Post on the topic of relict plants. Relic plants - interesting facts - all about plants
(from the Latin word - the remainder), or "living fossils" - species of plants and animals, preserved outwardly unchanged for hundreds of millions of years. This happens when their habitat changes relatively little. Relics are now most often found in the oceans and in the tropics.
For example, the Lingula, a marine brachiopod that lives in shallow burrows on the tidal strip or at shallow depths in the Indian and Pacific oceans, has remained almost unchanged (judging by the fossil remains) for more than 300 million years! One of the species of horseshoe crabs, which lives in coastal tropical waters, has existed in almost unchanged form for about 200 million years. The cistepero fish of the coelacanth, which lives at depths of several hundred meters off the coast of Southeast Africa, is about 300 million years old.
Among terrestrial animals, relics include, for example, the reptile of the Mesozoic time, the tuatara, which lives in New Zealand, and a rodent that is found only in the Betpak-Dala desert (Kazakhstan).
Among the plants, an example of a relic is the Ginkgo tree from gymnosperms, several tens of meters high. It survived in the South East Asia and is practically indistinguishable from trees found in fossil form in layers that are more than 150 million years old. From the Mesozoic era, a mammoth tree growing in the Sierra Nevada (North America) has come down to us. The relics include such valuable plants as ginseng, tau-sagyz.
Relics can persist under new conditions of existence, changing more or less noticeably, adapting to these conditions. Relict forms are widespread, but nowadays they are found only in certain small areas. Sometimes these are the remains of whole flora and fauna of the previous geological times.
Presentation on the topic: Relic forms as evidence of evolution








![]()










1 of 19
Presentation on the topic:
Slide No. 1

Slide Description:
Slide No. 2

Slide Description:
Ginkgo Ginkgo is one of the oldest woody plants on earth. The ginkgo is at least 200 million years old. This "silver apricot" can be called the same age as the dinosaurs. True, then there were many plants of the Ginkgo class on Earth, and now only one species remains of them, Ginkgo biloba is a deciduous tree, the height of which reaches 25 - 35 m.Previously, this tree could be found only in China and Japan, but now it adorns botanical gardens, streets and parks of European and North American cities.
Slide No. 3

Slide Description:
Metasequoia Another Chinese relic is the coniferous tree Metasequoia Glyptostrobus, named after its resemblance to the American sequoia. Until 1941, metasequoias were known only in the form of fossils, but then their living specimens were also found. Once the genus metasequoia was widespread in Northern Eurasia and North America, but then began to die out due to climate change and competition with broadleaf trees. It is currently ancient tree grows wild only in the Chinese provinces of Hubei, Sichuan and Hunan.
Slide Description:
TAXODIUM MEXICAN It grows in Mexico at an altitude of 1400-2300 m above sea level, reaching in the south to Guatemala, and in the north to Texas. Average age these trees are 600 years old, but individual specimens reach more than two thousand years of age and 40-50 meters in height with a trunk diameter of about 9 m. from Tula ". This plant, reaching a height of only 30 m (with a trunk girth of 34.5 m and a diameter of 11 m), strikes with its unnaturally thick trunk. When assessing his age, opinions differed greatly - they even named 10,000 years. Most likely, it is not older than 4000 years.
Slide No. 6

Slide Description:
Horsetails The class of these amazing plants includes about 30 species. All modern horsetails are perennial herbs. But once upon a time, even before the appearance of dinosaurs, there were also arboreal forms of horsetails. These were huge plants, the height of which reached 25 m, and the trunk diameter reached 50 cm. Today's horsetails are mostly small - up to 1 m in height. But there are also larger species, for example, the South American giant horsetail, which grows up to 10-12 m in height with a trunk diameter of only 2-3 cm. Horsetails are common on most continents of our planet, they are not only in Antarctica and Australia.
Slide No. 7

Slide Description:
Velvichia This plant grows in the southwestern part of Africa, the Namib and Kalahari deserts. Its appearance amazed scientists so much that they gave it the Latin name - amazing Velvichia. Their surprise can be understood, because this strange plant turned out to be unlike either a tree, or a bush, or a grass. Its short, thick trunk protrudes only 15-50 cm above the soil surface, and the rest of it is hidden underground. At the same time, Velvichia leaves can reach 6 m in length and almost 2 m in width. According to the results of radiocarbon analysis, the age of some of the Welwitschia is more than two thousand years. Velvichia is one of the three representatives of the once numerous class of oppression (Gnetóphyta) that have survived to this day.
Slide No. 8

Slide Description:
Lung-breathing fish Fish, capable of breathing not only oxygen dissolved in water, but also atmospheric air through the lungs, appeared at least 300 million years ago. Most of them became extinct or evolved into amphibians, but some species have survived to this day. In northeastern Australia, the horntooth lives. He, like other fish, breathes with gills, but every 40-50 minutes rises to the surface of the water to breathe air. However, he cannot stay in the air for a long time, and if you pull the cattail out of the water, he will die. Fish of the liverworm family live in tropical Africa and South America... These long, eel-like fish can live their entire lives in temporary bodies of water that dry up in drought. During the dry period, they hibernate: they burrow into the soil and switch to breathing atmospheric air.
Slide No. 9
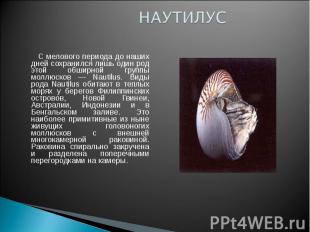
Slide Description:
NAUTILUS From the Cretaceous period to the present day, only one genus of this vast group of mollusks has survived - Nautilus. Species of the genus Nautilus live in warm seas off the coast of the Philippine Islands, New Guinea, Australia, Indonesia and the Bay of Bengal. These are the most primitive living cephalopods with an external multichamber shell. The shell is spirally twisted and divided into chambers by transverse partitions.
Slide No. 10

Slide Description:
LATIMERIA The only species of coelacanth fish that has survived to this day - coelacanth - is very different in lifestyle from the fossil predecessors that inhabited fresh waters and shallow waters off the coast. Near the Comoros, apparently only about 200 specimens were taken (until 2000). The length of the fish ranged from 43 to 180 cm, weight from 19.5 to 95 kg.
Slide No. 11

Slide Description:
Purple frog This animal is considered the oldest frog: it appeared about 100 million years ago. For a long time it was considered extinct, but in 2003 it was discovered in the western part of India. The current habitat of this living fossil is only 14 square meters. km. These animals got their name because of their color: adults have a dark purple or purple color. The lifestyle of purple frogs is unusual: most they spend their lives underground, feeding on termites, and only come to the surface for two weeks a year, during the mating season. The length of an adult animal is 5 - 9 cm.
Slide No. 12

Slide Description:
Tuatara tuatara or tuatara has been preserved on Earth since the time of the dinosaurs. The order to which this reptile belongs, reached its heyday about 225 million years ago, but almost all of its representatives have become extinct. Tuatara is also called three-eyed, since on the crown of her head there is a kind of organ with a layer of light-sensitive cells and a semblance of a lens. This parietal eye can distinguish between light levels. The tuatara live on rocky islands off the coast of New Zealand. Their body length is 40 - 60 cm, depending on the sex and age of the animal.
Slide No. 13

Slide Description:
Crocodiles It is believed that the first crocodiles appeared on Earth about 150 million years ago. These animals are called the closest relatives of the extinct dinosaurs. Moreover, over millions of years, crocodiles have hardly changed. In terms of the level of organization of the nervous, circulatory and respiratory systems, these animals are higher than other reptiles. So, the representatives of this order have a four-chambered heart, and the rest of the reptiles have a three-chambered heart. Representatives of the crocodile squad are found in all tropical countries... Most of them live in fresh water, but some are found in coastal sea waters.
Slide No. 14

Slide Description:
Gull RELICT The relic gull was essentially rediscovered in 1969 by the Kazakh ornithologist E. M. Auezov on Lake Alakol. It turned out that another colony of relict gulls exists far from the first - on the Torey lakes in Transbaikalia. In these two colonies, the number of nesting birds in different years ranges from several tens to 300 pairs. Often nests die during storms, or birds suddenly abandon them for some unknown reason. In some years, gulls do not nest at all. It is believed that there are only 600-800 pairs of relic gulls in the world.
Slide Description:
Slide No. 17

Slide Description:
VYKHUKHOL The desman lives in the floodplains of small rivers of the entire Don basin and the middle section of the Volga; in smaller quantities - in the floodplain of the lower half of the Ural River and re-acclimatized on some tributaries of the Dnieper. In favorable conditions, the desman lives up to 4 years. In Russia, a special subcommittee has been created for the protection of desman and protection from extinction of this valuable endemic of Russian nature.
Loose plants, rare species, genera, plant families, more numerous and / or more widespread in the geological past. It follows from the definition that not all rare plants are relict. Rarity may be the natural state of a species throughout its history. Recently appeared species with a limited area of distribution (neoendems) may also be rare. Many relict plants have limited habitats (i.e., they are paleoendemics), within which they are quite common, while others are widespread, but occur sporadically, without continuous habitats. Examples of the former are Gnetum and Welwitschia, representatives of the once flourishing oppression group. Although their distribution is very local, they can act as dominants of the vegetation cover. The third modern genus of oppressive - Ephedra (Ephedra), on the contrary, has a very wide range, but in many parts of it is rare plant... Local abundance can compensate for the limited range in terms of survival.
The belonging of a plant to the relict group is established mainly from paleobotanical data, indicating its more significant role in the composition of vegetation of the past. Indirect indications can be taxonomic isolation (for example, in the case of ginkgo, the only modern representative of the once diverse order of gymnosperms) and, in the case of widespread distribution, the discontinuity of the range. Thus, the ancient genus of flowering plants Platanus (Platanus) has limited natural ranges in the Mediterranean, Central Asia and North America. The lotus has the same torn area. In both cases, the vast continuous areas of these plants, which existed in the geological past, have been partially restored thanks to cultivation in culture.
The reason for the relictness in most cases is a change natural conditions associated with the Pleistocene glaciation (both directly in the area of distribution of glaciers, and due to climatic influences beyond it). Against this background, competition (especially for slow-growing plants from fast-growing competitors), the spread of pests, changes in the composition of pollinating animals, and human economic activity also play a role (see Ginkgo, Metasequoia, Yew, etc.). Most often, the fate of relict plants is associated with the communities in which they have existed for millions of years. Most of the relics of the northern hemisphere are elements of almost extinct arctot-tertiary vegetation, fragments of which have survived in the mountainous regions of East Asia. Relict plants show a steady tendency towards a decrease in the number and / or range (the exception is only a few species settled by humans). Therefore, special measures are needed to protect them. A high concentration of relict plants usually serves as the basis for the allocation of a specially protected natural area - a nature reserve or wildlife sanctuary. In Russia and the CIS countries, the Transcaucasia, Altai, Sayan Mountains, mountains are the richest in relics Central Asia, Primorye, that is, mountainous areas not affected by the ice sheet and retained a high diversity of habitats.
Relic plants are living fossils. They have come down to us from ancient times without significant changes over the past millions of years and bear the features of those plants of the Mesozoic era, which people have long found in the layers of the earth and geological rocks in the form of fossils or imprints.
The most ancient plants
Among the most ancient plants are blue-green algae, traces of which are found in deposits that are 3 billion years old. Blue-green algae are primitive asexual organisms, they grow in our time in salt and fresh waters, in wet places between rocks and even in hot springs. After all, they can withstand temperatures up to + 85 ° C.More than 300 million years ago, the planet was covered with huge forest thickets, which consisted of ferns, horsetails and huge lyre-like plants. All large representatives of flora as a result of climatic changes have now turned into coal beds in the depths of the earth. Relic plant species have gradually learned to adapt to change. They were able to live up to our times.
Examples of relic plants
Here are some well-known plants that grew 200 million years ago:- Selaginella selagovidnaya is an alga that grows in the moss bogs of Northern Russia. Horsetails originated in the Carboniferous period and inhabited almost all continents of the world, have a stem with nodes and internodes, instead of leaves they have scales, reproduce by spores and roots. Plaunas are evergreen herbs that originated in the Carboniferous period, have come down to our time, only having changed in size. They have creeping stems, from which branches grow upward, have a root system, reproduce by spores and vegetatively (roots, nodules, branches). Magnolia is an archaic flowering plant. The genus of magnolia, ancient in origin, appeared when bees did not yet exist, so its flowers are pollinated by beetles. It grows in the south in the cities of Crimea and the Caucasus, where you can find whole streets planted with these beautiful flowering trees.

Relics from America
Some woody species and relict plants that have come down to us from the Tertiary period also grow in North and South America:- Taxodium is a summer-green deciduous tree, widespread 20 million years ago. This is confirmed by fossilized leaves in brown coal deposits, the source of which they became over time. Long-lived tree: one specimen in the vicinity of Mexico City is 5 thousand years old, it is called the giant from Tula. Their longevity is explained by the tree's resistance to decay and good resistance to pests developed over millions of years. The trunk is cracked, ribbed, thinning upwards. One of the types of taxodiuam is the marsh cypress, which can grow in water, since it has pneumatophores (above-ground outgrowths).
- Chilean araucaria is a coniferous tree growing in South American countries (Chile and Argentina), in nature reaches 60 m, branches are located almost horizontally, the needles are thick and tough, can be stored for up to 15 years. It is a very hardy ancient plant.
Ancient healing tree
Ginkgo bipartisan is a gymnosperm plant, a relict tree up to 40 m tall with fan-like leaves. Grows in forests in a limited area of Eastern China.Ginkgo Biloba is Latin for “silver apricot”. The tree has a powerful trunk with a rough bark, turning into a spreading crown. The leaves of this relic are amazing: pale green with wavy edges, divided into 2 lobes, they are located on thin petioles. The plant is also a unique long-liver: some trees growing in Japan and China are about 4 thousand years old.
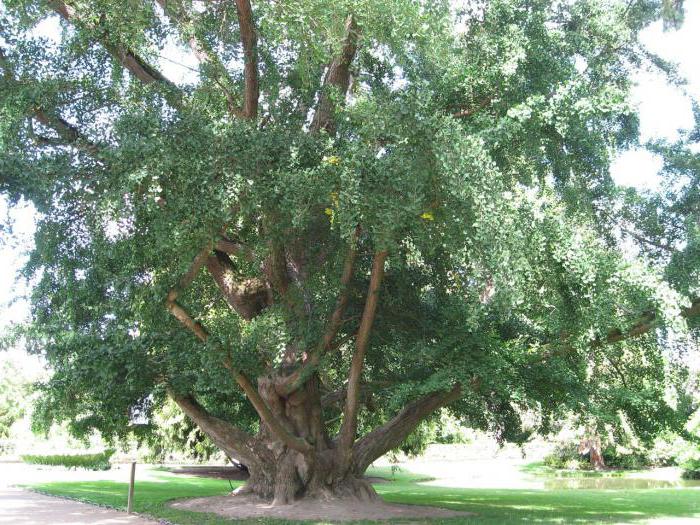 The seeds and fruits of this tree were brought to Europe by the Dutch scientist E. Kempfer in the 18th century. The tree turned out to be cold-resistant and undemanding to the soil, resistant to diseases, due to which it became widespread in Europe and America. He was planted in parks and squares.
The seeds and fruits of this tree were brought to Europe by the Dutch scientist E. Kempfer in the 18th century. The tree turned out to be cold-resistant and undemanding to the soil, resistant to diseases, due to which it became widespread in Europe and America. He was planted in parks and squares.
Even ancient Chinese manuscripts dating back to 3000 BC. e., describe its unique medicinal properties... In oriental medicine, it was used to cure diseases of the lungs and liver, heal wounds and burns, and used it as a remedy for longevity.
Its leaves, which contain many biologically active substances, have medicinal properties, which are now widely used in modern medicine to improve blood supply and stimulate memory, treat migraines and dizziness, hemorrhoids, male impotence, etc.

Fern: interesting facts
Ferns are ancient relict plants that appeared 350 million years ago, during the time of the dinosaurs. There are 10 thousand species. They are interesting in that they reproduce not by seeds, but by spores, therefore they never bloom. The fern is widespread on all continents of the world, grows in forests (lower and upper tier) and on tree trunks, in swamps, in rocks, in water (rivers and lakes), etc. On the territory of Russia, one of the species of ferns grows - the female cochidian, which can vary greatly in the size and shape of the leaves.
On the territory of Russia, one of the species of ferns grows - the female cochidian, which can vary greatly in the size and shape of the leaves.
In the forest, there is also a male fern, which belongs to the genus of shititniks. It is with him that the ancient Slavic rituals and beliefs are associated, according to which you need to look for the mythical fern flower. If you find him, he will reveal all the secrets to its owner, give the gift of clairvoyance and power over otherworldly forces. According to Slavic beliefs, it blooms once a year on the eve of the holiday of Ivan Kupala (July 7).
The female kochedyzhnik also has its own meaning: since ancient times, it has been considered a reliable witch's root, with which you can impose a curse on a person.
Relics of Russia
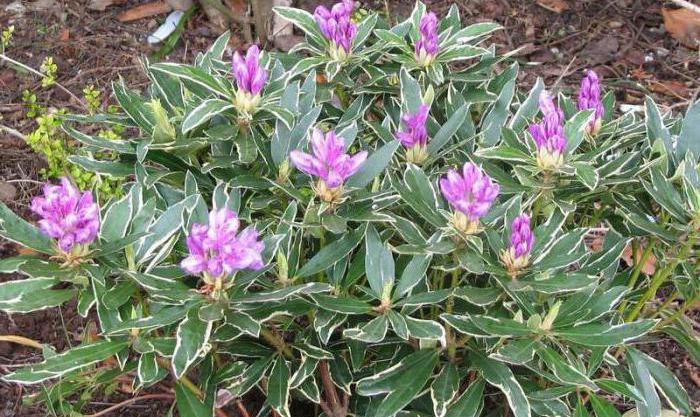
Ancient plant species preserved from the Tertiary period (2-65 million years ago):- Pontic rhododendron is an evergreen ornamental shrub 1.5 m high, which still grows in some areas of the Caucasian seaside. It has a characteristic leaf color: green with a creamy white edging. It blooms from April to June with lilac-pink flowers.

- The iron tree, which forms entire forests in the mountainous regions of Azerbaijan, is a relic deciduous tree with very strong and heavy wood (art products and machine parts are made from it). Amur velvet (Amur cork tree) is a very common tree in Primorye up to 25 m high , lives up to 300 years. Berries have medicinal properties.
Relics of Primorye
The nature of the Primorsky Territory has developed under the influence of great climatic changes and the proximity of the ocean and includes the following preserved relict plants:- The Kalopanax tree (white walnut) has a black trunk planted with sharp thorns, for which it got its name "Devil's tree". Its height is up to 30 m, it lives up to 150 years, wood is used for making musical instruments, because it has high resonance properties. Rhododendron is a “rose tree” that loves humid mountain slopes; form flowering rhododendrons. Rhodiola rosea ("golden root") is an ancient medicinal plant, for the root of which the ancient Chinese emperors hunted, sending expeditions to Altai. Komarov's lotus is a beautiful aquatic relict plant of the Tertiary flora growing in the south of the Far East of Russia, the most cold-loving of the lotus family.

- The pointed yew is the ancestor of the yew, which grew in the Jurassic period during the era of the dinosaurs, grows in Primorye and Khabarovsk Territory, Sakhalin.
Relics of the Caucasus and the Black Sea coast
The mountains of the Caucasus during the Ice Age turned out to be a natural barrier that prevented the cold from penetrating the Black Sea coast.Relict plants Krasnodar Territory preserved due to the uniqueness of the climate of this region and despite economic activity a person who is gradually replacing forest lands and using them for their own needs. These plants include:
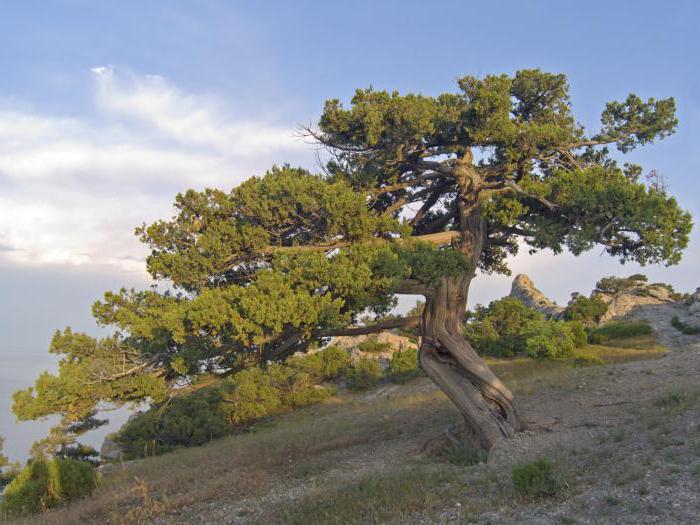
- Evergreen boxwood is the slowest growing shrub (1 mm per year), lives up to 500 years, is presented both in the form of a tree and a shrub. It is often used for landscaping parks in cities and gardens, where various green figures are created using boxwood shrubs. Tall Juniper is an evergreen coniferous tree with a cone-shaped crown that lives up to 600 years. Height - up to 12-16 m. Preserved only on the Black Sea coast, between Anapa and Gelendzhik. Propagated by seeds carried by birds, it is drought-resistant and can grow on rocky or limestone slopes of mountains, in crevices, belongs to ornamental and essential oil plants.

- Berry yew is an evergreen coniferous tree that appeared many million years ago. Its advantages are the absence of resin in the wood and its deep red color, which is why it is very popular in the manufacture of valuable furniture. Also has bactericidal properties. One of the long-lived trees ( maximum age is 1500 years). It grows in the Caucasus, near Anapa and Novorossiysk, and then spreads east to the Caspian Sea. Pitsunda pine is one of the subspecies of the Calabrian pine, a relict tree of the Tertiary period the Black Sea coast, listed in the Red Book of Russia. It is undemanding to soil and moisture, it grows quite quickly. It has light green soft needles up to 15 cm long, in the mountains it reaches a height of 400 m.The main area is located near Gelendzhik, as well as Tuapse, Anapa, Dagomys, etc.
Conclusion
After reading this informative article, all schoolchildren and adults now know which plants are called relict, because here are the most popular and interesting of them that have come down to us through many millions of years of the existence of planet Earth.The era of dinosaurs has long passed, and huge lizards can be found only in the museum and cinema. Some representatives of flora and fauna from distant historical times have survived to this day. They are called relics.
Relics
Millions of years ago, our world looked quite different. Plants and animals have changed significantly since then. Representatives of wildlife who have not lost too much contact with distant ancestors are called relics. They have a number of characteristics that were found in long-extinct plants and animals, and are not similar to modern species.
A relic animal or plant can often be called a living fossil. Unknowingly, they are often associated with the period of the existence of dinosaurs. However, the era of the dinosaurs lasted from the Triassic period (225 million years ago) to the Cretaceous (65 million years ago), the relics may also belong to later periods.
The term itself appeared in 1885, thanks to Oskar Peschel, an anthropologist and geologist from Germany. Sometimes not only living beings, but also landscapes and minerals are called relics. For example, the tundra-steppe landscape typical of Siberia is considered relict. It existed back in the days of rhinos, tours, therefore it is often referred to as the mammoth prairie.
Classification
Relics are divided into groups, depending on the era in which their species began to exist. They can be tertiary and quaternary. Neogene, or Tertiary, are species that have retained their characteristics since at least the Pliocene period. These include the Colchis chestnut, holly, blueberry, wintergreen, boxwood.
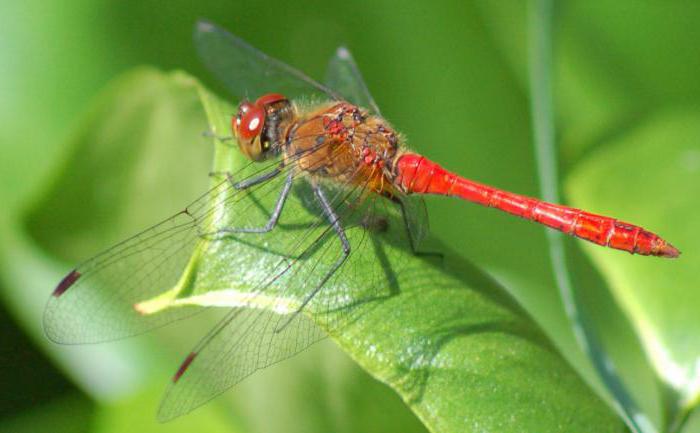
The division also takes place according to climatic conditions. There are glacial relics. They lived on earth since the Ice Age and are found in caves, rocks. The Common Viper is a typical glacial relic animal, like the gadfly deer and some dragonflies. Among the plants are blueberries and cranberries.

There are other classifications that separate relics in relation to plant formations (formational), as well as in relation to the geomorphological conditions in which they lived (edaphic). Research helps to determine how the climate has changed in their habitats, what changes have occurred in soil, water, etc.
Relic animals
Examples of living fossils living in our time can be found without difficulty. Most of them are paleoendemic. Their habitat is not too wide and rather isolated, which allowed them to preserve many of the features unchanged.
The lack of study of many parts of our planet suggests that not all prehistoric species are known. For example, the relict animal coelacanth is a detachment of coelacanths, which has long been considered extinct. In 1938, the fish was accidentally discovered by the curator of a museum in South Africa among the catch of fishermen. It turned out that this is the only species that survived to this day.

The well-known crocodiles are also living fossils. This relict animal lived on the planet 85 million years ago, although their crocodilomorph ancestors appeared about 250 million years ago. Their dimensions reached 15 meters in length. Most of the ancient species became extinct even before the Cenozoic.
The habitual habitats of crocodiles have practically not changed since antiquity. Therefore, semi-aquatic reptiles did not have to adapt to new conditions and managed to preserve their appearance as it was millions of years ago.
Relic animals: list
Below is an approximate list of modern relics that live in different parts of our Earth.
Name of the species or order | Habitat | Years of appearance |
Dipnoi | Africa, Australia, South America | 419.2 million liters. n. |
Tuatara | New Zealand | 95 million liters n. |
Mudfish | North America | 250 million liters n. |
Purple frog | India (Western Ghats) | 134 million liters n. |
Horseshoe crabs | Southeast Asia, Atlantic coast North America | |
Crocodiles | South America, Central America, Africa, Southeast Asia, Australia | 85 million liters n. |
Lao Rock Rat | Southeast Asia, Laos | 44 million liters n. |
Coelacanth | Indian Ocean | More than 65 million liters. n. |
Single-pass | New Guinea, Australia, Tasmania | 217-160 million liters. n. |
Europe, Southeast Asia, North America | 500 million liters n. |
Conclusion
Relics are animals, plants, fungi, landscapes and even minerals that have not changed or changed to a small extent since the appearance of their species. V modern world there are quite a large number of living fossils that appeared several million years ago.
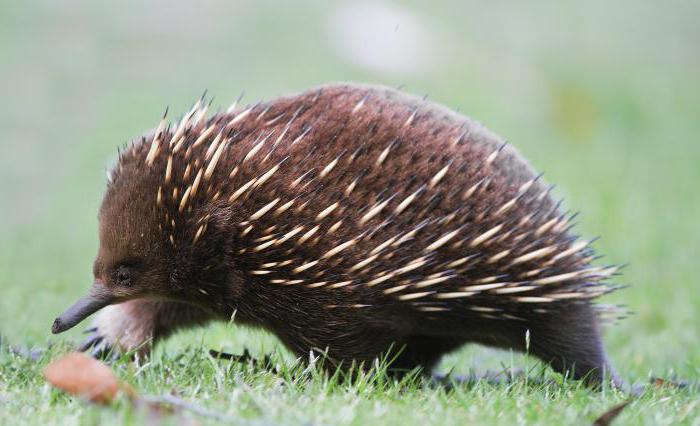

The conservation of these species was facilitated by stable climatic conditions as well as isolation. Who knows, maybe their list is much larger than the one that is known to mankind now.
