Comets, asteroids, meteors and meteorites. What are asteroids and what is known about them? Mysterious neighbors of the Sun
Asteroids? First of all, I would like to say that this is the name given to rocky solid bodies that move in elliptical orbits around the Sun, like planets. However, space asteroids are much smaller in size than the planets themselves. Their diameter is approximately within the following limits: from several tens of meters to a thousand kilometers.
Test your knowledge
With all the different space rocks flying to and from Earth last Friday, you may have been wondering about the correct terminology, since a rock from space has different names depending on what it's made of and where it's located.
This link should be sent to every mainstream media outlet and every film producer in Hollywood! So, if a meteoroid becomes a meteorite, then a meteorite, what do asteroids and comets do when they hit the earth? Do they keep their original names, or do they adopt meteor and then meteorite names? Maybe since they are so big, no one will leave them, so it doesn't matter. The term "meteoroid" is poorly defined here. It says the meteoroid is "smaller than an asteroid" and "less than a kilometer." In fact, an object in the 700 or 800 meter category definitely falls into the "asteroid" category. This is similar to what happened about how people react when an asteroid is heading towards the earth. It's based on science, but it's written funny. Participant. . Question 1.
When wondering what asteroids are, a person involuntarily thinks about where this term even came from and what it means. It is translated as “star-like,” and was introduced in the 18th century by an astronomer named William Herschel.
Comets and asteroids can be seen as point sources of a certain light, more or less bright. Although in the visible range, data does not emit anything - it only reflects the sunlight that falls on it. It should be noted that comets are different from asteroids. The first is their different appearance. The comet is easily recognized by its brightly glowing core and the tail that extends from it.
If you build Mars into the Garden of Eden, it will not be temporary, since Mars is not large enough to hold an atmosphere permanently. Answer: You are absolutely right. Mars is a small planet and therefore its gravitational field is not strong enough to maintain a dense atmosphere all the time, but it is enough to retain an atmosphere for thousands or millions of years, which is enough for us. Mars, there will be enough atmosphere to accommodate all our needs for future generations.
But this means that future generations, thousands of years from now, will have to replenish the atmosphere again. However, for our purposes this does not matter. Second question: Have you hit comets and asteroids on Mars causing a lot of destruction to the surface? Answer: We mentioned in the program that it would be possible to heat Mars with nuclear power plants, but this would be a very slow, expensive and possibly dangerous plan. A much faster plan would be to take comets and meteors to Mars. We also noted that if you aim the comet or meteorite carefully, you can control your orbit.
Most of asteroids that are known to astronomers today move between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars at a distance of approximately 2.2-3.2 AU. e. (that is, from the Sun. To date, scientists have discovered about 20 thousand asteroids. Only fifty percent of them are registered. What are registered asteroids? These are celestial bodies that have been assigned numbers, and sometimes even proper names. Their orbits have been calculated with very great accuracy. It should be noted that these celestial bodies usually have the names that were assigned to them by their discoverers. The names for asteroids are taken, as a rule, from ancient Greek mythology.
This means that you can lightly place a comet or meteor into the orbit of Mars, and then slowly descend to the surface as the orbit decays. This means that most of the comet or meteor will burn in the atmosphere and release water vapor. The point is that we can precisely target a comet or meteor so that we can minimize surface damage but maximize energy transfer, which is what we need to heat Mars.
Question 3: What is the time frame for terraforming Mars? A good guess is that by mid-century we will have our own astronauts on Mars. So, the first colonies will be established later in the 21st century. Terraforming did not begin until many decades after this. So we're talking about the mid-22nd century, before terraforming can be considered serious. But, as Carl Sagan liked to point out, we must become two species of the planet, because it is simply too dangerous to stake the future of humanity on one planet.

In general, from the above definition it becomes clear what asteroids are. However, what else is characteristic of them?
As a result of observations of these celestial bodies through a telescope, it was discovered interesting fact. The brightness of a large number of asteroids can change, and in a very short time - this takes several days, or even several hours. Scientists have long hypothesized that these changes in the brightness of asteroids are associated with their rotation. It should be noted that they are determined, first of all, by their irregular forms. And the first photographs that captured these celestial bodies (the photographs were taken with the help of this theory) confirmed this theory, and also showed the following: the surfaces of the asteroids are completely pitted with deep craters and craters of various sizes.
Next: How to deflect meteors and comets. Asteroids and comets are believed to be ancient remnants early years education of our solar system more than four billion years ago. From the very beginning of life on Earth to the recent spectacular impact of Comet Shoemaker-Levy 9 on Jupiter, these so-called "small bodies" have played key roles in many of the fundamental processes that have shaped the planetary environment in which we live.
Comets are bodies of ice, rock and organic compounds that can be several miles in diameter. Comets are believed to originate from a region beyond the orbits of the most distant planets. Scientists believe that gravitational disturbances periodically drive comets out of this population, setting these "dirty snowballs" on orbital courses that bring them closer to the Sun. Some, called long-period comets, are in elliptical orbits of the Sun that extend far beyond the planets and back.
![]()
The largest asteroid discovered in our solar system was previously considered to be the celestial body Ceres, whose dimensions were about 975 x 909 kilometers. But since 2006 it received a different status. And began to be called And the other two large asteroid(under the names Pallas and Vesta) have a diameter of 500 kilometers! Another interesting fact should also be noted. The fact is that Vesta is the only asteroid that can actually be observed with the naked eye.
Others, called short-period comets, travel over more short orbits closer to the Sun. When comets are exposed to more intense sunlight from the inner solar system, the ices in the comet's nucleus begin to evaporate and fall off. The released gas forms a thin atmosphere around the core, called a coma, while the dust previously in the core forms a tail thousands of miles long and can sometimes be seen from Earth. Believing that comets, as noted, on the early earths billions of years ago, caused major changes in the early oceans, atmosphere and climate of the Earth and may have delivered the first carbon molecules to our planet, triggering the process of the emergence of life.
Asteroids, comets, meteors, meteorites - astronomical objects that seem the same to those uninitiated in the basics of science celestial bodies. In fact, they differ in several ways. The properties that characterize asteroids and comets are quite easy to remember. They also have certain similarities: such objects are classified as small bodies and are often classified as space debris. What a meteor is, how it differs from an asteroid or comet, what their properties and origin are, will be discussed below.
Most asteroids are made of rock, but some are made of metal, mainly nickel and iron. They range in size from small boulders to objects hundreds of miles in diameter. A small part of the asteroid population may be burnt-out comets, whose lions evaporate and are blown into space. Almost all asteroids are part of the Main Asteroid Belt, with orbits in the vast region of space between Mars and Jupiter.
Some asteroids pass very close to the Earth's orbit around the Sun. Scientists have found evidence that asteroids hit our planet in the past. Typically, asteroids and small debris called meteoroids are too small to survive passage through Earth's atmosphere. As they burn up on their descent, they leave behind a beautiful trail of light known as a meteor or shooting star. However, large asteroids sometimes crash into Earth and create craters, such as Meteor Crater in Arizona near Flagstaff.
Tailed Wanderers
Comets are space objects consisting of frozen gases and rock. They originate in remote regions of the solar system. Modern scientists suggest that the main sources of comets are the interconnected Kuiper belt and the scattered disk, as well as the hypothetically existing
Comets have highly elongated orbits. As they approach the Sun, they form a coma and a tail. These elements consist of evaporating gases such as ammonia, methane), dust and stones. The head of a comet, or coma, is a shell of tiny particles, characterized by brightness and visibility. It has a spherical shape and reaches its maximum size when approaching the Sun at a distance of 1.5-2 astronomical units.
Another impact site off the coast of Mexico's Yucatan Peninsula, now buried by ocean sediment, is believed to be the event that led to the extinction of the dinosaurs 65 million years ago. Luckily for us, these large asteroid impacts are rare. A smaller rocky meteoroid or comet less than 100 yards in diameter is believed to have entered the atmosphere over the Tunguska region of Siberia. The resulting shock wave knocked down trees over hundreds of square miles.
The Earth and all the other planets and moons in our solar system have been constantly being bombarded by asteroids and comets since they formed - just look at the Moon's craters through a small telescope or a good pair of binoculars. Air Force, as well as decisions on how to improve the illumination of the sky as seen from the Southern Hemisphere.
At the front of the coma is the comet's nucleus. As a rule, it has a relatively small size and an elongated shape. At a significant distance from the Sun, the nucleus is all that remains of the comet. It consists of frozen gases and rocks.
Types of comets
The classification of these is based on the periodicity of their revolution around the star. Comets that orbit the Sun in less than 200 years are called short-period comets. Most often they fall into the inner regions of our planetary system from the Kuiper belt or scattered disk. Long-period comets are treated with a period of more than 200 years. Their “homeland” is the Oort cloud.
Detailed orbital data should be shared with other researchers within 24 hours of receipt, followed by an attempt to reach consensus on the object's long-term orbital path within 48 hours. The most dangerous asteroids, those capable of causing major regional or global disasters, are extremely rare.
The greatest risk comes from objects larger than half a mile to a mile that are large enough to disrupt the Earth's climate on a global scale by injecting large quantities dust into the stratosphere. Such an event could depress temperatures and the amount of surface sunlight around the globe, leading to loss of food crops and related problems. Ocean exposure can cause large ocean waves or tsunamis.
"Minor planets"
Asteroids are made of hard rock. They are much smaller in size than planets, although some representatives of these space objects have satellites. Most of the small planets, as they were called before, are concentrated in the Main Planet, located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.

Such global disasters are qualitatively different from other more common hazards that we face every day, given that these common events occur with much greater frequency but affect fewer people. No person should have to worry about being hit by a comet or asteroid. Daily threat to the average person from illness, automobile accidents, household accidents, and other natural Disasters much higher.
Mysterious neighbors of the Sun
It is very possible that we can divert a large asteroid or comet that may collide with the Earth from its orbit using existing technologies. The potential answer depends on the execution time. If we can predict the event at least 10 to 100 years in advance, then conventional missiles and explosives are likely to be adequate even for bodies half a mile in size. However, if we detect an object just a few years before impact, these technologies may not be sufficient.
Total number of similar cosmic bodies, known for 2015, exceeded 670 thousand. Despite such an impressive number, the contribution of asteroids to the mass of all objects in the Solar System is insignificant - only 3-3.6 * 10 21 kg. This is only 4% of the same parameter of the Moon.
Not all small bodies are classified as asteroids. The selection criterion is diameter. If it exceeds 30 m, then the object is classified as an asteroid. Bodies with smaller dimensions are called meteoroids.
Such a response would be coordinated within the United States by the Departments of Defense and Energy and would likely involve international partners. An international team of astronomers has discovered that this unusual object in the asteroid belt is essentially two asteroids orbiting each other, with cometary features. These include a bright halo of material called coma, and a long tail dust.
A strange comet-like asteroid first discovered more than a decade ago is even stranger than previously thought. Astronomers have discovered that it actually consists of two asteroids orbiting around it. Max Planck (Germany) says the pair represents the first known binary asteroid that can also be classified as a comet. 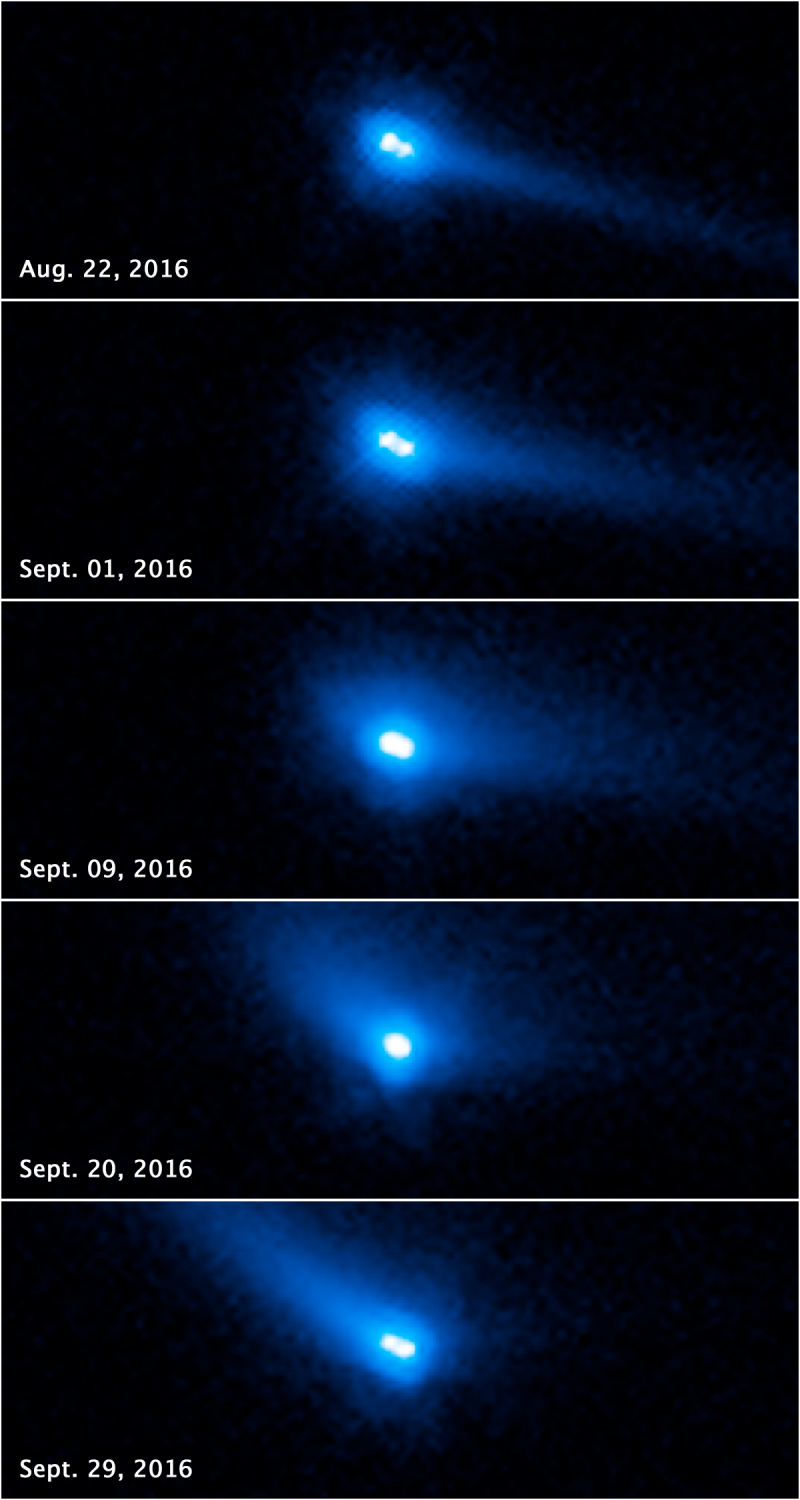
Agarwal.
Asteroid classification
The grouping of these cosmic bodies is based on several parameters. Asteroids are grouped together by the characteristics of their orbits and the spectrum of visible light that was reflected from their surface.
According to the second criterion, three main classes are distinguished:
- carbon (C);
- silicate (S);
- metal (M).
Approximately 75% of all asteroids known today belong to the first category. As equipment improves and more detailed research of such objects occurs, the classification expands.
Hubble images confirmed persistent activity in the binary system - with a bright comet-like coma of material surrounding the asteroids flowing into a long tail. The tail initially produced relatively large dust particles measuring one millimeter in size.
Its cometary properties are thought to result from an initial collision that exposes volatile elements previously buried deep inside. The authors found strong signs of sublimation water ice due to increased solar heating - similar to how the tails of comets are created.
Meteoroids
A meteoroid is another type of cosmic body. These are not asteroids, comets, meteors or meteorites. The peculiarity of these objects is their small size. Meteoroids are located between asteroids and cosmic dust in size. Thus, they include bodies with a diameter of less than 30 m. Some scientists define a meteoroid as a solid body with a diameter from 100 microns to 10 m. According to their origin, they are primary or secondary, that is, formed after the destruction of larger objects.
Understanding the origin and evolution of main-belt comets—including asteroids that behave like them—will help scientists understand how the solar system as a whole forms. The sightings also reveal information about his past. Surface ice cannot survive in the asteroid belt for the age of the solar system - but it can be protected for billions of years by a fire-resistant dust mantle just a few meters thick.
Its two components are members of a group of 11 asteroids believed to have been created by a massive object collapsing about 5 million years ago. Digital clock, just minutes before strike, represents a space mission to stop giant asteroids and a hero who saves humanity from a safe end. Sounds at least like the plan Hollywood dreamed of with Armageddon, but in reality: no chance!
As the meteoroid enters the Earth's atmosphere, it begins to glow. And here we are already approaching the answer to the question of what a meteor is.
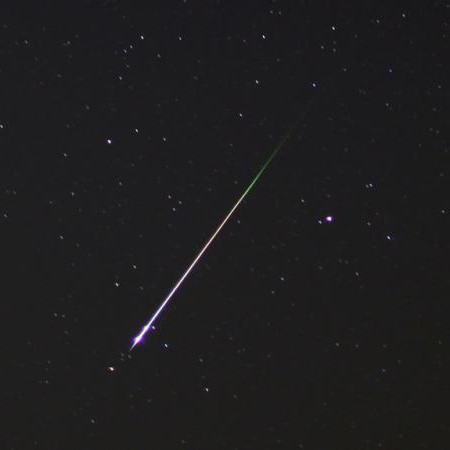
Falling star
Sometimes, among the flickering luminaries in the night sky, one suddenly flashes, describes a small arc and disappears. Anyone who has seen something like this at least once knows what a meteor is. These are “shooting stars” that have nothing to do with real stars. A meteor is actually an atmospheric phenomenon that occurs when small-sized objects (the same meteoroids) enter the air envelope of our planet. The observed brightness of the flare directly depends on the initial dimensions of the cosmic body. If the meteor's brilliance exceeds a fifth, it is called a fireball.
Observation
Such phenomena can only be admired from planets with an atmosphere. Meteors on the Moon or Mercury cannot be observed because they do not have an air envelope.
At suitable conditions"shooting stars" can be seen every night. The best place to view meteors is in good weather and at a considerable distance from a more or less powerful source of artificial lighting. Also, there should be no Moon in the sky. In this case, up to 5 meteors per hour can be seen with the naked eye. The objects that give rise to these single “shooting stars” revolve around the Sun in very different orbits. Therefore, it is impossible to accurately predict the place and time of their appearance in the sky.
Streams
Meteors, photos of which are also presented in the article, as a rule, have a slightly different origin. They are part of one of several swarms of small cosmic bodies rotating around the star along a certain trajectory. In their case, the ideal viewing period (the time when anyone can quickly figure out what a meteor is by looking at the sky) is pretty well defined.
A swarm of similar space objects is also called meteor shower. Most often they are formed during the destruction of the comet's nucleus. Individual particles of the swarm move parallel to each other. However, from the surface of the Earth, they appear to be coming from a specific small area of the sky. This section is usually called the radiant of the flow. The name of a meteor swarm is usually given by the constellation in which its visual center (radiant) is located, or by the name of the comet whose disintegration led to its appearance.
Meteors, photos of which are easy to obtain if you have special equipment, belong to such large showers as the Perseids, Quadrantids, eta Aquarids, Lyrids, and Geminids. In total, the existence of 64 streams has been recognized to date, and about 300 more are awaiting confirmation.
Heavenly stones
Meteorites, asteroids, meteors and comets are related concepts according to certain criteria. The first are space objects that fell to Earth. Most often, their source is asteroids, less often - comets. Meteorites carry invaluable data about various parts of the solar system beyond Earth.
Most of these bodies that hit our planet are very small in size. The most impressive meteorites in terms of their dimensions leave traces after impact that are quite noticeable even after millions of years. A well-known crater near the city of Winslow in Arizona. The fall of a meteorite in 1908 is believed to have caused the Tunguska phenomenon. 
Such large objects “visit” the Earth once every few million years. Most of the meteorites found are quite modest in size, but do not become less valuable for science.
According to scientists, such objects can tell a lot about the formation of the solar system. Presumably, they carry particles of the substance from which the young planets consisted. Some meteorites come to us from Mars or the Moon. Such space wanderers make it possible to learn something new about neighboring objects without the huge costs of distant expeditions.
To remember the differences between the objects described in the article, you can briefly outline the transformation of such bodies in space. An asteroid, consisting of solid rock, or a comet, which is a block of ice, when destroyed, gives rise to meteoroids, which, when entering the planet's atmosphere, burst into meteors, burn up in it, or fall, turning into meteorites. The latter enrich our knowledge of all the previous ones.
Meteorites, comets, meteors, as well as asteroids and meteoroids are participants in continuous cosmic motion. The study of these objects makes a great contribution to our understanding of the structure of the Universe. As equipment improves, astrophysicists are obtaining more and more data about such objects. The relatively recently completed mission of the Rosetta probe clearly demonstrated how much information can be obtained from a detailed study of such cosmic bodies.




