Flood hazards. How dangerous is a flood? Low or small
FLOODING is a significant flooding of an area as a result of a rise in the water level in a river, lake or sea during snowmelt, rainfall, wind surges, congestion, ice jams, etc.A special type includes floods caused by wind surges of water into river mouths. Floods lead to the destruction of bridges, roads, buildings, structures, cause significant material damage, and at high speeds of water movement (more than 4 m/s) and high heights of water rise (more than 2 m), they cause the death of people and animals. The main cause of destruction is the impact on buildings and structures of hydraulic shocks from the mass of water floating with high speed ice floes, various debris, watercraft, etc. Floods can occur suddenly and last from several hours to 2 – 3 weeks.
Floods can be worse when there is little vegetation along the river banks. Land with little vegetation generally has less capacity to absorb water. The result is that more water reaches the river and its tributaries. Flash floods are the most dangerous. They are caused by very heavy rains or dam failure. When this happens, the result can be a very fast flow that catches people by surprise before they can escape. Flash floods often occur in mountainous areas or where there are dry river beds.
Types of flood
Depending on the cause of the occurrence, floods are divided into 5 types:
- flood – flood resulting from melting snow and the release of a reservoir from its natural banks
- flood – flooding associated with heavy rainfall
- floods caused by large accumulations of ice that block a river bed and prevent water from flowing downstream
- surge floods , occurring due to a strong wind that drives water in one direction, most often against the current
- floods resulting from dam break or reservoirs.
| High water | Flood | Congestion | Zazhor | Wind surge |
| a periodically repeated, fairly long-term rise in water levels in rivers, usually caused by spring melting of snow on the plains or rainfall. Floods low areas terrain. | an intense, relatively short-term rise in the water level in a river, caused by heavy rains, downpours, and sometimes rapid melting of snow during thaws. Unlike floods, floods can occur several times a year. A particular threat is posed by the so-called flash floods associated with short-term but very intense downpours, which also occur in winter due to thaws. | clogging of the riverbed by a stationary ice cover and accumulation of ice floes during the spring ice drift in narrowings and bends of the riverbed, restricting the flow and causing a rise in the water level in the place of ice accumulation and above it. Jam floods form at the end of winter or early spring, and arise due to non-simultaneous opening of big rivers, flowing from south to north. The exposed southern sections of the river in its course are being dammed accumulation of ice in the northern regions, which often causes a significant increase in water levels. Jam floods are characterized by a high and relatively short-term rise in the water level in the river. | ice plug, accumulation of inland, loose ice during winter freeze-up in narrowings and bends of the riverbed, causing water to rise in some areas above the level of the main riverbed. Jam floods form at the beginning of winter and are characterized by a significant, but less than during a jam, rise in the water level and a longer duration of the flood. | rising water levels at the mouths of large rivers and on windy areas of the coast of seas and large lakes, reservoirs caused by the impact of strong winds on the water surface. They are characterized by a lack of periodicity, rarity and significant rise in water level, and, as a rule, short duration. Floods of this type have been observed in Leningrad (1824, 1924), the Netherlands (1953). |
|
|
|
|
|
Causes of floods:
- Long rains
- Snow melting
- tsunami wave
- Bottom profile
- Dam failure
- Other natural and man-made causes
Flood classification:
1. storm (rain);2. floods and floods (associated with melting snow and glaciers);
3. gluttony and congestion (associated with ice phenomena);
4. blockage and breakthrough;
5. surge (wind on the coasts of the seas);
6. tsunamigenic (on the coasts from underwater earthquakes, eruptions and large coastal landslides).
River floods are divided into the following types:
1. low (small or floodplain) - low floodplain is flooded;
2. medium - high floodplains are flooded, sometimes inhabited or technogenically cultivated (arable lands, meadows, vegetable gardens, etc.);
3. strong - terraces with buildings, communications, etc. located on them are flooded, often requiring evacuation of the population, at least partially;
4. catastrophic - vast areas are significantly flooded, including cities and towns; emergency rescue operations and mass evacuation of the population are required.
In such a flow, a channel that was completely dry could fill with water within a few minutes. In cities where there are few green spaces and rainwater drainage depends on pipelines built to capture that water, trash accumulated in the streets ends up clogging culverts and causing flash floods that could have been avoided.
Hurricane Harvey, which has hit Texas since Friday and is already considered the worst in the state's history in 50 years. The local government estimates that around 30,000 people may be homeless, and at least 450,000 people have been directly or indirectly affected by damage and flooding caused by the phenomenon.
According to the scale of manifestation, there are 6 categories of floods:
1. The Flood;
2. continental;
3. national;
4. regional;
5. regional;
6. local.
Anthropogenic causes of floods:
Direct causes are associated with the implementation of various hydraulic engineering measures and the destruction of dams.Indirect - deforestation, drainage of swamps (drainage of swamps - natural runoff accumulators increases runoff to 130 - 160%), industrial and residential development, this leads to a change in the hydrological regime of rivers due to an increase in the surface component of runoff. The infiltration capacity of soils decreases and the intensity of their washout increases. Evapotranspiration is reduced due to the cessation of interception of precipitation by the forest floor and tree crowns. If all forests are removed, the maximum flow can increase to 300%.
There is a decrease in infiltration due to the growth of impervious pavements and buildings. The growth of waterproof coatings in urbanized areas increases floods 3 times.
Human activities leading to floods:
1. Restriction of the living cross-section of the flow by along-channel roads, dams, and bridge crossings, which reduces the channel's throughput capacity and increases the water level.
2. Disruption of the natural regime of flows and water levels, as happens in the lower Volga as a result of seasonal regulation of flow by overlying reservoirs: the need for winter energy forced a 2-3-fold increase in water flows in winter, which, in the presence of ice cover, is accompanied by an increase in water levels (winter floods), often above high water levels.
3. Development of territories in the lower reaches of reservoirs for long-term flow regulation. Economic development of floodplains increases the maximum flow.
After passing through Houston, Harvey weakened into a tropical storm, the National Weather Service said Sunday. Today, authorities are concerned that Houston's reservoirs and dams will overflow due to the volume of accumulated water.
Difference between flood and flood
The state government has issued a return order for residents of some counties where the storm is expected to arrive in the next few hours. Harvey got on South coast Texas on Friday was a Category 4 hurricane but quickly lost strength. However, the amount of precipitation was more than 40 centimeters.
Flood classes
1. Low. Typically cause minor damage. Covers small coastal areas. Agricultural land is flooded to less than 10%. They hardly dislodge the population from the current rhythm of life. Repeatability – 5-10 years.
2. High. Cause significant damage (moral and material). Cover large areas of river valleys. About 10-15% of the land is flooded. They disrupt both the everyday and economic life of the population. Partial evacuation of people is very likely. Frequency – 20-25 years.
And it has already been confirmed that he will visit the state tomorrow, alongside First Lady Melanie, but there are no plans to visit the affected areas. On Sunday, more than 2,000 people were rescued according to the Houston mayor's office. Boats, helicopters and trucks were used for the rescue. Most of them were rescued from housing projects in poor areas of the metropolis, where the Latino population lives primarily with large numbers of illegal immigrants, as well as part of the black American community.
The city's dams and reservoirs had to be opened according to the volume of accumulated water. Overall, flooding and damage caused by the storm affects an area home to more than six million people. The estimate is that 50 counties are directly impacted by the storm.
3. Outstanding. They cause great material damage, covering river basins. Approximately 50-70% of farmland is under water, as well as a certain part settlements. Major floods not only disrupt everyday life, but also paralyze economic activity. It is necessary to evacuate material assets and the population from the disaster zone and protect the main objects of economic importance. Repeatability – 50-100 years.
Even areas that are not flooded suffer from a lack of electricity and insulation as many roads have been damaged by winds and rivers that have overflowed. Temporary shelters in Houston, San Felipe, Victoria and Corpus Christi, where the hurricane arrived Friday, are overwhelmed. At a press conference, Texas Governor Abbott said the public should prepare to receive more water in the coming days and therefore more dangerous floods.
What are floods like?
Neighboring states are also beginning to prepare for the arrival of the storm, which is moving into Louisiana after Hurricane Katrina struck 11 years ago and wreaked havoc in New Orleans. President Trump has authorized the state to declare a state of emergency or warning, which provides greater freedom to release resources and prepare for possible refunds.
4. Catastrophic. They cause enormous material damage, spreading over vast areas within one or more river systems. Lead to human casualties. More than 70% of the land, many settlements, utilities and industrial enterprises are flooded. Production and production are completely paralyzed economic activity, and the everyday life of the population is changing. Periodicity – 100-200 years.
The city is under water. Various canals that crisscross the city and its suburbs began giving way on Saturday evening. Local press counted at least six dead on Sunday morning. In some parts of Houston, water fell onto the roofs of houses, flooding streets and entire neighborhoods. The rain is expected to continue at this rate for several days.
On Sunday morning, the United States National Weather Service issued a warning saying, "This event is unprecedented and its impacts are unknown and beyond what we have ever seen." Authorities have carried out 250 vehicles to date. Mayor Sylvester Turner said the flooding was "catastrophic and life threatening." Turner said that since Saturday evening they have received more than a thousand emergency calls.
Hazards:
1. height of water level change;2. the rate of its change;
3. duration of the rise period;
4. accompanying phenomena (wind, landslides, soil erosion, stormy streams, destruction of agricultural products, livestock, loss of life, etc.).
Water flow as a damaging factor
Characteristics of water flow as a damaging factor:
Panic spread throughout the entire population. Some people tried to escape in their cars, but this created big problems because vehicles stuck in the water. Several tornadoes formed in the suburbs of the city. A tornado left at least 50 homes destroyed in a Missouri area in west Houston. Houston and Galveston received 60 inches of water between Saturday and Sunday morning, according to the National Weather Service.
Houston Police Chief Art Acevedo advised people in the hardest-hit areas to take to their roofs. Don't go on the roof unless they have an ax to break the roofs to get out, he said. Houston's mayor defended his decision not to evacuate the city Sunday morning at a news conference. There was no way to know which areas would be most affected. More than 800 people were staying at 23 shelters in Texas and Louisiana as of Saturday night, according to the American Red Cross.
1. Highest water level.
2. Highest water consumption.
3. Current speed.
4. Flood area.
5. Repeatability of value highest level water.
6. Duration of flooding.
7. Water temperature.
8. Providing the highest water level.
9. Start time of the disaster.
10. The rate of water level rise during the entire flood period.
Meanwhile, in the Houston suburbs, Fort Bend County is among those at greatest risk of catastrophic flooding as the Brazeau and San Bernard rivers cut through large residential areas within their territory. District Judge Robert Hebert said, "The Army Corps of Engineers predicts that the rise in water levels at Barker Dam will reach unprecedented levels," he said. This level will exceed last year's flow by several centimeters. We are very concerned about additional rainfall forecast that night which could raise the upper dam level.
11. Depth of flooding of the territory in the area under consideration.
Damaging factors:
The combined impact of waves, wind, and rainfall causes flooding of the area. This is accompanied by significant erosion of the coast, leading to the destruction of buildings and structures, erosion of railway and highways, accidents on public utility networks, destruction of crops and other vegetation, casualties among the population and the death of domestic animals and natural ecosystems. After the water recedes, buildings and land sag, and landslides and collapses begin.Consequences of floods:
The main features of the situation that arises during such natural disasters are: the rapid increase in strength damaging factors, the difficulty of accessing victims, the destructive nature of the situation, the low survival rates of victims, and the presence of complex weather conditions(mudflows, ice drift, heavy rains, etc.).The amount of damage depends on:
1. - lifting height;
2. - rate of water level rise;
3. - flood areas;
4. - timeliness of the forecast;
5. - presence and condition of protective structures;
6. - degree of population and agricultural development of the river valley;
7. - duration of standing flood waters;
8. - frequency of recurrence of floods (with repeated rises in the water level, the damage is less than with the initial one).
We empty the entire first floor and place the most valuable items one meter above the ground. "We have food and water to survive for several days if the water had prevented us from leaving," he explained. Barros toured in his neighborhood, where most local residents traveled on foot to assess damage and potential flooding in rivers near their homes. Some people even used canoes for locomotion.
Texas Gov. Greg Abbott had yet to announce new evacuation areas as of Saturday afternoon. On this moment Evacuation orders were issued for 22 Texas cities and counties. Hobby International, one of Houston's airports, announced that all flights were canceled "due to the amount of water on the runways," while George W. Bush International operated on a limited basis. "There are catastrophic, life-threatening flooding outbreaks," the National Weather Service tweeted. This is a very dangerous situation!
The passage of floods (flooding of agricultural land) after harvesting leads to less damage than before harvesting.
The severity of emergencies during channel floods depends not so much on the absolute value of the water level rise, but on its value relative to the altitudinal location of populated areas.
How to prepare for a flood?
If your area frequently suffers from flooding, learn and remember the boundaries possible flooding, as well as elevated, rarely flooded places located in close proximity from places of residence, the shortest routes to them. Familiarize family members with the rules of conduct during organized and individual evacuation, as well as in the event of sudden and violent flooding. Remember the storage locations for boats, rafts and building materials for their manufacture. Make a list of documents, property and medicines to be removed during evacuation in advance. Place valuables, necessary warm clothes, food supplies, water and medicines in a special suitcase or backpack.
Do not travel unless you have indicated this option. The situation in the great Texas city occurs when coastline trying to evaluate hurricanes. Harvey touched down Friday evening as a Category 4 between Corpus Christi and Houston and destroyed homes and boats in coastal villages. It was the strongest hurricane to arrive in the United States since Wilma in Port Aransas, one of the first cities hit by the hurricane. There are boats that flew and crashed into some buildings.
The number of requests for help to service centers already exceeds 2 thousand. Gov. Greg Abbott said 3,000 security personnel and 600 boats had been deployed. rescue operations. The city's convention center has become a haven to meet demand. The rains will lead to "prolonged, dangerous and potentially catastrophic flooding" next week, according to the National Weather Service. President Donald Trump, who announced disaster, is scheduled to arrive in Texas on Tuesday.
HOW TO ACT DURING A FLOOD
If there is a warning signal about the threat of flooding and evacuation, immediately, in the prescribed manner, leave (leave) from danger zone possible catastrophic flooding to a designated safe area or to elevated areas, taking with you documents, valuables, necessary items and a two-day supply of non-perishable food. At the final evacuation point, register.Before leaving home, turn off the electricity and gas, turn off the fire in heating stoves, secure all floating objects located outside the building or place them in utility rooms. If time permits, move valuable household items to the upper floors or attic of a residential building. Close the windows and doors, if necessary and if there is time, board the windows and doors of the first floors from the outside with boards (shields). In the absence of organized evacuation, until help arrives or the water subsides, stay on the upper floors and roofs of buildings, on trees or other elevated objects. At the same time, constantly give a distress signal: during the day - by hanging or waving a clearly visible banner, tacked to the staff, and in dark time– with a light signal and periodically with a voice. When rescuers approach, calmly, without panic or fuss, and taking precautions, get into the swimming craft. At the same time, strictly follow the requirements of rescuers and do not overload the watercraft. While driving, do not leave the designated places, do not board the aircraft, and strictly follow the requirements of the crew. It is recommended to get out of a flooded area on your own only if there are such serious reasons as the need for assistance medical care victims, a continuing rise in the water level with the threat of flooding of the upper floors (attic). In this case, it is necessary to have a reliable swimming device and know the direction of movement. During your independent deployment, do not stop sending the distress signal.
Contaminated dishes and furniture surfaces must be disinfected with boiling water or a special product

Reports in the international press had previously said five people had died, although only two deaths had been confirmed in the city so far. According to local media, this is an elderly woman who drowned after leaving her car in a flooded area of Houston. A man was also killed when he was trapped in a house fire during a storm in Rockport, according to a source in Aransas County, Texas, including 12 wounded.
Provide assistance to people floating in water and drowning.

IF A PERSON DROWNS
Throw a floating object to a drowning person, encourage him, call for help. When getting to the victim by swimming, take into account the current of the river. If the drowning person does not control his actions, swim up to him from behind and, grabbing him by the hair, tow him to the shore.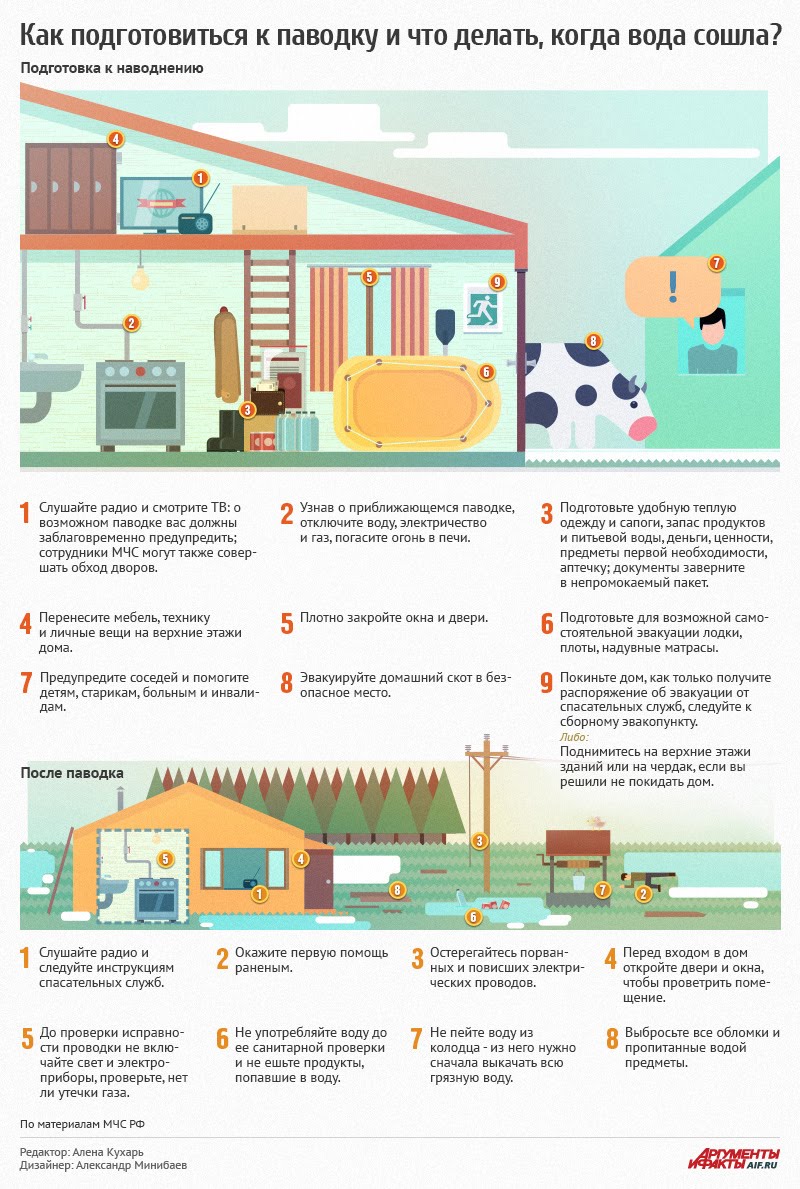
Abbott says 250 roads in Texas are closed due to... high water. Emergency responders in Houston, struggling to reach people at risk, urged citizens to climb to rooftops instead of going into attics to quickly escape the water. Authorities also warned that more than 2 million people in the city are confined to their homes because many roads are under water. About 250,000 people lack power in the state.
If you're avoiding flooding, don't stick to the attic as a last resort. The National Weather Service said it recorded more than 612 millimeters of rain in the past 24 hours. The department also said flooding in the region is expected to worsen and become "historic" with the possibility of similar records in other areas of Texas.
HOW TO ACT AFTER A FLOOD
Before entering a building, check whether it is in danger of collapsing or falling of any object.Ventilate the building (to remove accumulated gases). Do not turn on electric lighting, do not use open flame sources, and do not light matches until the room is completely ventilated and the gas supply system is checked to ensure that it is working properly. Check the serviceability of electrical wiring, gas supply pipelines, water supply and sewerage. Do not use them until you have verified that they are in good working order with the help of a professional. To dry the premises, open all doors and windows, remove dirt from the floor and walls, and pump out water from the basements. Do not eat food that has been in contact with water. Organize the cleaning of wells from applied dirt and remove water from them.
Main characteristics of concepts
Follow official orders to ensure your safety. Hobby Houston canceled all flights Sunday due to standing water that had accumulated on the runway. The second said the arrival area was flooded and the National Weather Service had issued a flood warning for the surrounding area. On Saturday, President Donald Trump urged emergency crews to "remain fully mobilized" because the effects of Harvey will be felt for days, according to the White House.
Flood is one of the types of flooding of lower parts of a river floodplain, delta, and coastal zone of the sea, which is catastrophic in nature.
The main cause of flooding on river banks is high water or floods of rare frequency, and sometimes ice jams and jams. Floodplain- part of the bottom of a river valley that is flooded only during high water.
You should try to swim to the nearest actually accessible unflooded place, taking into account the drift of the current, moving at an angle to it
But rescue efforts are hampered by strong winds. The Texas coast is home to nearly a third of the country's oil refining activity. The Gulf of Mexico accounts for 20% of the country's production. According to Saturday's bulletin, 112 platforms were drained, corresponding to 24.5% of daily oil production and 26% of gas production.
At the time, President George W. Bush was heavily criticized for his slowness and late action to help the much-needed and largely African-American region. There can be several causes for floods, which vary depending on whether there is a flood or a sea flood.
Delta– lowlands in the lower reaches of large rivers, cut through by a network of branches and channels.
Flooding- this is the process of filling lower parts of the surface with water as a result of an increase in the water level of a watercourse, reservoir or groundwater. Flooding is for humans.
High water– phase of the river water regime, repeated annually in the data climatic conditions in the same season. Floods are characterized by the highest water content and a high and prolonged rise in water. Floods are caused by melting snow and glaciers.
Congestion- this is a accumulation of ice floes in the river bed, causing a decrease in the free cross-section and a rise in the water level.
Zazhor– accumulation of slush (inland ice) and small broken ice in the river bed under the ice cover, causing constriction of the living section and, as a result, rising water.
In estuaries, flooding can occur as a result of surges caused by strong winds and fluctuations in atmospheric pressure. Large floods caused by breaches of protective dams and embankments have been reported more than once. Thus, in 1889, a breakthrough in the Yellow River channel led to a catastrophic flood - the flooding of 22,000 km2 of land and the death of almost 1 million people. Floods in St. Petersburg occur almost every year. The duration of floods is up to 90 days.
Protecting people in flood conditions - timely warning and evacuation. To protect against floods, there are special protective structures and dams. Fighting river floods is most effective by creating reservoirs.
Flood emergencies
Flooding is the flooding of an area with water as a result of heavy rains, melting snow, glaciers, ice jams, wind pressure, and more. The main cause of floods is lapses in the activities of the services responsible for hydraulic structures. Water streams during floods they pose a direct danger to people. Brick buildings receive:
- weak destruction at water speed V=1.5 m/s and height h=2.5 meters;
- average – at V=2.5 m/s and h=4 meters;
- strong – at V=3 m/s and h=6 meters.
Floods result in epidemics, destruction of various communications, destruction of crops, and death of livestock.
What to do
Floods happen in certain places and usually during certain periods. Flood statistics are well known. Using information about the floods that have occurred, hydraulic structures must be erected in the necessary places and a regime for regulating water flow must be developed. However, in case of unforeseen circumstances (residual risk), a catastrophic flood plan is developed.
It is planned to monitor the water level. If necessary, a “Threat of Flooding” signal is given. The most effective measure to protect people is planned evacuation. Those who did not have time to evacuate are required to be rescued by the appropriate rescue services. Floating craft and helicopters are used. The public must act in accordance with the instructions of the authorities.
