Is the moon a planet? Where did the Moon come from and what is it? Planets of the Solar System. Earth and Moon
The moon is the night star of our planet, to which we are so accustomed. From the surface of the Earth it looks different - sometimes sickle-shaped, sometimes round, like cheese.
But today we will not talk about her. Few people think that there are many moons similar to ours in the Solar System. Officially, there are more than 180 of them. Of these, 19 are quite large: giant satellites that have an almost regular spherical shape. But, since they do not revolve around the Sun, it is not customary to call them planets.
They first learned about moons far from Earth in 1601. Since then, the moons surrounding Jupiter have been named after their discoverer, Galileo Galilei.
In the 20th century, new powerful telescopes, automatic probes and spacecraft recorded many other satellites around the planets of the Solar System.
Since 2000, even more high-precision equipment has appeared, which has helped identify a record number of new moons. Every day there are more and more discoveries. By studying new discoveries, researchers discover facts of scientific interest.
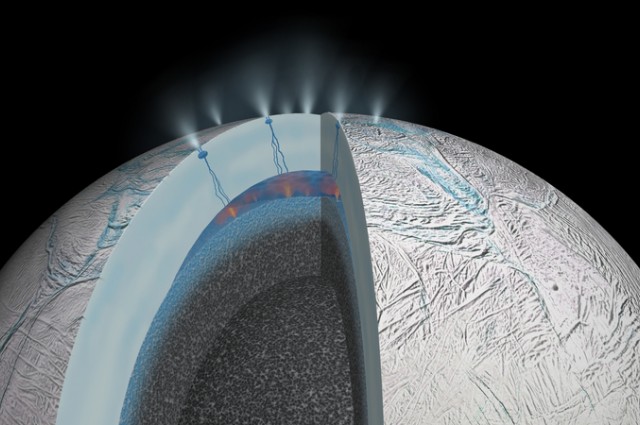
Enceladus - satellite of Saturn
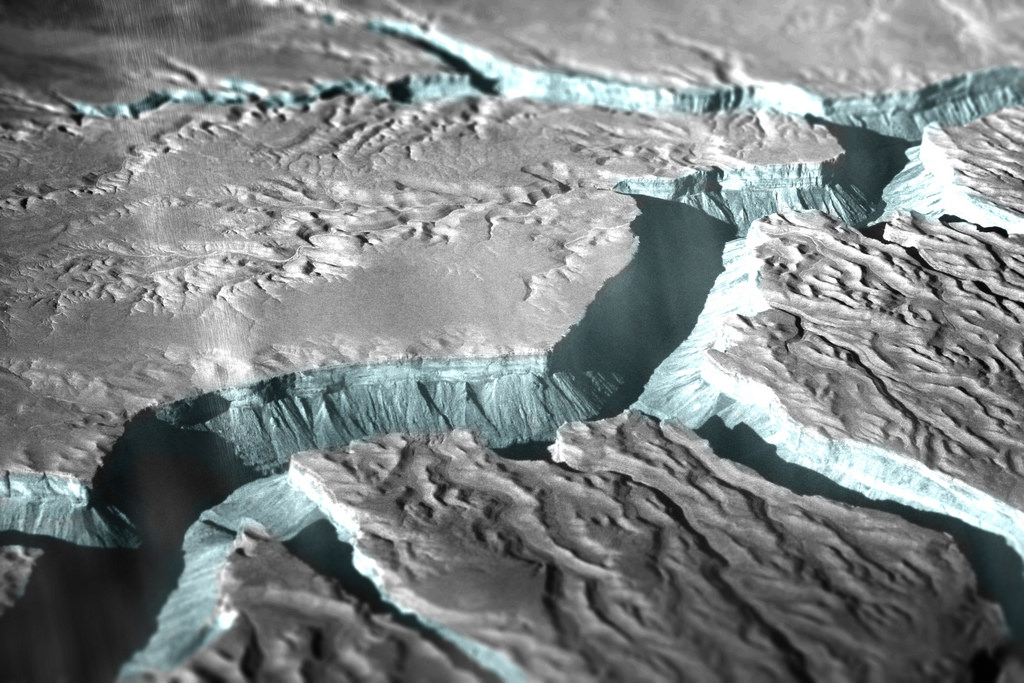
Geysers discovered on Enceladus
Saturn's moon Enceladus spews huge fountains of water into space. NASA admits that this satellite could become a suitable place for people to live outside of our planet.
Pluto and its moons
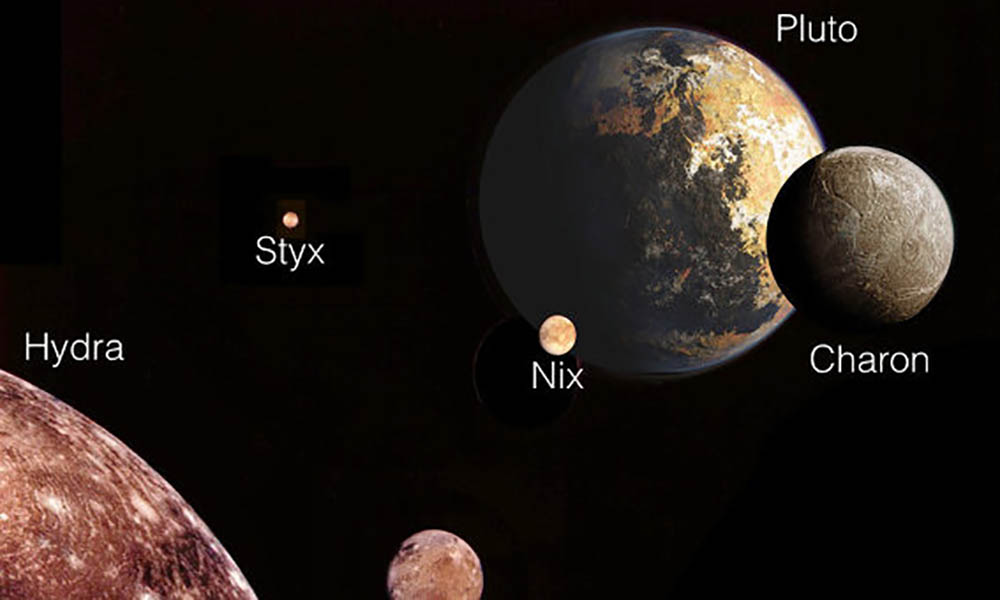
Pluto has a total of 5 satellites - Charon, Hydra, Nix, Kerberos and Styx
In addition to Charon, Pluto has 4 more moons that randomly rotate around their axis. These satellites could have been formed as a result of the collision of large space objects.
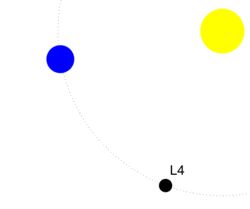
General orbit
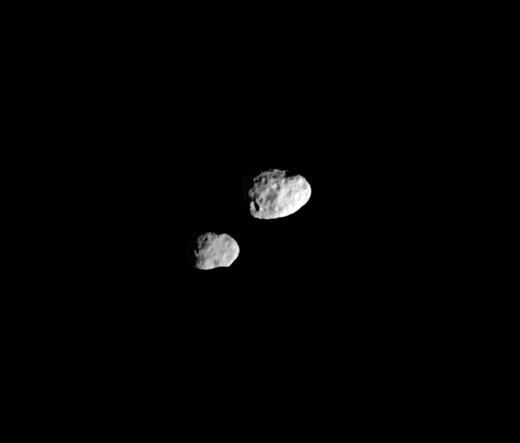

“Gemini” is the name given to the two co-orbital satellites of Saturn
Saturn's moons Epithemaeus and Janus are co-orbital. They move almost in the same orbit, but never collide! This is because the gravitational force of the moons and Saturn provokes the acceleration of the movement of one satellite and the slowdown of the other.
Moon giants
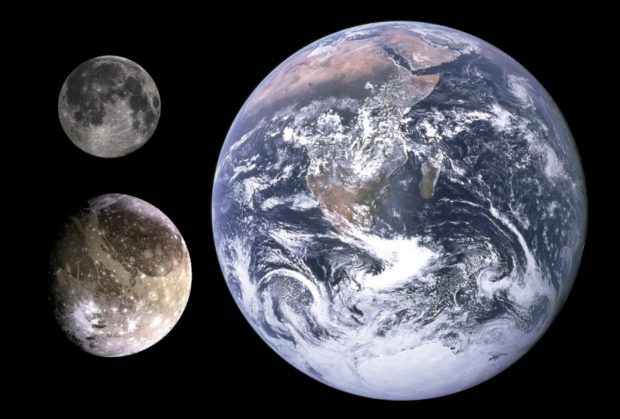

Ganymede and Titan are the two largest moons in the Solar System. Both are larger than the planet Mercury.
Neso: Neptune's distant moon
Scientists were surprised that Neso's flight path was "tied" to Neptune
Neso is Neptune's farthest moon. It takes 26 years for a satellite to complete a full revolution around its planet.
Satellite of Mars
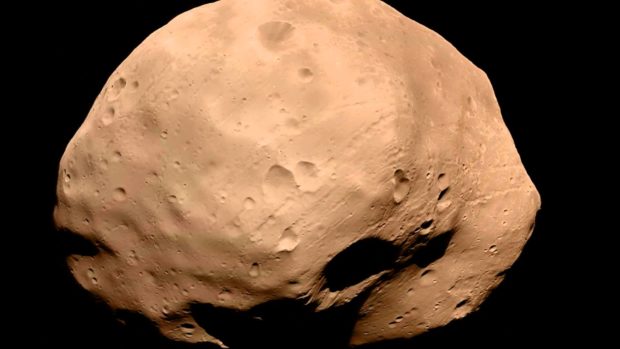
Phobos rises in the west of Mars and sets in the east every 11 hours
Phobos is a moon that passes through the sky of Mars twice a day. While Mars rotates around its axis, the satellite manages to orbit the planet twice.
Triton
Triton is the seventh of the list of the largest satellites of the Sun System
Neptune's largest moon has many geysers that erupt into the atmosphere over a distance of about 8 kilometers.
Water is an ideal environment for the development of life
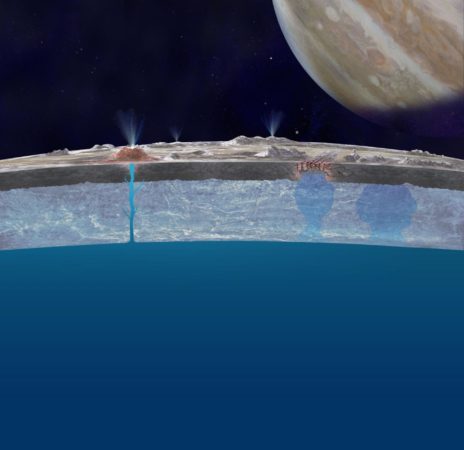
In 2020, an automatic interplanetary station will be sent to the sixth satellite of Jupiter. The mission objective is to search for living microorganisms in subsurface waters
Europa, the moon of Jupiter, has more water than our planet Earth. Scientists admit that beneath the icy surface of Europa lies an ocean up to 170 kilometers deep.
Moons of Jupiter

Jupiter currently has 67 moons; more than any other planet in the Sonic System
It is assumed that in fact Jupiter has many more satellites than is commonly believed. Their number can reach one hundred units.
Saturn's moon Iapetus
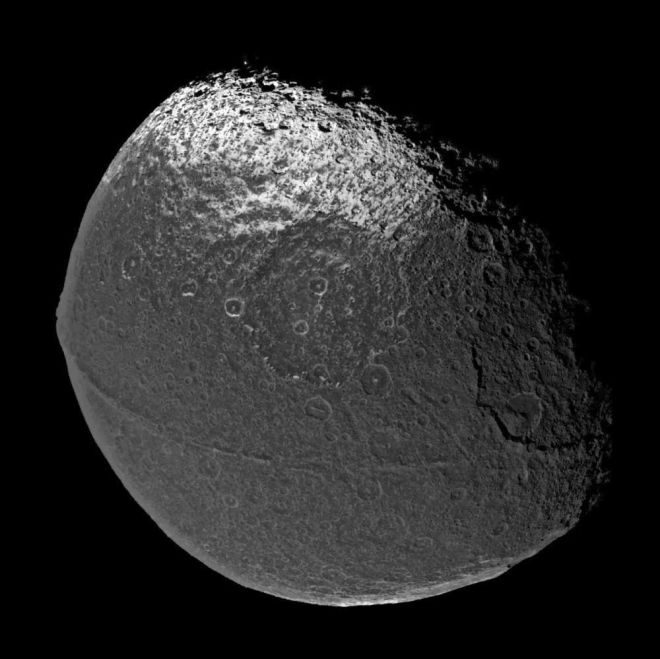

This satellite of Saturn has an unusual shape
Saturn's moon, Iapetus, has an equatorial ring. It rises above the surface of the moon at a level of 13 km, which makes Iapetus look like a walnut.
The Mystery of the Rings
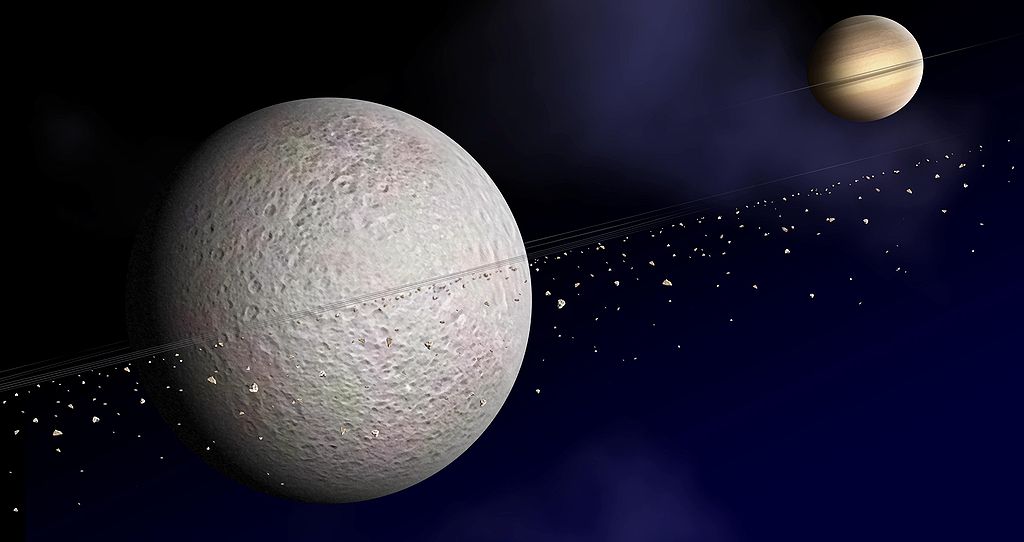

Rhea is Saturn's second largest moon
Rhea, Saturn's moon, may have rings. If this is so, then it is the only “ringed” satellite in the Universe.
The fearsome Mimas
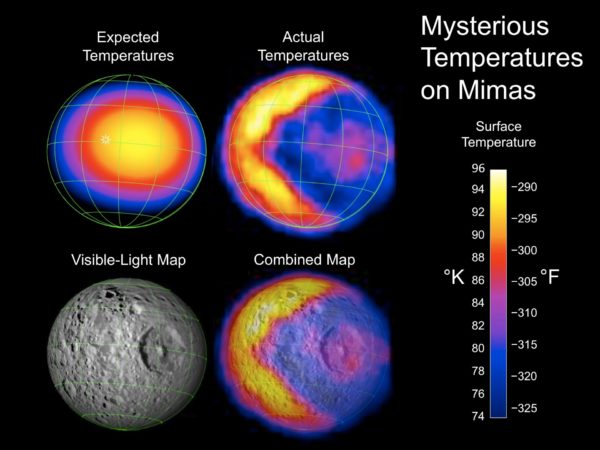
In the thermal image, Mimas looks like Pac-Man, a computer game character.
Mimas, Saturn's moon, looks just like the Death Star from " Star Wars" For those who don’t know: that’s the name of the battle space station in the film, a spherical superweapon.
Cosmic acceleration
![]()
You can't jump like that on Deimos; except with insurance
Mars' moon Deimos has a rotational acceleration of 5.2 m/s. A sports jump with a running start on the surface of the satellite would cause an increase in speed, as a result of which a person would be able to fly into outer space.
Fearful
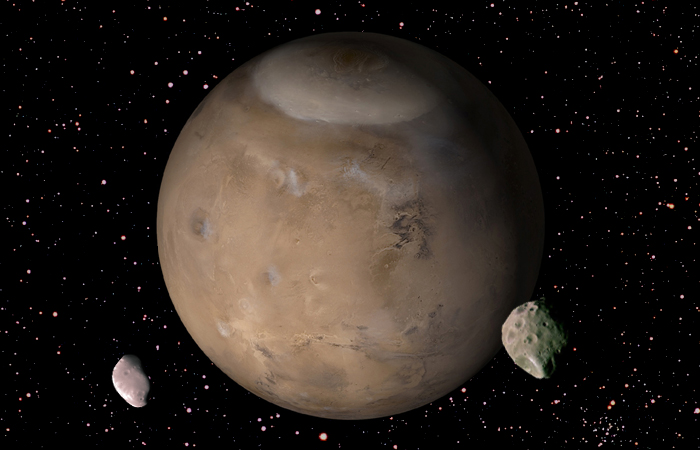

Mars and its two satellites - Phobos and Deimos
The satellites of Mars, Phobos and Deimos, are translated from Latin as “fear” and “horror.” The moons were given such names because of their proximity to the red planet. After all, Mars got its name during the times Ancient Rome, in honor of bloodthirsty god war.
The Coming Clash
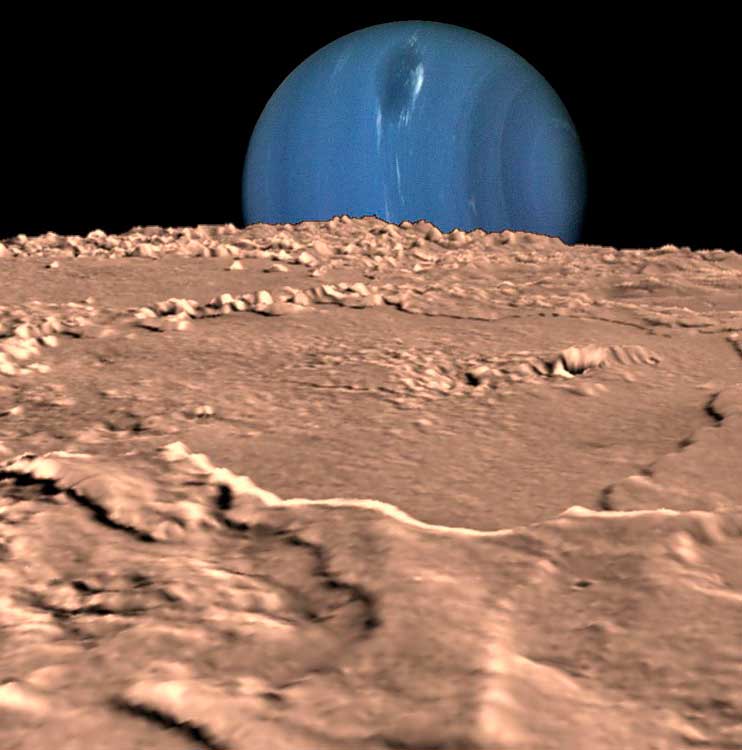

Triton is gradually approaching Neptune
Someday Neptune's gravity will be destroyed by Triton, its closest satellite. As a result, Neptune will acquire the same ring as Saturn.
Familiar names
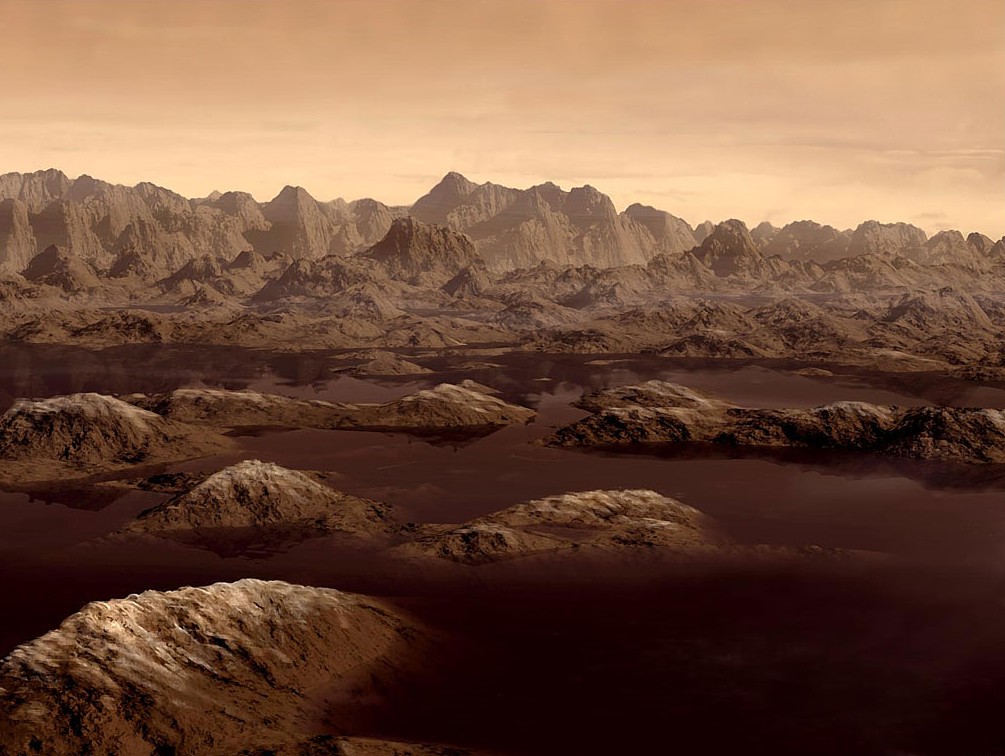

The surface of Titan is quite textured
The Mountains of Titan were named exactly like those in Tolkien's Lord of the Rings trilogy. Erebor, Orodruin, the hills of Nimloth, Gandalf, and Faramir - all these fantasy places can be found on the map of the moon of Saturn. One can only guess why extraterrestrial landscapes were given such symbolic names. Maybe scientists are hiding something from us?
Destruction of Galileo
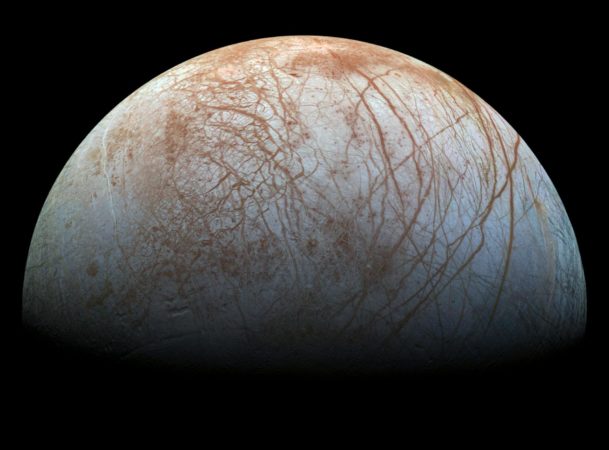

Scientists have been studying the Europa satellite for forty years
After spacecraft Galileo completed an exploration mission and self-destructed in Saturn's atmosphere. Scientists were afraid that terrestrial microorganisms might remain at the installation. But on Europa, the mysterious moon of Saturn, in the underground ocean, signs of extraterrestrial life may be discovered.
An old dream

What is impossible on Earth is possible somewhere in the Universe
Titan, Saturn's moon, has a very dense atmosphere and low gravity. Being in such conditions, a person could fly like a bird. But the presence of hydrogen cyanide above its surface is fatal to us.
Speed of light

With the mutual approach and distance of the Earth and Jupiter, the time of eclipses either shortened or increased
Danish astronomer Ole Römer first calculated the speed of light in the 1670s while studying eclipses of Jupiter's moon Io.
deserted place

The moon has no atmosphere, no clouds. The Sun, Earth, and starry sky are visible there 24/7
No man has set foot on the moon for more than 40 years. It seems that the interest of space researchers in our natural satellite has temporarily faded.
Two parts of one whole
The Moon and the Earth are so connected with each other that there is no doubt that if our planet did not have a natural satellite, the history of its development would be completely different, and life would simply not exist on it.
Let's start with the fact that the Moon, or as it is also called, Selene, has a direct influence on the earth's axis, allowing the Earth to maintain a tilt of 23 degrees, thanks to which suitable conditions for life. This gives us the opportunity to see day and night for approximately the same period of time throughout the day (for example, the angle of inclination of Uranus is almost 98 degrees, and therefore its poles are in darkness for 42 years and the same amount of time is constantly illuminated by the sun's rays).
In addition, the Moon in the sky slows down the rotation of our planet by a tiny microsecond every day - if it did not do this, the Earth would begin to rotate so quickly that the day would soon be equal to six hours, maybe even less. This would definitely affect the development of plants and animals, and also lead to an increase in the speed of air flows, as a result of which storms would become commonplace.
One of the most famous effects of Selena on our planet is its effect on the ebb and flow of the tides: if the Earth did not have a natural satellite, the tides would be several times stronger. The depth depends on the Earth's satellite: it attracts water located in the equator region, therefore the depth of the ocean in the center of the Earth is much deeper than near its poles.
The Moon is a natural satellite of the Earth, whose diameter is almost 3.5 thousand km, and its length along the equator is about 11 thousand km (in area it is three and a half times smaller than our planet). Selena is located at a distance of 385 thousand km from the Earth, and therefore, after the Sun, it is considered the second brightest object in the sky. According to scientists, the age of the satellite is at least four billion years.
There are many versions of how exactly our planet got its satellite. One of them says that the Earth and the Moon were formed simultaneously. Another suggests that Selene was formed at a great distance from our planet, and while flying nearby, it found itself in the zone of Earth’s gravity and was unable to “escape.”
Recently, based on data obtained from analyzing samples of lunar soil, scientists have put forward a new theory that this moment accepted as the main one. We are talking about a giant collision, when more than 4 billion years ago the protoplanet Earth (a large planetary embryo) collided with the protoplanet Theia, and the collision occurred not in the center, but tangentially.
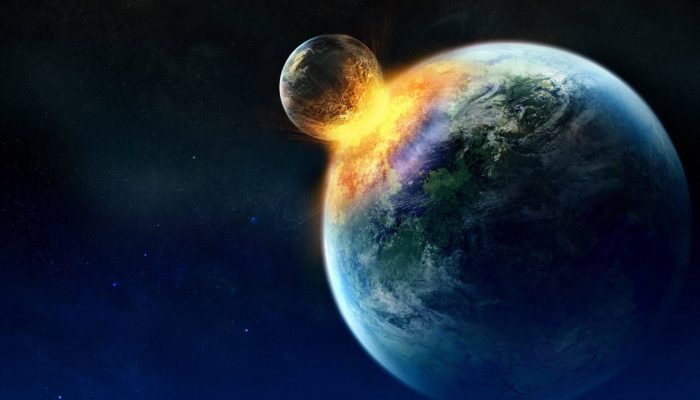

Theia suffered more, throwing out the bulk of its constituent elements into Earth's orbit, while the Earth released only a small fraction of the Earth's mantle. Combining, these substances formed the embryo of the Moon. It is worth noting that after the collision with Theia, our planet increased its rotation speed for five hours, changing the angle of its axis.
What does the Earth's satellite consist of?
The surface of the Moon is completely covered by regolith, consisting of dust and tiny meteorite fragments, which often fall onto the surface of the Moon unprotected by the atmosphere (the thickness of such a layer can range from several centimeters to tens of kilometers). The Earth satellite itself consists of:
- The crust is very heterogeneous and ranges from zero meters under the Moscow Sea (a 600 m thick layer of basalt separates it from the lunar surface) to 105 km (under the Korolev crater, located on the dark hemisphere of the Moon). Although the Korolev crater is located on the dark side of the Moon, a thicker layer is still located on the hemisphere visible to us;
- Three layers of mantle;
- Cores.
The invisible side of Selena
Since the period with which a satellite rotates around the Earth almost coincides with the time it rotates around its axis, with earth's surface Only one hemisphere of the satellite can be seen, while the far side of the Moon is almost never visible. The only exceptions are the edges located on the eastern and western dark sides of Selene. Once a month you can see the northern ones, and once every fifteen days - its southern regions(this makes it possible to observe almost sixty percent of the satellite from Earth).







Before the advent of spacecraft, the far side of the Moon was completely unexplored, and therefore, with the advent of appropriate technology, scientists learned a lot of new and interesting things about Selene. For example, several new geological formations were discovered on its dark side, indicating that seismic movements inside the satellite continued for at least 950 million years after, according to the version accepted at that time, the “geological death” of the Earth’s satellite occurred.
According to the data obtained, seismic activity on the satellite still exists today, and ground vibrations often last about an hour. Over five years of observations, about thirty such moonquakes were recorded, lasting ten minutes and reaching magnitude 5.5 (on earth, such vibrations last no more than two minutes).
It was discovered that the surface of the dark hemisphere differs from that visible from Earth - there are a huge number of craters, most of which arose as a result of falling meteorites, and is dominated by mountainous terrain. But there are few lunar seas here - only two: the Sea of Dreams and the Sea of Moscow.
Relief of Selene
The surface of the Moon consists of mountain ranges and lunar seas - huge, round-shaped lowlands that were once flooded by lava that came to the surface, and therefore they are all covered with a thick layer of basalt (because of this, they are characterized by a darker color than other parts relief). The largest lunar storm, with a length of about 2 thousand km.
Despite the fact that basically all the lunar maria are located on the visible side of Selene, it is on its reverse side that the largest impact depression, the South Pole-Aitken basin, is located (from our planet you can only see its dark edge). Its dimensions are 2400 by 2050 km, and its depth is about 8 km, occupying almost a quarter of the satellite’s hemisphere. This pool is interesting because of what is in it. nadir Selena, and the distance from the lowest to the highest high point is about 16 km.
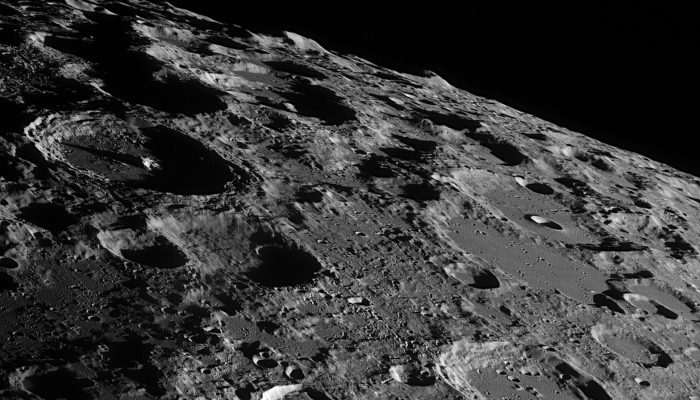

Another interesting geological formation is a huge tunnel discovered near one of the volcanic plateaus, the Marius Hills: its diameter is 65 m and its depth is about 80 m. It is clear evidence of the volcanic activity of Selene, since it was formed due to the solidification of flows of molten rock.
What does a satellite look like from Earth?
The Earth and the Sun are constantly changing their location in relation to each other, the boundary between the illuminated and unlit parts of the lunar hemisphere is constantly shifting, so Selena changes its outline every day, forming different phases of the Moon. One thing remains unchanged: the illuminated part of the satellite always points in the direction where the Sun is located. Interestingly, the synodic month on the satellite (the time that passes between two identical phases of the Moon) is several days shorter than on Earth, is variable and lasts on average about 29.5 days.
Despite the fact that the Moon in the sky gives the impression that it is glowing itself, in reality the surface of the Moon only reflects the sun's rays, so only the area illuminated by the Sun can be seen from the Earth. It is believed that the Moon in the sky goes through certain phases, briefly characterized as “Waxing Moon” - “Full Moon” - “Waning Moon”:
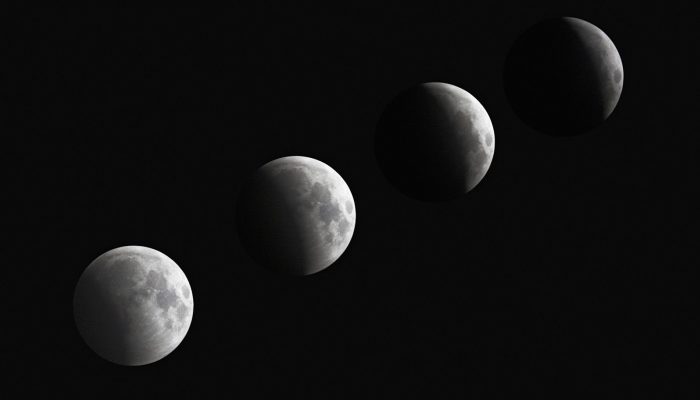

New moon
During a new moon, the dark Moon is almost never visible. The only exception is a few minutes when it appears against the background of the Sun during, or when two days before or after the new moon in very good weather a slightly marked grayish disk of the earth’s satellite appears in a clear sky.
During this phase of the Moon, the satellite is not visible because it is located between the Earth and the Sun almost on the same line.
If they are placed exactly on the same straight line, you can observe solar eclipse, as the Earth's satellite begins to cast its shadow, 200 km in diameter. The Moon in the sky is located as close as possible to the Sun, and the far side of the Moon is facing the surface of our planet.
New Moon
The new moon is visible in the sky for only a few minutes in the form of a narrow crescent and appears immediately after the Sun sets on the third day after the new moon. After this phase, the new Moon begins to grow rapidly and with each subsequent night everyone has the opportunity to begin to observe such a phenomenon as the growing Moon. It is interesting that in ancient times the beginning of the lunar or solar month always began from the moment when the new Moon appeared in the sky.
First quarter
On the seventh night after the new moon, the waxing Moon appears in a semicircle in the west just after the Sun goes below the horizon (usually seen in the first half of the night). The waxing Moon at this stage is located in the east and is at an angle of 90° to the Sun. The sun's rays illuminate the western half of the Moon and show people in the Northern Hemisphere the right side of the Moon, and those in the Southern Hemisphere the left.







At this stage of the Moon's phase, the waxing Moon is already quite bright and the light it emits is quite enough for objects on the ground to begin to cast shadows. Interestingly, when the waxing Moon is at this stage, one can observe the smallest level of rise at high tide and its smallest fall at low tide.
Full moon
On the fourteenth night, the waxing Moon reaches its peak as the Sun begins to fully illuminate it - the full moon arrives. The full moon remains in the sky all night. It appears even before the Sun has completely set, and leaves the sky after it rises.
At this phase, the full Moon is opposite the Sun, and the Earth is located in the middle (the full Moon is always extremely bright due to the fact that the Sun shines on the visible hemisphere, and shadows on the lunar surface disappear completely). If the full Moon is on the same line, you can observe a lunar eclipse.
Last quarter
Literally a day later, the full Moon begins to thin out. Since this happens almost imperceptibly to the human eye, it appears as if the full Moon is visible in the sky for several nights. Already seven days after the full moon, the waning moon again shows earthlings its half. The waning Moon is visible only in the second half of the night.
Old Moon
Having finally shown people its half, the night luminary becomes smaller, turns into a thin sickle, and then the dark Moon disappears completely - and after a while the waxing Moon appears again in the sky.
Memo to observer
So that the observer does not confuse which phases of the Moon are waxing and which are waning, it is enough to remember the basic rule: if the Earth’s satellite resembles the Latin letter “D” and is visible at the beginning of the night, there is a waxing Moon in the sky. If the sickle looks like the letter “C” and is shown before dawn, the waning Moon is before the beholder.
The Moon itself is already unique in that it is the only spherical satellite in orbit. The reason for this shape is thought to be that its mass is large enough to pull matter uniformly towards the center of the satellite.
Size Moon is just over one-fourth the diameter of the Earth (3475 km) and that too unique phenomenon. So far, astronomers have not been able to detect a satellite of any planet with large or at least the same dimensions relative to the size of the planet.

However, despite such a significant size for a satellite, the mass of the Moon is relatively small. This also indicates the low density of the satellite. The explanation for this phenomenon lies in the reason for the formation of the Moon. Scientists have a version that during the birth of the Earth, some huge cosmic body the size of . As a result of this collision, a large amount of outer mantle and crust was thrown into Earth's orbit. Gradually coming together under the influence of gravitational forces, the material formed the satellite we know today as the Moon. Given that the Earth's outer mantle is much less dense than its inner layers, this concept goes some way to explaining the Moon's low density.
Observations from Earth allow us to see numerous craters on the surface of the Moon. The reason for the existence of such a relief is quite simple. Unlike the Earth, the Moon is not a geologically active body, it does not have an atmosphere, and there is no volcanic activity. This is why the surface of the Moon remains unchanged for centuries.
The diagram below highlights the eight different phases of the moon: full moon, waxing moon, first quarter, waxing moon, full moon, waning moon, third quarter and waning moon.


Structure of the Moon
The Moon is a differentiated cosmic body and according to its structure is divided into crust, mantle and core. Despite the fact that the Moon is the second densest satellite in the solar system (after Io), its inner core is considered to be very small in size, since its diameter is only about 700 kilometers, which is an insignificant indicator relative to the size of the satellite.
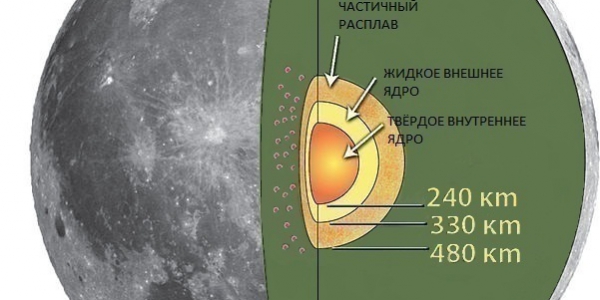
The inner core has a shell saturated with iron and has a radius of about 240 kilometers. The outer core also consists mostly of iron, only molten; its thickness is approximately 300 kilometers.
There is also a partially molten boundary layer near the lunar core. According to the calculations of planetary scientists, it was formed as a result of processes of fractional crystallization of a huge magma ocean 4.5 billion years ago. The thickness of this layer is about 480 kilometers.
Like the Earth, the Moon's mantle consists mainly of ultramafic rocks, which, unlike those contained in the crust, contain minor impurities of silicon oxides and fairly large amounts of iron and magnesium. Olivine and pyroxene are the main rock-forming minerals.
The average thickness of the lunar crust is about 50 kilometers. Due to periodic moonquakes caused by the Earth's gravity, cracks can appear in it.
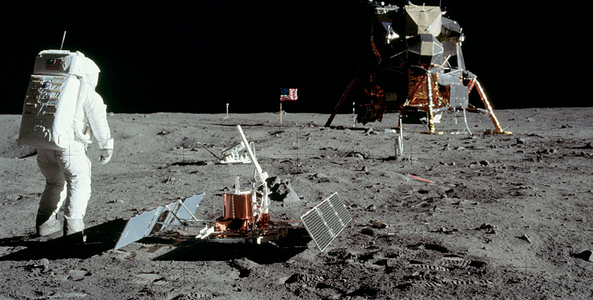
First man on the moon
Twelve representatives of humanity were lucky enough to walk on the surface of the Moon. It was started by Neil Armstrong in 1969 as part of the Apollo 11 mission, and the last one at the moment was Gene Cernan in 1972 with the Apollo 17 mission. Since 1972, human flights to the Moon were stopped, and the study of the Earth's satellite remained in the field of automatic spacecraft.
In the near future, man may visit the Moon again. The plans of leading space agencies such as NASA, Roscosmos and ESA are related to this. Perhaps already in the 2020s the first space station will appear on the Moon.
Man's first step on the moon
“That’s one small step for a man, one giant leap for all mankind.”, - Neil Armstrong said this famous phrase when he descended to the surface of the Moon.
The Moon has no dark side. Both sides of the Moon receive the same amount of sunlight, but given that the Moon is connected to the Earth by tidal forces, earthlings can always see only one side of it. This side reflects sunlight and people can see it even with the naked eye, then information about the so-called “dark side” was obtained using spacecraft.
The ebb and flow of the tides on Earth are carried out precisely with the help of the Moon. They arise as a result of its gravitational attraction. High tides occur on the side of the Earth that is currently facing the Moon, while low tides occur on the other side.
Every year, the Moon slowly moves away from the Earth by about 3.8 centimeters. According to scientists, this process will continue for another 50 billion years.
If you were on the moon, you would weigh much less. Moon gravity is much weaker than Earth's gravity. This is due to the fact that its mass is much less. That is, your weight on the Moon would be only one-sixth (about 16.5%) of your weight on Earth.
In the 50s, the United States planned to detonate an atomic bomb on the Moon. The secret project was developed at the height of the Cold War and was called Project A119. The main goal of such an extraordinary plan was to demonstrate military and space superiority to the USSR. Fortunately, the idea was never implemented.

The Moon has no atmosphere. The surface of the Earth's satellite is absolutely not protected from cosmic rays, meteorites, asteroids, comets and solar winds. This is why there are such huge temperature fluctuations on the Moon, and why its entire surface is covered with craters. The lack of an atmosphere also means that not a single sound can be heard on the Moon, and the sky is always black.
There are tremors happening on the Moon. The Earth's gravitational pull leads to small moonquakes that occur several kilometers below the surface and form small ruptures and cracks. The Moon is believed to have a molten core like the Earth.
The Moon is the fifth largest natural satellite in the Solar System. It is much smaller than the main satellites
Having explored the structure of the Solar System and dwarf planets in one of the previous ones, this article includes the natural satellites of the Solar System. This is one of the most interesting directions in exploratory astronomy, since there are moons larger than planets, and beneath their surface there are oceans and possibly life forms.
Let's start with the planets' satellites terrestrial group. Since Mercury and Venus do not have natural satellites, acquaintance with the satellites of the Solar system should begin with the Earth.
Terrestrial planets: Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars.
Moon
As you know, our planet has only one satellite - the Moon. This is the most studied cosmic body, as well as the first one that man managed to visit. The Moon is the fifth largest natural satellite of a planet in the solar system.
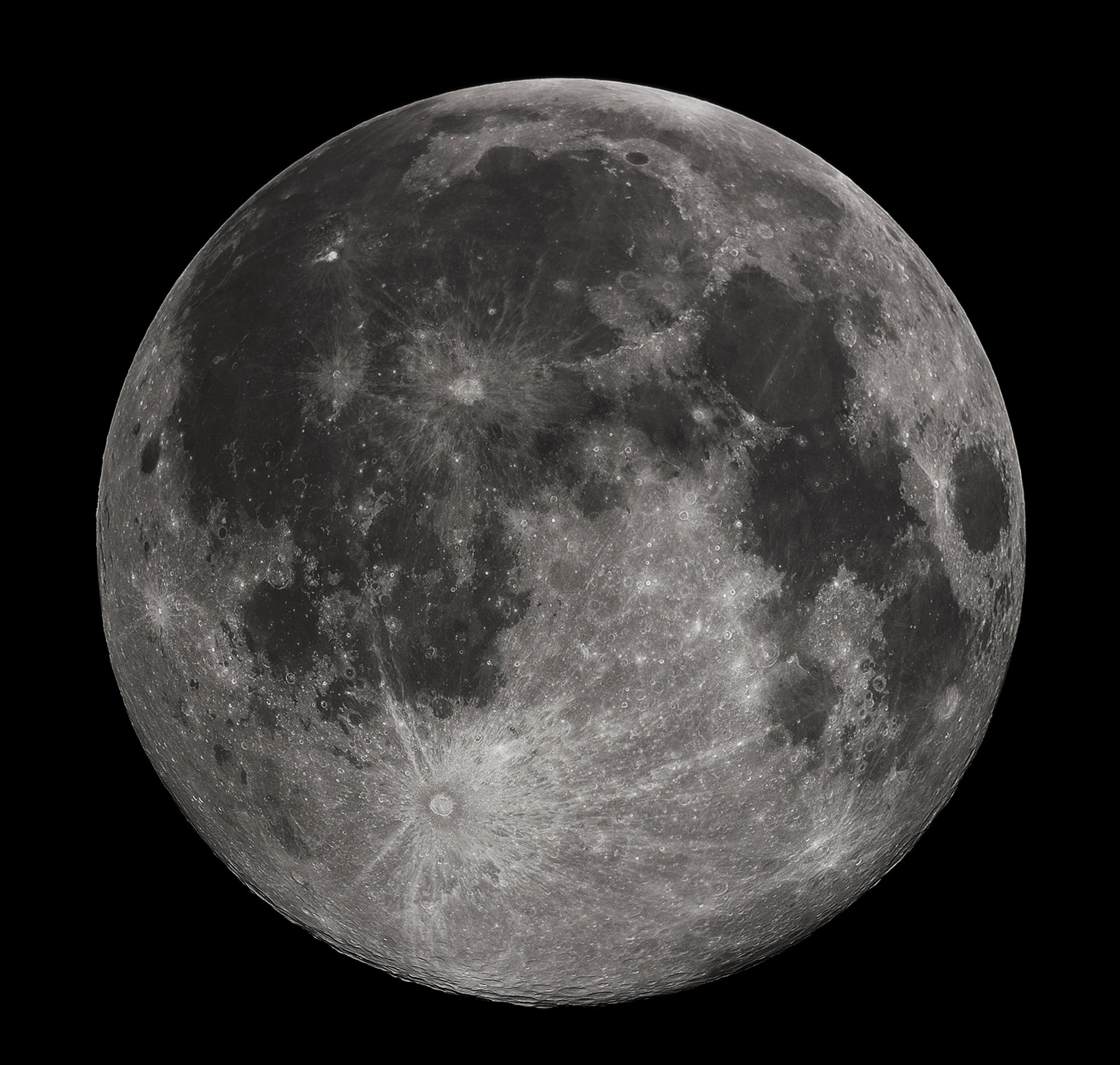

Although the Moon is considered a satellite, it would technically be considered a planet if it had an orbit around the Sun. The diameter of the Moon is almost three and a half thousand kilometers (3476); for example, the diameter of Pluto is 2374 km.
The Moon is a full participant in the Earth-Moon gravitational system. We have already written about another such tandem in the Solar System - o. Although the mass of the Earth's satellite is not large and is a little more than a hundredth of the mass of the Earth, the Moon does not revolve around the Earth - they have a common center of mass.
Can the Earth-Moon system be considered a double planet? The differences between a binary planet and a planet-moon system are thought to lie in the location of the system's center of mass. If the center of mass is not located under the surface of one of the objects of the system, then it can be considered a double planet. It turns out that both bodies rotate around a point in space that is located between them. According to this definition, the Earth and Moon are a planet and a satellite, and Charon and Pluto are a double dwarf planet.
As the distance between the Earth and the Moon constantly increases (the Moon moves away from the Earth), the center of mass, which is now below the surface of the Earth, will eventually move and end up above the surface of our planet. But this happens quite slowly, and it will be possible to consider the Earth-Moon system as a double planet only after billions of years.
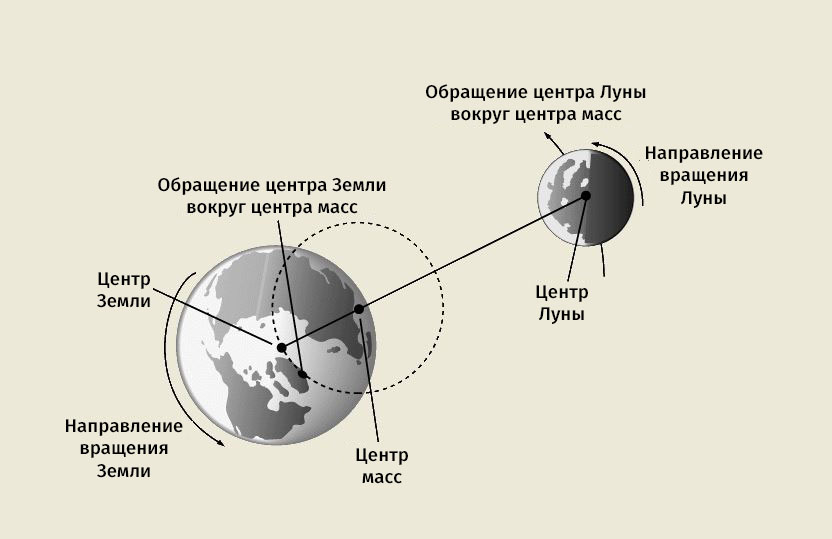
Earth-Moon system
Among cosmic bodies The Moon influences the Earth most strongly, except perhaps the Sun. The most obvious phenomena of the satellite's impact on the Earth are lunar tides, which regularly change the water level in the World Ocean.
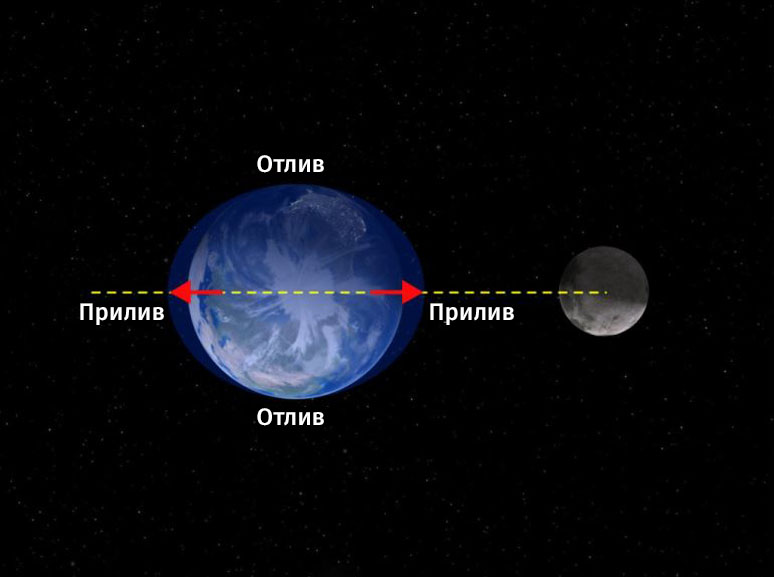
Earth view from the pole (high tides, low tides)
Why is the surface of the Moon all covered with craters? Firstly, the Moon does not have an atmosphere that would protect its surface from meteorites. Secondly, there is no water or wind on the Moon, which could smooth out the places where meteorites fell. Therefore, over four billion years, a large number of craters have accumulated on the surface of the satellite.
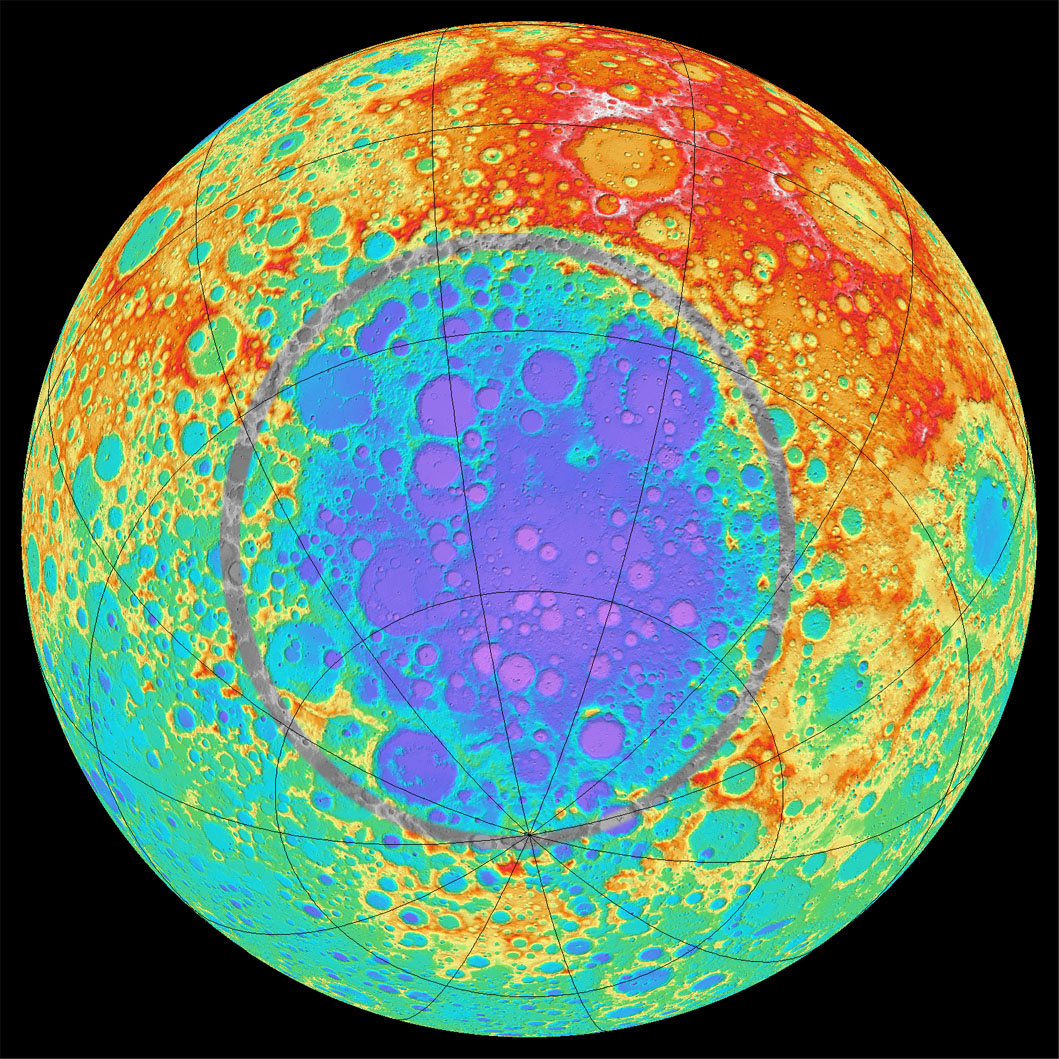
The largest crater in the Solar System. South Pole - Aitken basin (red - highlands, blue - lowlands).
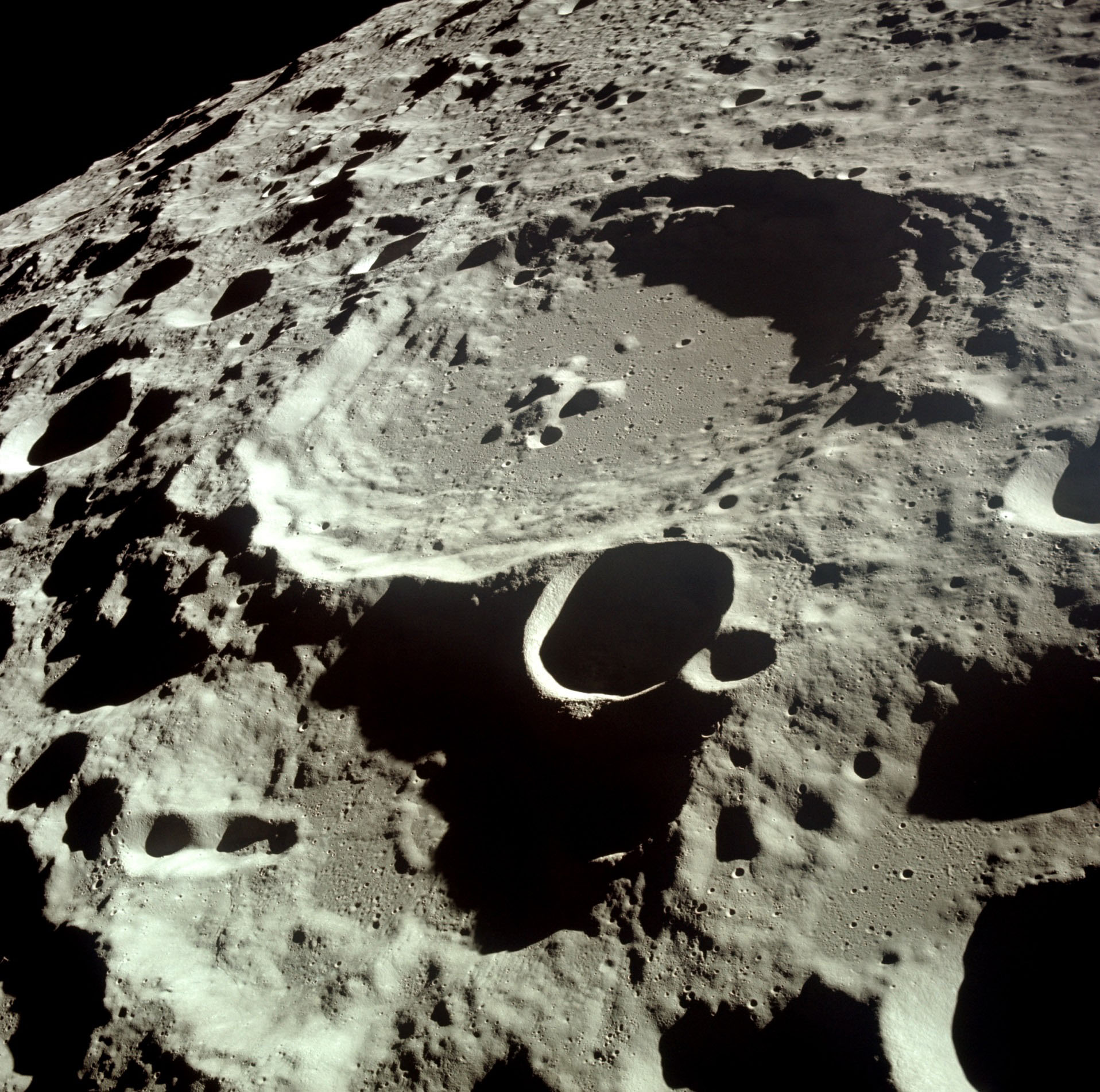

Lunar crater Daedalus: diameter 93 km, depth 2.8 km (image from Apollo 11).
The Moon, as already mentioned, is the only satellite visited by man and the first heavenly body, samples of which were delivered to Earth. The first person to set foot on the moon was Neil Armstrong on July 21, 1969. In total, twelve astronauts visited the Moon; The last time people landed on the moon was back in 1972.
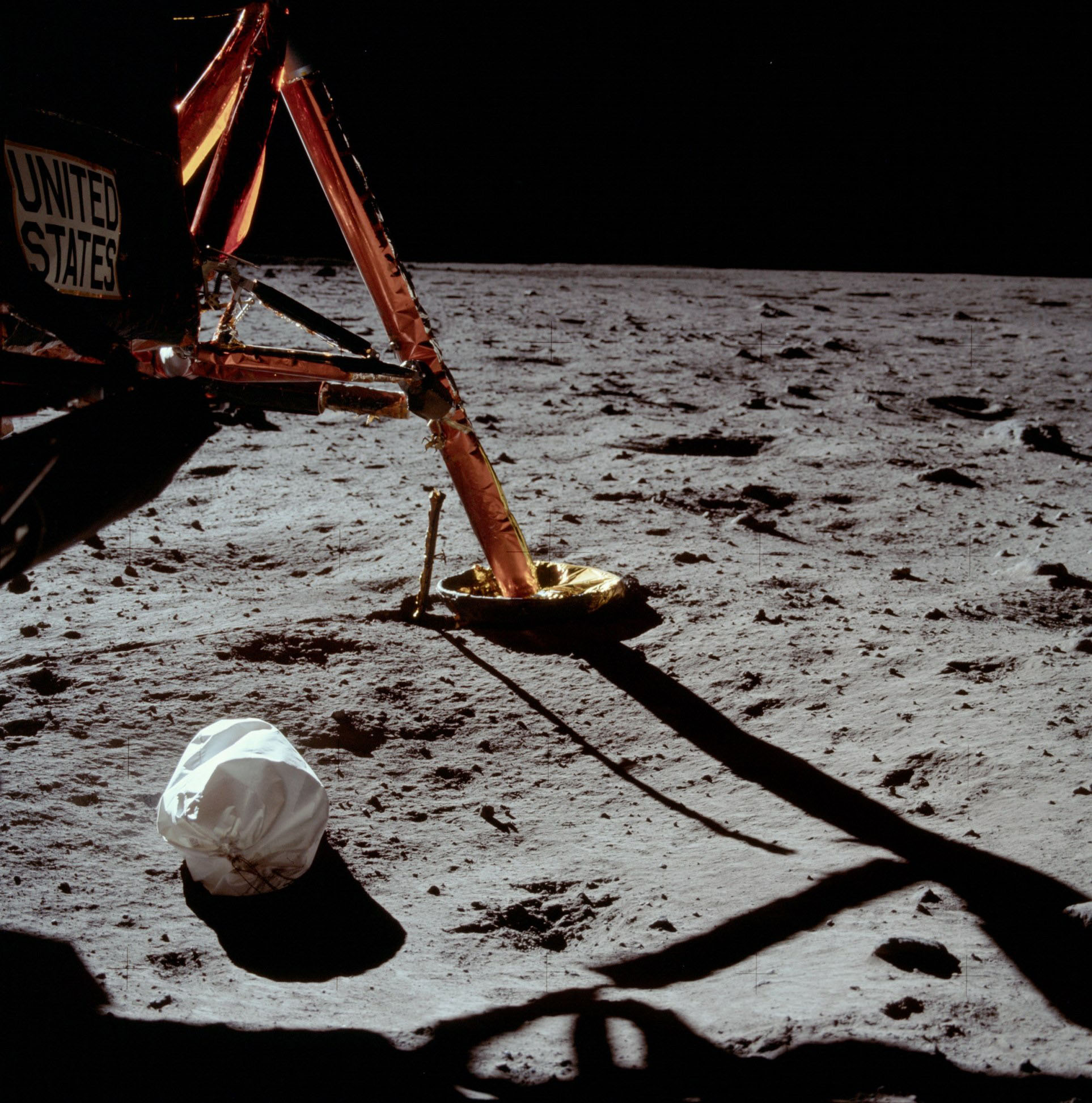

The first photograph taken by Neil Armstrong after walking on the surface of the Moon.
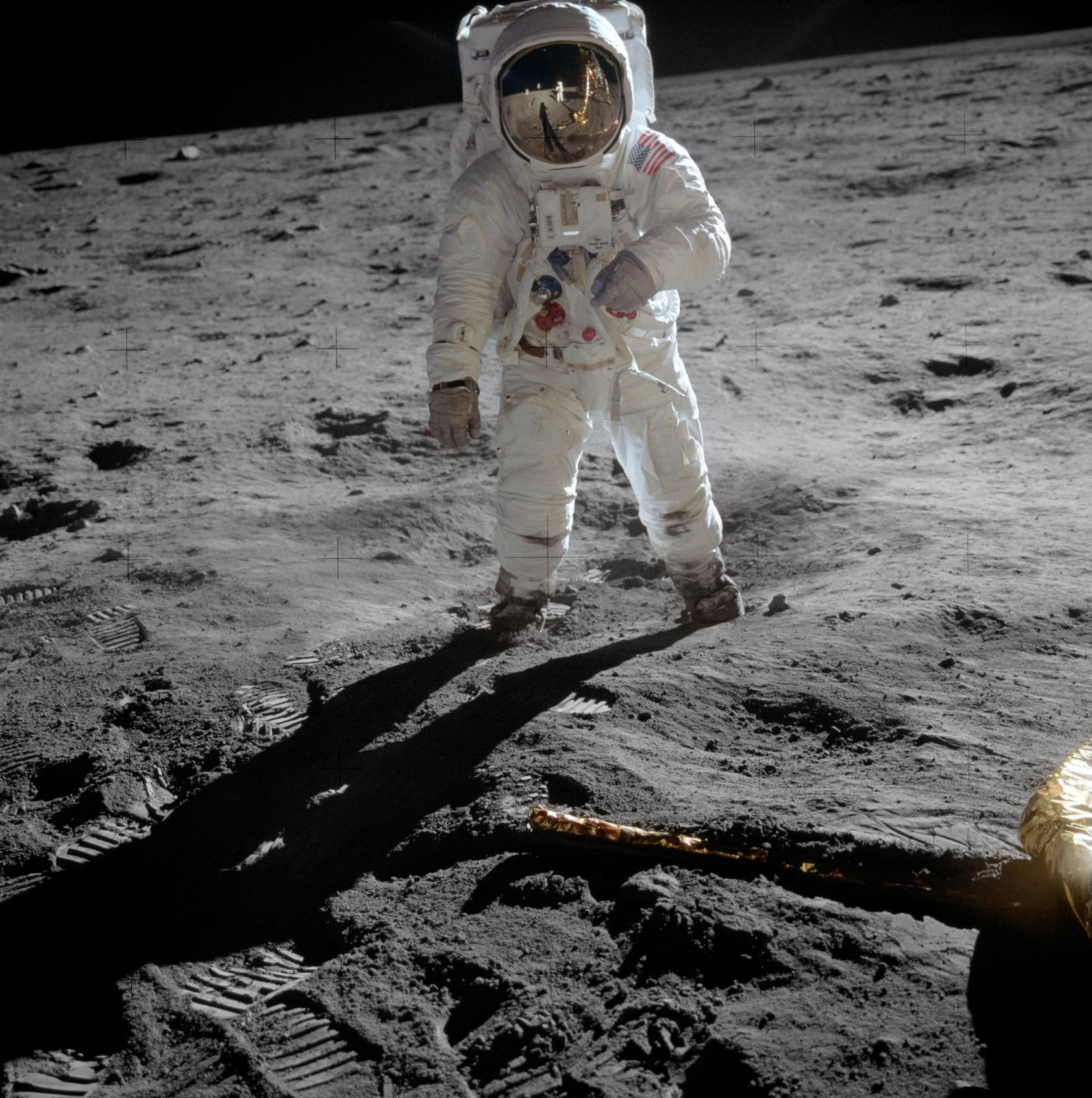

Edwin Aldrin on the Moon, July 1969 (NASA photo).

Before scientists obtained soil samples from the Moon, there were two fundamentally different theories about the origin of the Moon. Adherents of the first theory believed that the Earth and the Moon were formed at the same time from a cloud of gas and dust. Another theory was that the Moon was formed elsewhere and then captured by the Earth. The study of lunar samples has led to the emergence of a new theory about the “Giant Impact”: almost four and a half (4.36) billion years ago, the protoplanet Earth (Gaia) collided with the protoplanet Theia. The blow did not land in the center, but at an angle (almost tangentially). As a result, most of the substance of the impacted object and part of the substance of the earth's mantle were thrown into low-Earth orbit. From these debris the Moon was assembled. As a result of the impact, the Earth received a sharp increase in rotation speed (one revolution in five hours) and a noticeable tilt of the rotation axis. Although this theory also has shortcomings, it is currently considered the main one.
Formation of the Moon: The collision of Theia with the Earth, which is believed to have created the Moon.
Moons of Mars
Mars has two small moons: Phobos and Deimos. They were discovered by Asaph Hall in 1877. It is noteworthy that, having become disillusioned with the search for Martian satellites, he already wanted to give up observation, but his wife Angelina was able to convince him. The next night he discovered Deimos. Six nights later - Phobos. On Phobos, he discovered a gigantic crater that reaches ten kilometers in width - almost half the width of the satellite itself! Hall gave him Angelina's maiden name, Stickney.

Image of the satellites of Mars, respecting scales and distances.
Both satellites have a shape close to a triaxial ellipsoid. Because of their small size, gravity is not strong enough to compress them into a round shape.
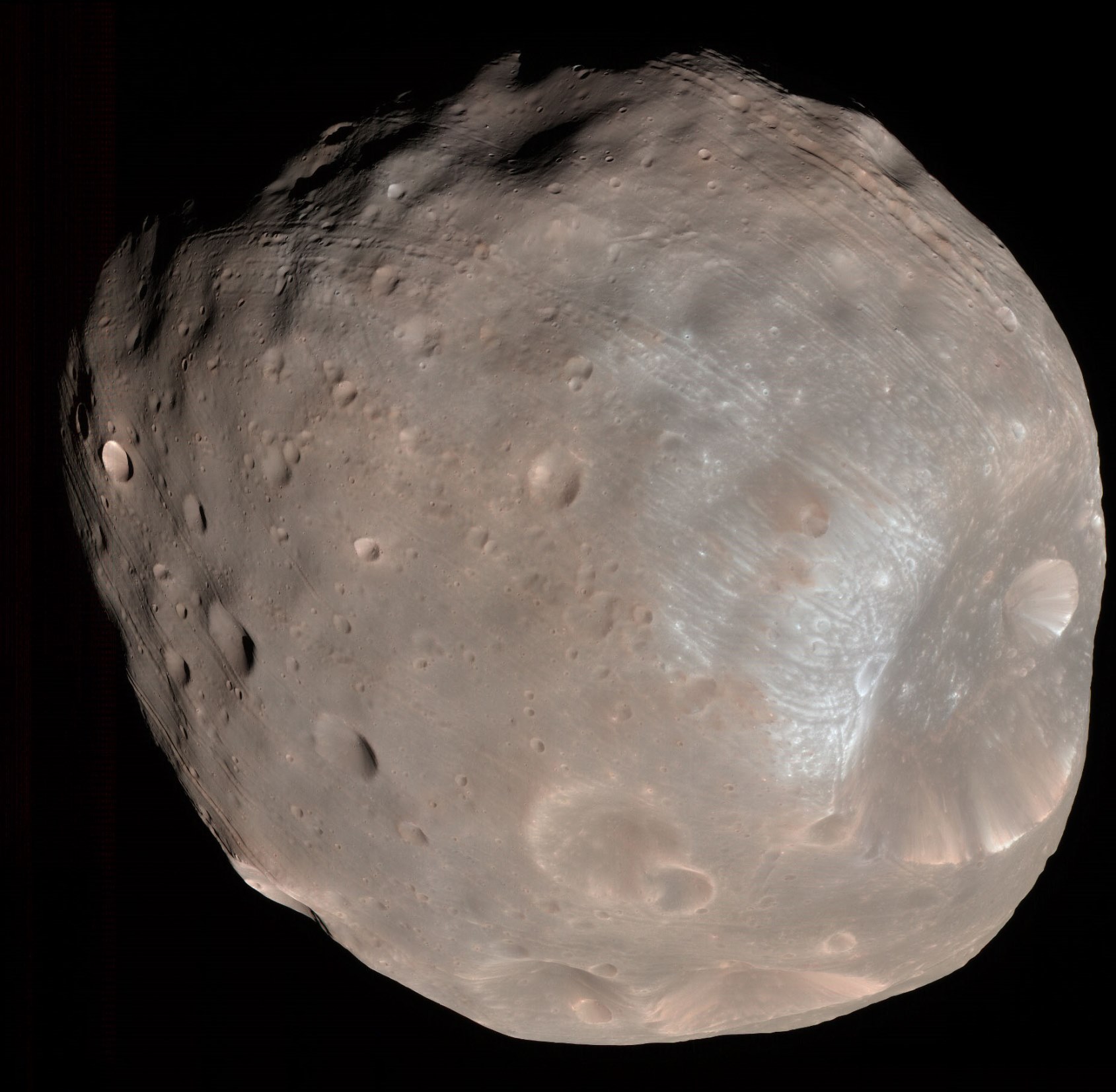

Phobos. Stickney Crater can be seen to the right.
Interestingly, the tidal influence of Mars gradually slows down the movement of Phobos, thereby reducing its orbit, which will ultimately lead to its fall onto Mars. Every hundred years, Phobos becomes nine centimeters closer to Mars, and in about eleven million years it will collapse on its surface, if the same forces do not destroy it even earlier. Deimos, on the contrary, is moving away from Mars, and over time will be captured by the tidal forces of the Sun. As a result, Mars will be left without satellites.
There is practically no attraction on the “Martian” side of Phobos, or rather, almost none. This is caused by the proximity of the satellite to the surface of Mars and the strong gravity from the planet. In other parts of the satellite, the gravitational force is different.
The satellites of Mars are always turned to the same side, since the period of revolution of each of them coincides with the corresponding period of revolution around Mars. In this regard, they are similar to the Moon, the far side of which is also never visible from the surface of the Earth.
The sizes of Deimos and Phobos are very small. For example, the radius of the Moon is 158 times greater than the radius of Phobos and approximately 290 times greater than the radius of Deimos.
The distances from the satellites to the planet are also insignificant: the Moon is at a distance of 384,000 km from the Earth, and Deimos and Phobos are 23,000 and 9,000 kilometers away from Mars, respectively.
The origin of Martian moons remains controversial. They could be asteroids captured by the gravitational field of Mars, but the difference in their structure from the objects of the group of asteroids of which they could be part speaks against this version. Others believe that they were formed as a result of the collapse of the satellite of Mars into two parts.
The next material will be devoted to the satellites of Jupiter, of which as many as 67 have been registered today! And perhaps there are life forms on some of them.
Planets of the Solar System. EARTH.
Our planet - the Earth - moves around the Sun in a close to circular orbit (eccentricity 0.017), the radius of which - 149.6 million km - is taken as 1 astronomical unit. The orbital period is 365.256 Earth days or 1 year. The average orbital speed is 29.8 km/s.
Planet Earth.
The period of rotation around the axis is sidereal day - 23h56m4.099s. The inclination of the earth's equator to the orbit is 23°27" and ensures the change of seasons. The mass of the Earth is M = 5.974 10 24 kg, the average density is 5.515 g/cm 3. The equatorial radius of the planet is R = 6,378 km. The Earth has a pear-shaped shape, called geoid. The compression is 0.0034 (the polar radius is R = 6,356 km). The oblateness of the Earth from the poles is explained by rotation. The acceleration of gravity on the surface is, on average, g = 9.78 m/s 2: at the poles it is greater by the equator is smaller.
Structure of the Earth
Direct exploration of the earth's depths is not yet possible: the deepest wells barely reach the ten-kilometer mark. However, seismology has provided clues to the internal structure of the Earth. The fact is that the speed of seismic waves depends on the density and elasticity of the rocks through which they pass. They are reflected and refracted at the boundaries between different layers. The structure of the earth's lithosphere was established from seismograms.
Thickness. Compound
Of the total mass of the Earth, the crust makes up less than 1%, the mantle - about 65%, the core - 34%. Near the Earth's surface, the increase in temperature with depth is approximately 20° per kilometer. Rock Density earth's crust is about 3000 kg/m3. At a depth of about 100 km, the temperature is approximately 1800 K. The lower, internal boundary between the crust and mantle is called the Mohorovicic section.
Elastic waves propagate in the mantle as in a solid. In the mantle, the speed of propagation of seismic waves increases abruptly, which is associated with a sharp increase in the density of the substance to 5600 kg/m 3. The next most intense reflection is observed at a depth of 2900 km (Wiechert-Gutenberg surface). At this depth, longitudinal and transverse seismic waves are strongly reflected. From this we can conclude that the liquid core lies below: transverse waves do not propagate in liquids. This layer of molten metal is called the outer core. At the center of the Earth there is a solid iron core with a density of about 10,000 kg/m 3 (1.7% of the Earth's mass). The border between them, about 5 km thick, runs at a distance of approximately 1220 km from the center.
Composition of the Earth by chemical elements.
On Earth, as a result of active volcanic activity, lava, steam and gases are emitted from the inner parts of the mantle and the upper part of the Earth, the crust, is still being formed. There are about 800 active volcanoes on the planet. The crust and upper layers of the mantle form the lithosphere. Its border is located at a depth of about 70 km. The lithosphere is split into a dozen large plates, at the boundaries between which earthquakes and volcanic eruptions constantly occur. Lithospheric plates“float” in a layer of increased fluidity located beneath them to a depth of 250 km, called the asthenosphere. The main components of the Earth's atmosphere are nitrogen and oxygen. The remaining gases: water vapor, carbon dioxide, neon, methane, hydrogen and others make up about 1%. Atmospheric pressure at sea level - 1 atm = 101325 Pa = 760 mm Hg. Art.
According to modern ideas, most of the craters abundantly covering the surface of the Moon were formed when large meteorites and small asteroids collided with the surface 3.5 billion years ago. The energy released during the explosion evaporated not only the substance of the meteorite, but also part of the rocks at the site of impact. Encounters with very large asteroids caused giant cracks in the lunar surface through which liquid molten lava flowed. This is how seas and oceans appeared on the Moon.
 Crater formation.
Crater formation.
The Italian astronomer Giovanni Riccioli in the 17th century assigned the names to the hills and depressions on the Moon: Alps, Apennines and Caucasus, Ocean of Storms, seas of Rain, Cold and Tranquility, craters Tycho, Pythagoras, Ptolemy, etc. At the suggestion of Soviet astronomers, the International Astronomical Union placed 18 names of newly discovered formations on the first map of the far side of the Moon. This is how the Sea of Moscow, the craters Hertz, Kurchatov, Lomonosov, Maxwell, Mendeleev, Sklodovskaya-Curie, and Tsiolkovsky appeared on the Moon. Of course, there are no seas on the Moon. The lunar seas are completely dry and represent vast lowlands that were once filled with basaltic lava. The moon is a lifeless body, devoid of atmosphere, seas and oceans. During the lunar day, the surface temperature can change by 300 degrees (from -170° C to +130° C). Under such conditions, water cannot exist in a liquid state.
Map of the surface of the Moon (view through a telescope). Another map of the Moon
In 1999, the Lunar Prospector spacecraft, on command from Earth, left its lunar orbit and crashed into a crater near the south pole. Before this, the satellite circled in orbit for almost 18 months and revealed some evidence of the presence of hydrogen, one of the components of water, above the crater. It has been suggested that there could be up to 300 million tons of ice on the Moon. It was believed that the impact would cause some of the water to evaporate and be thrown upward along with the dust. Scientists hoped that water vapor could then be detected using ground-based and space telescopes. But, unfortunately, no traces of water were found.
 A small step for one person is a huge step for all humanity. Neil Armstrong, first man on the moon. July 20, 1969.
A small step for one person is a huge step for all humanity. Neil Armstrong, first man on the moon. July 20, 1969.

This trace will remain on the Moon for millions of years.
Thanks to the research of the Luna spacecraft and the landings of American astronauts on the surface, the surface soil of the Moon has been well studied. The astronauts brought about 385 kg of moon rocks to Earth. The constant bombardment of the Moon by tiny meteorites is the reason that its entire surface, 9-12 meters deep, is covered with a layer of fine crushed sintered matter, which has formed a compacted spongy mass. This thin layer of the lunar surface is called regolith. Regolith is a good thermal insulation material, so even at a depth of several centimeters a constant temperature is maintained. None of the rocks brought to Earth were ever exposed to water or atmosphere or contained organic remains. The moon is an absolutely dead world. The far side of the Moon is ideal place for astronomical observations: it protects instruments from radiation from the Earth, and the night on the Moon lasts 14 Earth days. The absence of an atmosphere makes observations in any range possible. Someday space stations will be built on the Moon and astronomical observatories. Rich reserves of iron, aluminum and silicon would be a good source of building materials, and the hydrogen and oxygen contained in rocks would be raw materials for producing air and water.
Source of information: "Open Astronomy 2.5", LLC "PHYSICON"
