Antarctica: nature. Fauna and flora of Antarctica
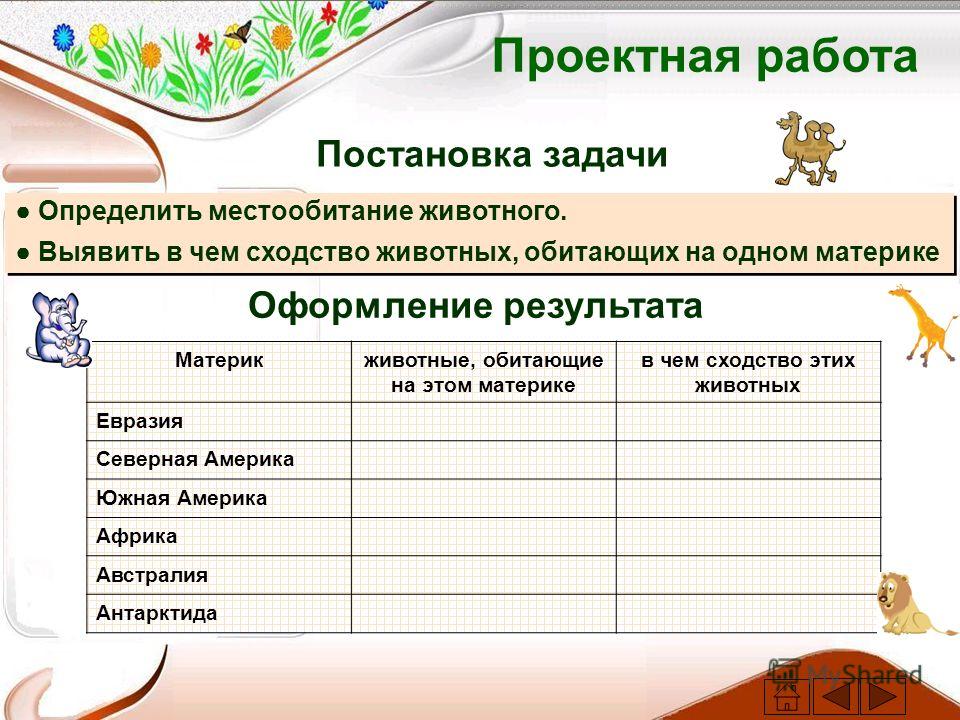
Continentanimals living on this continent, what are the similarities between these animals Eurasia North America South America Africa Australia Antarctica Project work Formalization of the result Statement of the problem Determine the habitat of the animal. Identify the similarities between animals living on the same continent. Determine the habitat of the animal. Identify the similarities between animals living on the same continent
Brown bear BROWN BEAR is a predatory mammal of the bear family. Body length 1.7–2.2 meters, weight 100–340 kg. The brown bear inhabits deciduous and coniferous forests of Eurasia and North America. These are tightly built animals, with an elongated facial region, small eyes and ears, a sloping back and short tail. The fur is thick, brown, of various shades. The paws are powerful, five-fingered, the claws are strong and strongly curved. The largest brown bears, found in the Russian Far East and Alaska, can reach 2.5 m in length and weigh up to 750 kg.

Brown bear Brown bears are active at any time of the day. In winter they fall into a shallow sleep. They make dens in holes, caves or thick dead wood. A bear's winter rest is not hibernation, since it maintains normal body temperature and, in case of danger, can immediately wake up and jump out of the shelter. They swim well and fish on sandbanks. Bears are good at climbing trees, destroying bee nests. They usually lead a solitary lifestyle. In addition to berries, roots, honey, insects, vertebrates, they can feed on carrion.

Red fox FOXES Found in Eurasia, North America, Africa, brought to Australia. Foxes have a squat body, a head with an elongated sharp muzzle, large pointed ears, eyes with vertical oval pupils. Body length up to 90 cm, tail up to 60 cm. In most cases, the back is bright red, the belly is white, sometimes black. It lives not only in forests, but also in the tundra, steppes, deserts and mountains. It settles in independently dug or abandoned holes, sometimes in hollows.

Red fox The fox's diet consists of rodents, mainly voles, hares, young ungulates, birds, various plants, fish, reptiles, and carrion. During the hunt, it exhibits very complex forms of behavior (it is no coincidence that in Russian folklore it is a symbol of cunning and intelligence). field hares ungulates reptiles

Boar BOAR Wild boar is widespread in North Africa(almost exterminated) and in Eurasia from Western Europe to the Far East. Acclimatized in several American countries. Length cm, weight kg. The head is large, wedge-shaped, extended forward. The ears are long and wide, the eyes are small, and the snout has a snout. The body is covered with elastic bristles, longer and denser in winter. On the back the bristles form a ridge. Color ranges from light brown to almost black. Striped piglets.

Wild boar Habitats are varied. Leads a herd lifestyle. Omnivorous. It feeds on rhizomes, tubers and roots of plants, fruits, nuts, berries, as well as green parts of plants, insects and small animals - mollusks, fish, rodents, insectivores, birds, etc.

Ussuri tiger One of the most ferocious predators Eurasia. The Ussuri tiger is one of the attractions of the Primorsky Territory. The Amur (Ussuri) tiger can be considered one of the largest and most beautiful representatives of the cat family. It stands out, first of all, for its large size (body length up to 2.4 m, tail up to 90 cm), as well as very fluffy, soft and relatively light-colored fur. The tiger lives alone and marks the boundaries of its territory with marks on trees. The tiger warns its rivals with a roar that can be heard within a radius of 3 km.

Amur tiger Body length 2–3 m, tail more than 1 m, weight 200–300 kg. Lives in the south of the Russian Far East, in Eastern China and on the Korean Peninsula. Its diet is based on wild boars and deer, as well as smaller animals. Can roam over distances of up to km. Currently, the number of Amur tigers living in natural conditions is about 400 individuals, the bulk of which are concentrated in Russia.


Giraffe GIRAFFE Lives in the savannas of Africa, south of the Sahara. The giraffe is the tallest animal in existence. Body length 3–4 m, height at the withers up to 3.7 m, height 5-6 m, weight kg. The giraffe has a relatively small head on a disproportionately long neck, a sloping back, long legs and a tongue (up to 40–45 cm). The giraffe has only seven cervical vertebrae and has small horns (sometimes 2 pairs) covered with black hair. The spotted color varies greatly. Capable of moving at speeds of up to 50 km/h, as well as jumping over obstacles and swimming well. Usually forms small herds (7-12 individuals), less often up to

Gorillas GORILLAS Gorillas live in western and central Africa. The largest of the apes. The body length of males reaches 180 cm, body weight 250 kg or more. The body of gorillas is massive, with a large belly; broad shoulders; the head is large, the eyes are widely spaced and deep-set; the nose is wide, the nostrils are surrounded by ridges; upper lip, short; the ears are small and pressed to the head; the face is naked, black. The gorilla's arms are long, with wide hands. The brush is used when collecting food. Legs are short. The coat is short, thick, black; adult males have a silver stripe on the back and a small beard. great apes

Raccoon Raccoon RACCOON Widespread in the forests of Central and North America. Medium-sized animal (body length up to 60 cm, tail up to 25 cm). The body is stocky, on short legs, with long mobile toes. The head is wide, with a short thin muzzle and large ears. The fur is thick, long, brownish-gray. The muzzle has a characteristic black mask with white trim. The tail has 5-7 wide black or white rings. It makes its homes in hollows and rock crevices. It feeds on amphibians, crayfish, fish, rodents, as well as berries, fruits, and nuts. Before eating prey, it rinses it in water (hence the name).

Skunk An amazing animal lives in North America - the skunk. Its jet-black fur is colored with two wide white stripes leading to its bushy tail. When moving in search of food, the skunk often holds its tail vertically, which is why it is visible from afar. However, predators are in no hurry to attack him. The fact is that in defense, the skunk sprays a sharp-smelling liquid at the offender, which causes an attack of dizziness and nausea.

Giant anteater In pampas, bushland and sparse forests South America There is an amazing animal - a giant anteater. It is distinguished by a narrow and slender body with an elongated, tube-shaped head. Long claws grow on the second and third fingers of the anteater's front paws. With their help, he destroys the strong walls of termite mounds or digs up anthills. After this, the anteater squeezes its narrow head into the crack and licks the insects, using a long tongue covered with sticky saliva.

Anaconda B tropical forests South America is home to the largest snake - the anaconda. Its average length ranges from 5 to 6 meters, although individual specimens can reach 10 and even 11 meters in length. Anaconda inhabits quiet river backwaters and small channels in the Amazon and Orinoco river basins. It swims well and can stay under water for a long time. Hiding at the bottom, the anaconda hunts from behind gardens, lying in wait for small ungulates, waterfowl and young caimans. She waits out the dry season by burying herself in the bottom silt and falling into torpor.

Koala The koala, or marsupial bear, lives in the forests of Eastern Australia. The koala spends most of its time in the crown of trees, eating eucalyptus leaves. He doesn't eat anything other than them. He descends to the ground only to move from one tree to another. Europeans first learned about it in 1880, when the London Zoo bought a live animal. Because of its thick and beautiful fur, an uncontrolled hunt began for the koala. As a result, by the beginning of the twentieth century it was on the verge of extinction. The Australian government passed a law banning hunting and creating a network of nature reserves to protect it.

Kangaroo The giant gray kangaroo lives in the equalips savannas of Eastern Australia. This is the largest modern marsupial, reaching 1.5 meters in height. Fleeing from danger, the gray kangaroo makes 9-meter jumps. The kangaroo is a true symbol of Australia. It is not for nothing that he and the emu were placed on the coat of arms of this country.

Emperor Penguin The largest penguin found in Antarctica is the Emperor Penguin. It was discovered by the outstanding Russian navigator, Admiral Farad Bellingshausen during a trip to Antarctica. Huge colonies of emperor penguins are located under the protection of cliffs near areas of open sea. Interestingly, emperor penguins hatch their chicks in the midst of the harsh Antarctic winter. In severe frosts, penguins gather in close groups, preventing the chicks and each other from freezing.

Australia is a continent that for a long time was in complete isolation from the rest of the world. During this time, the continent managed to form favorable for those living here living beings ecosystem.
Australia is famous for its unusual flora and fauna, after all most of of these are endemic (animals and plants that exist only on one continent).
Lives on the mainland about 12 thousand species of living beings, of which almost 9 thousand are endemic. Thanks to such unique flora and fauna, Australia is recognized as a continental reserve.
Representatives of the animal world
The most popular representatives are in the following video:
Which ones live only in this country?

Marsupial mammals: why are they found only here?
In Australia, marsupial mammals outnumber placental group of animals. However, in the rest of the world the opposite is true; placental animals have great advantages over their rivals, marsupials.
Thanks to the isolation of the mainland and years of evolution, marsupials became the main representatives of the animal world of Australia and occupied this position for quite a long time.
The situation began to change with the advent of civilization; the appearance of people and introduced animals reduced the population of marsupials. Due to the invasion human factor
a large number of marsupial species disappeared from the face of the Earth. Currently marsupials animals are under special protection and live in special reserves and national parks.
Megacities of Australia: description largest cities countries in our next.
Who else is around here?

This is one of the most mysterious and little-studied continents on our planet. Antarctica was discovered by two brave researchers - M. Lazarev and F. Bellingshausen. Their expedition confirmed the presence of Antarctica in the south of the globe. This happened in 1820.
Climatic conditions
The nature of Antarctica has the coldest climate on earth. In 1983, the absolute minimum was officially recorded - minus 89.2 degrees. In winter, temperatures range from -60 to -75 degrees. In summer it rises to -50. And only on the coast the climate is milder: the average temperature ranges from 0 to -20 degrees.

Precipitation is possible only in the form of snow, which is compressed under its own weight, forming new layers of ice.
However, Antarctica has rivers and lakes. They appear in the summer, and in the winter they are again covered with an ice crust. Today, scientists have discovered 140 subglacial lakes. Of these, only one does not freeze - Vostok.
Flora of Antarctica
The flora of the continent is extremely poor. The natural features of Antarctica are explained by its harsh climate. Most of all algae grow here - about 700 species. The ice-free plains and coast of the mainland are covered with lichens and mosses. Flowering plants on this harsh land there are only two - the Quito colobanthus and the Antarctic meadowsweet.
Colobanthus quito belongs to the carnation family. It is a low, cushion-shaped herbaceous plant with small pale yellow and white flowers. The height of an adult plant does not exceed five 5 centimeters.
Antarctic meadow grass is a cereal plant. It grows only in areas of the earth illuminated by the sun. These inconspicuous bushes grow up to 20 centimeters. The plant tolerates frost well. Even during flowering it is not harmed by frost.
The flora of Antarctica, represented by a few plants, has adapted to the eternal cold. Their cells contain little water, all processes are slow.
Animals
The natural features of Antarctica have left their mark on the fauna of the continent. The animals of this icy country live only where there is vegetation. Despite the harsh climate, dinosaurs lived in Antarctica in ancient times.
 Antarctic animals can be divided into two independent groups- water and land. It should be noted that there are no animals permanently living on land in Antarctica.
Antarctic animals can be divided into two independent groups- water and land. It should be noted that there are no animals permanently living on land in Antarctica.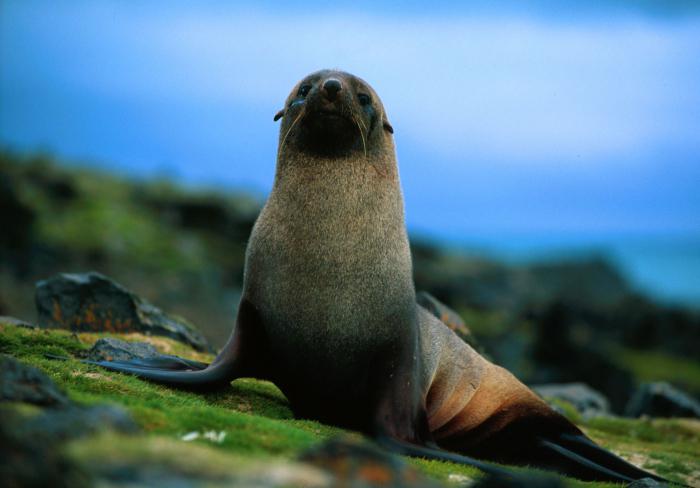 
The waters surrounding the mainland are rich in zooplankton, which is the main food for seals, whales, penguins and fur seals. Ice fish live here - amazing creatures that have adapted to existence in icy water.
Large animals of Antarctica include which attract large numbers of shrimp.
Blue-green algae and roundworms live in fresh lakes, and crustaceans and daphnia are found.
Birds
Antarctica is home to penguins, Arctic terns and skuas. The nature of the mainland does not allow living here more birds There are four species of penguins living in Antarctica. The largest population is imperial. Occasionally, petrels fly to the southern continent.
Mammals
Antarctica, whose nature is too harsh for animals to live in, can only boast of those species that are able to live both on land and in water. First of all, these are seals. In addition, leopard seals live on the coast and there are small sand or black and white dolphins, which whalers call
Predators of Antarctica
This continent is home to a wide variety of predators. Their diet mainly consists of planktonic crustaceans. Of these, it is necessary to highlight the leopard seal - the largest seal that feeds on krill. It lives at shallow depths. At the same time, it also has the reputation of a predator, which is capable of hunting large animals. Such hunting, however, is only seasonal and is intended to diversify the diet, which consists of squid and fish, but its basis is krill. A small number of these sea predators stays close to rookeries and penguin colonies. In most cases, these giants drift on ice floes along the peninsula and by the beginning of winter they gather in large numbers near South Georgia.
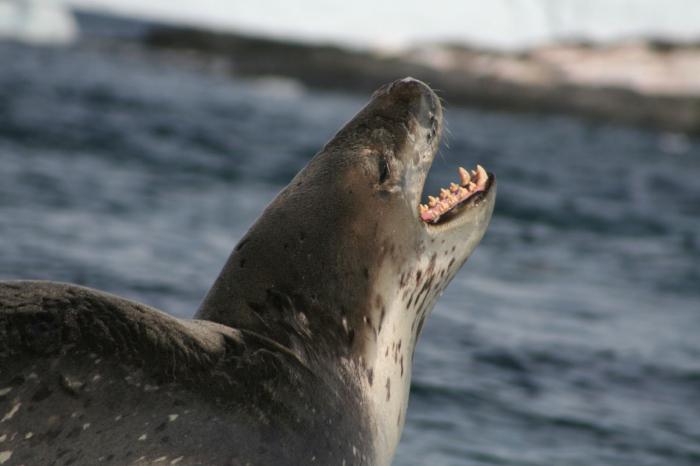

Leopard seals are real giants. The officially registered length is 3.8 meters, but larger animals have been encountered.
By autumn, leopards change their lifestyle and come close to the shore, along which inexperienced young fur seals and penguins descend.
Invertebrates
For whom the nature of Antarctica is completely suitable, it is invertebrate arthropods. Antarctica is home to 67 species of ticks and four species of lice. There are lice eaters, fleas and, of course, mosquitoes here. It should be noted that wingless ringing mosquitoes, which have a jet-black color, live only on the icy continent. These insects are endemic and belong to completely land animals.
The bulk of invertebrates and insects were brought to the southern continent by birds.
Tourism
Despite the harsh climate, about six thousand tourists come to Antarctica every year. Most of them go to the Antarctic Peninsula, where there is an airfield and a tourist base. In the 1990s, tourists began to visit the Ross Sea.
