they have a solid body that is marked by small craters on the surface. These objects can range from 1 m to 1000 km in diameter. The larger the asteroid, the more pronounced its shape. As asteroids move around the solar system, they follow an orbital path while rotating in place.
Types of asteroids
Asteroids are usually classified by their orbital path and spectral reflectance. In terms of orbital classification, an asteroid may be part of a group or family of asteroids. Asteroid clusters consist of large numbers of asteroids that rotate together in a relatively loose fit. On the other hand, families of asteroids can be found in close proximity and it is assumed that they arose as a result of the division of more large asteroid at some point in the past.
Asteroid spectral classification is based on the color, shape and reflective properties of these space objects. Asteroids were originally divided into three spectral categories: dark, rocky, and those that cannot be classified into the first two. Over the years, these categories have expanded as new types of asteroids have been discovered.
Difference between comets and asteroids
Researchers have identified many differences between comets and asteroids, primarily in their composition. As mentioned earlier, comets are made up of ice, rocks, dust and other organic compounds, while asteroids are made up of rocks and minerals. Due to differences in composition, these two astronomical bodies also react differently to the Sun and its heat. Comets become smaller over time as the ice begins to melt. Asteroids maintain their size and do not lose material as they pass by the Sun.
Another difference between comets and asteroids is their close proximity to the Sun. Comets can be found further from the Sun than asteroids, which explains their differences in composition. Their location away from the sun allowed comets to form and maintain ice. Most comets are found in the Kuiper belt or Oort cloud. The Kuiper Belt is located just beyond the orbit of Pluto, in the outermost regions of the solar system. The Oort Cloud is a region that contains countless comets orbiting the Sun at a distance of up to 21 trillion km. In contrast, most asteroids orbit the asteroid belt, which is located between Mars and Jupiter.
In addition to differences in composition and distance from the Sun, comets and asteroids also differ in appearance. As mentioned earlier, comets have a tail formation that points towards the Sun. Asteroids are different, and they don't have a tail or anything like that. A comet's tail, known as a coma, is the result of a difference in composition.
Comets and asteroids also tend to have different orbital shapes. Comets, for example, travel in more elongated orbits around the Sun. Asteroids tend to follow a more circular orbit and move in groups as they pass through the belts.
Cold objects, consisting of solid rocks (including metals) and ice, are part of the Solar System. These objects are asteroids, comets, meteoroids.
Comet
Comets are composed of a mixture of ice, frozen gas and dust. They travel around the Sun in very elongated orbits. As a comet approaches the Sun, ice and other volatile substances on its surface quickly evaporate, creating a stream of gas and dust. The solar wind and light pressure “blow away” the resulting gases with other substances away from the Sun. This is how the luminous tail of a comet is formed. The comet's tail can reach 10 million km.
Long-period comets with an orbital period of more than 200 years around the Sun come from regions further than the outer planets of the system, in the Oort cloud, which probably exists at a distance of almost a light year from the Sun, about a quarter of the way to our nearest star Proxima Centauri (distance it is 4.3 light years away, or 40 trillion km). It is believed that there are about a trillion comets in the Oort cloud. Short-period comets (periods of less than 200 years) come from the region of the outer planets - these are objects from the Kuiper belt located beyond the orbit of Neptune. Halley's Comet orbits the Sun every 76 years, making it the most... famous comet in history.
Asteroid
Most of the solar system's asteroids are concentrated in the belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Asteroids are, in all likelihood, part of protoplanetary matter - planetesimals, formed at the boundary of the hot and cold zones of the protoplanetary disk and preserved to this day. Carbon, metallic, silicate, etc. asteroids are known.
![]()
An asteroid can be knocked out of orbit under the influence of the gravitational field of large planets or another asteroid. Such a stray asteroid could collide with a planet or satellite and fall to the surface as a meteorite. Sometimes this leads to destruction. Some scientists believe that about 65 million years ago a meteorite crashed into the Earth, which led to the extinction of the dinosaurs.
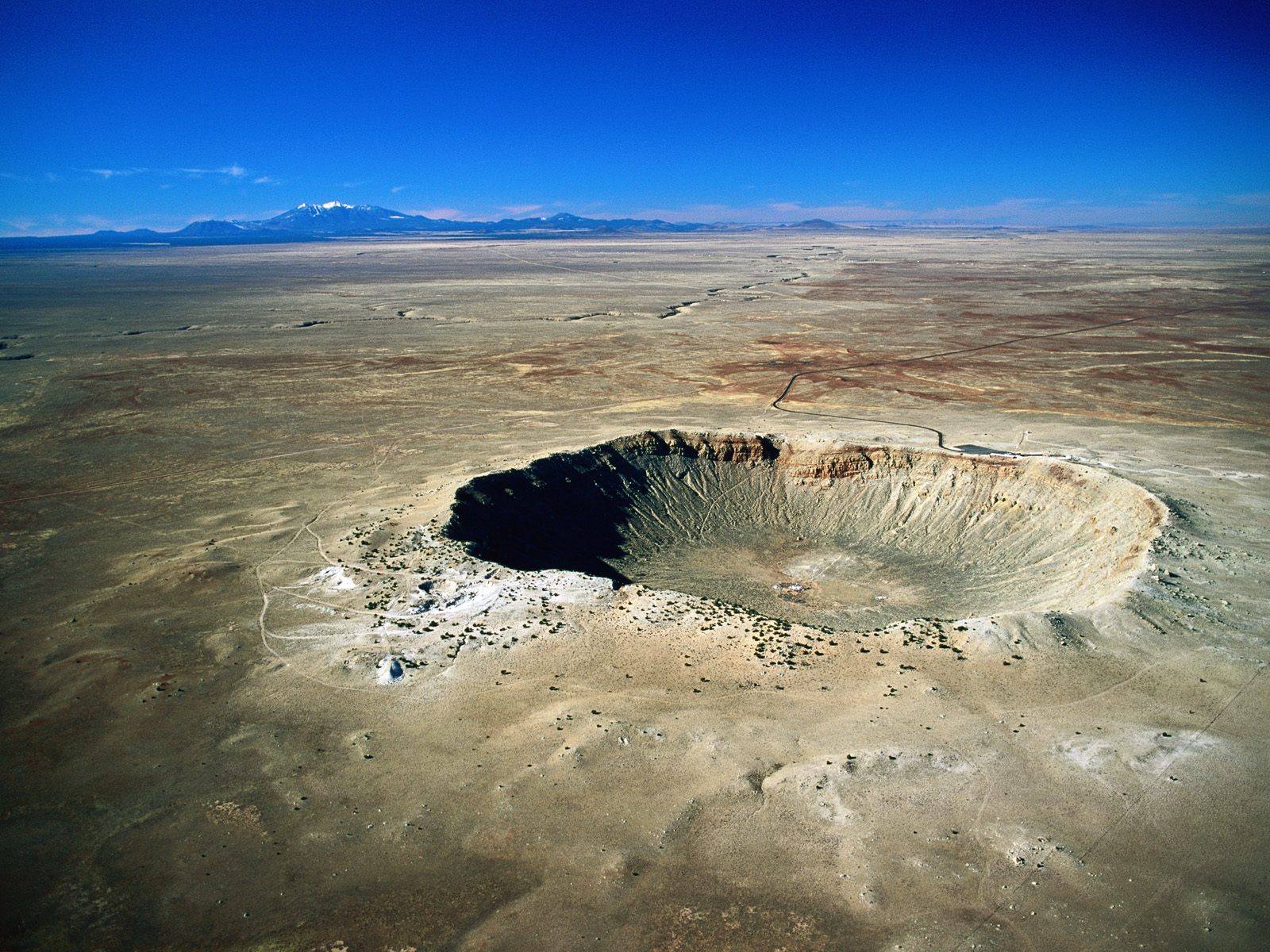 Cosmic dust, meteoroids - bodies larger than dust, but smaller than an asteroid, and asteroids themselves, which do not burn up, but crash into the Earth in the form of meteorites, fall to the Earth from space. Some of the meteorites are so large that they leave craters. The most famous place The Berringer impact crater in Arizona, USA is considered to be the site of a meteorite impact on Earth. This is the result of the fall of an iron meteorite weighing about 300 thousand tons, which collided with the Earth at a speed of 45-60 thousand km/h about 50,000 years ago.
Cosmic dust, meteoroids - bodies larger than dust, but smaller than an asteroid, and asteroids themselves, which do not burn up, but crash into the Earth in the form of meteorites, fall to the Earth from space. Some of the meteorites are so large that they leave craters. The most famous place The Berringer impact crater in Arizona, USA is considered to be the site of a meteorite impact on Earth. This is the result of the fall of an iron meteorite weighing about 300 thousand tons, which collided with the Earth at a speed of 45-60 thousand km/h about 50,000 years ago.
