Animals with small ears. The cutest wild animals
Ecology
According to scientists, eyes evolved about 540 million years ago as a common organ for detecting light. Today, vision is extremely important for many animals, including humans, and it has become very complex and diverse.
Take a look at some of the strangest and most incredible eyes in the animal kingdom.
12. Mountain goat
We all know that pupils are round, because round pupils are what we see most often (in humans), but this cannot be attributed to goats (and most other animals with hooves), which have horizontal slits that take on a rectangular shape when expanded. form. This gives goats the ability to see 320-340 degrees around them, meaning they can see almost everything around them without having to turn their head (for comparison, a person can see 160-210 degrees).
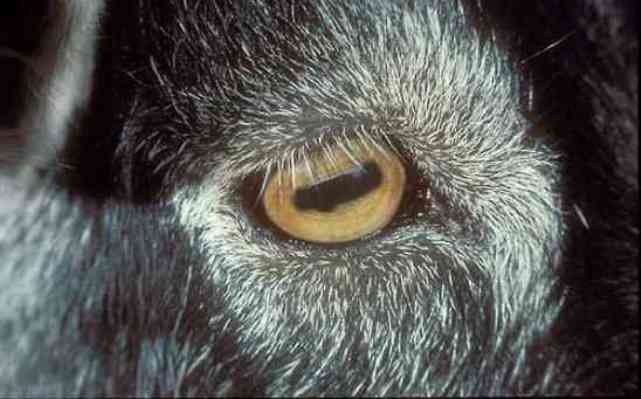
Consequently, animals with rectangular eyes can see better at night due to the presence of large pupils, which are very narrow during the day as they close to limit the access of light. Interestingly, octopuses also have rectangular pupils.

11. Trilobites
Trilobites were one of the most successful animal groups of all time, thriving for nearly 300 million years, long before dinosaurs inhabited the Earth. Although some species were eyeless, most had compound eyes similar to those of insects.
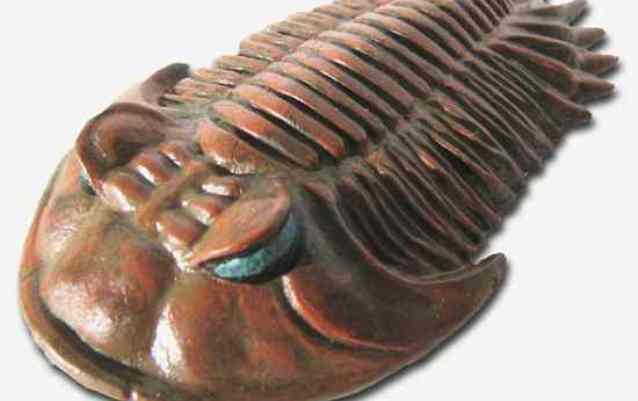

A strange fact about trilobite eyes is that the shell of their eyes was made of inorganic crystals of calcite (a mineral that is the main component of limestone and chalk). In its pure form, calcite is transparent, which is quite suitable as a material for the eye lens.
These crystal eyes are a unique feature of trilobites because the eyes of modern invertebrates are composed of the organic substance chitin. Due to their unusual composition, trilobite eyes were very stiff and unable to focus on anything; instead, trilobites adjusted focus using an internal eye mechanism, which not only resolved any potential problems associated with the mineral lens, but also gave the trilobites such good vision that they could keep both distant and near objects in focus at the same time.
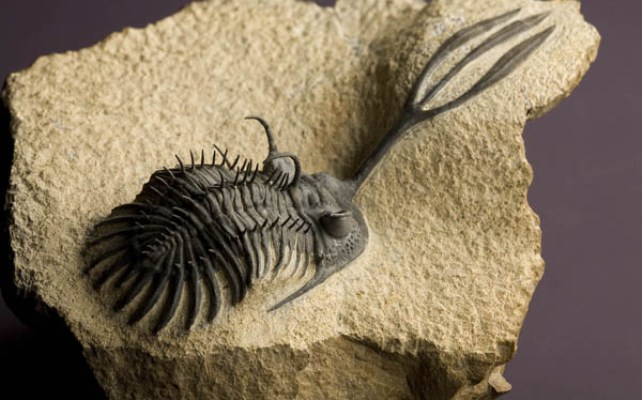

If this didn't seem strange enough, some trilobites had eyes at the end of elongated eyelids, while others had eyes that were like overhanging "bandages" that protected them from bright sunlight. Because the surface of their eyes was made of calcite, the fossils are very well preserved, so more is known about the vision of trilobites than about any other historical creature in general.
10. Tarsiers
The tarsier is a small (squirrel-sized) nocturnal primate that lives in tropical forests South-East Asia. It is the only exclusively carnivorous primate in the world, feeding on lizards and insects. There are even cases where they catch birds during their flight. Their most remarkable feature is undoubtedly their huge eyes, which are the largest of all mammals in relation to body size.
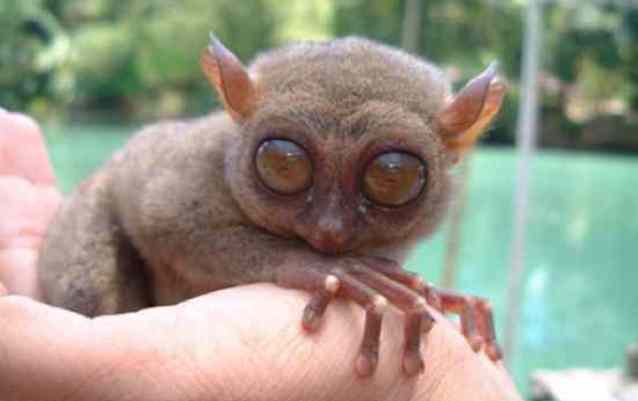

If human eyes were the same proportions as tarsier eyes, they would be the size of grapefruits. These huge eyes sit deep in the skull and cannot rotate in their sockets. To compensate for this, tarsiers have very flexible necks and can rotate their heads 180 degrees, much like an owl, in search of potential prey.
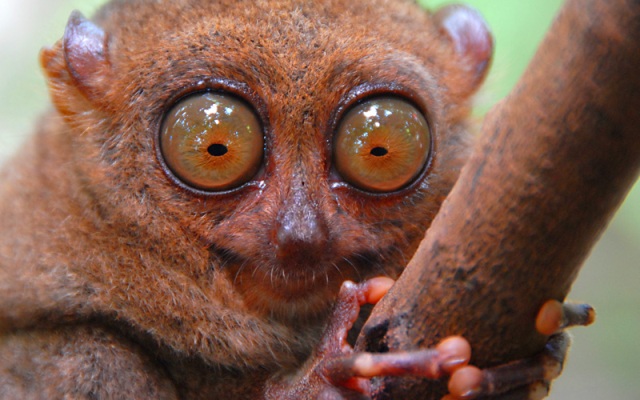

Each eye weighs more than the entire brain, and this animal's vision is very sharp. Moreover, tarsiers have excellent night vision, suggesting that they can even see ultraviolet light. On the other hand, they appear to have very poorly developed color vision, as is the case with many nocturnal animals (including domestic cats and owls).
9. Unique animal chameleon
The chameleon is known for its ability to change color. This helps it communicate and demonstrate its intentions and moods to other chameleons (only a few species use color changes for camouflage). These lizards also have very unusual eyes, their eyelids merge and cover almost the entire eyeball, except for a small hole through which the pupil can see.
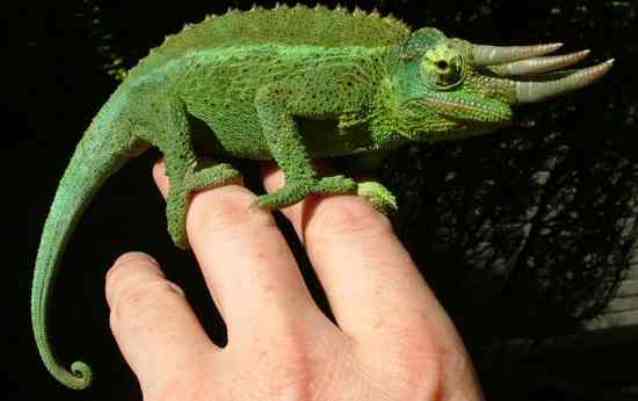

Each eye can move independently of the other, so the chameleon can simultaneously scan for prey and potential threats. This also suggests that the chameleon has a 360-degree field of view.

When a chameleon sees a potential prey (usually insects, although the largest species feed on mice and other small vertebrates), both eyes are aimed at it, thus achieving the effect of stereoscopic vision, which is very important in this context, considering that The chameleon captures prey by "firing" its tongue at high speed, a technique that requires precision in distance and depth perception. Chameleons have very keen eyesight, being able to see an insect from several meters away, and like tarsiers, they can see ultraviolet rays.
8. Amazing insect dragonfly
The dragonfly, which is arguably the most fearsome aerial hunter among insects, also has some of the most amazing eyes in the animal kingdom. They are so large that they cover almost the entire head, giving it the appearance of a helmet, and giving a 360-degree view.
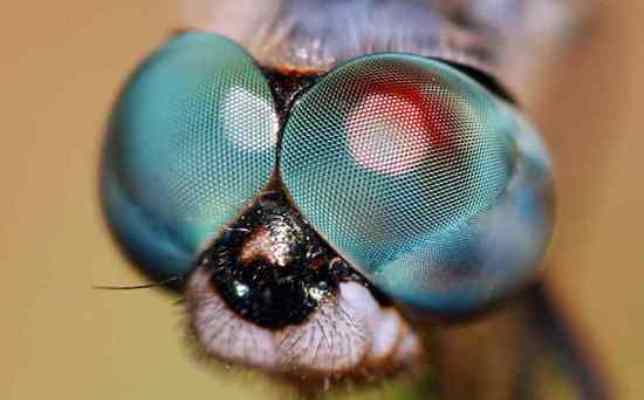

These eyes are made up of 30,000 visual elements called ommatidia, each of which contains a lens and a number of light-sensitive cells. Their vision is excellent, they can distinguish a wide range of colors and polarized light, they are especially sensitive to movement, so they can quickly recognize any potential prey or enemy.
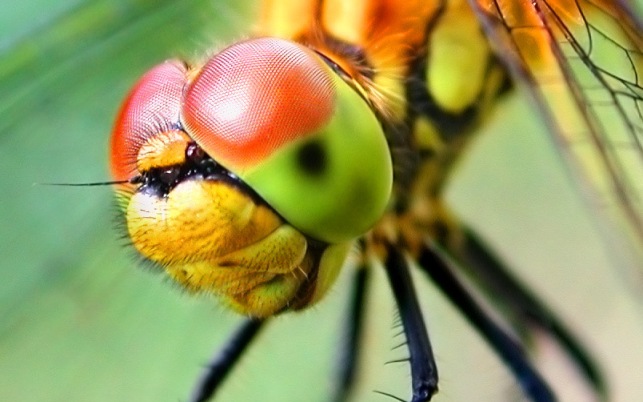

Some species of dragonflies that "hunt" at dusk have perfect vision in low light conditions, while we humans are barely able to see anything. Moreover, the dragonfly has three small eyes that can detect movement even faster than the big ones. These ocelli quickly send visual information to the dragonfly's central nervous system, allowing it to react in a fraction of a second.
Perhaps it is thanks to this feature that the origin of the unique acrobatic skills of insects can be explained. Although dragonflies are not the only insects with extra small eyes (some wasps and flies also have them), dragonflies have the most developed eyes.
7. Leaf-tailed gecko
The Satanic gecko (its second name) has rather surreal-looking eyes, their pupils are vertical and have a series of holes that widen at night, allowing these lizards to take in as much light as possible. The eyes also have many more light-sensitive cells than the human eye, giving animals the ability to detect objects and even see colors at night.
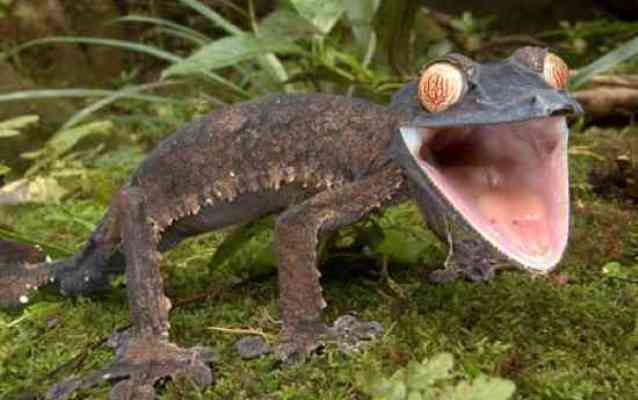

To give you an idea of just how amazing the gecko's night vision really is, it's simply worth noting that while cats and sharks can see six and ten times better than humans, leaf-tailed geckos and other nocturnal gecko species can see up to 350 times better than we can. dim light.
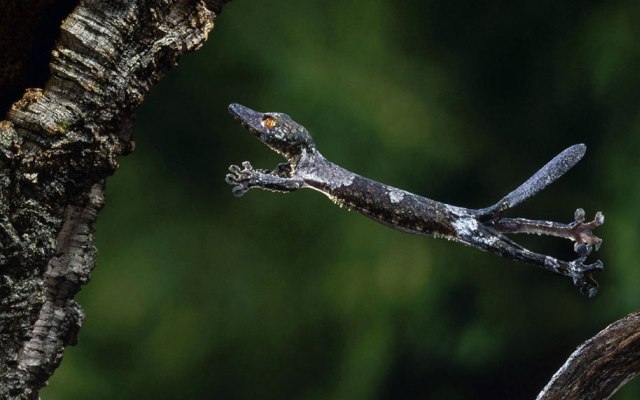

These animals also have strange, intricate patterns on their eyes that provide them with camouflage. These lizards have eyelids and their eyes are protected by a transparent membrane, which geckos clean with their tongue.
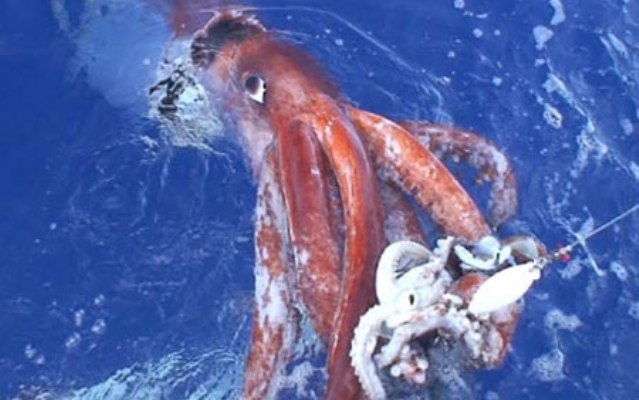
6. Colossal squid
Not to be confused with the better known but smaller giant squid. The colossal squid is the largest invertebrate known to science, and it also has some of the largest eyes in the animal kingdom. Each squid eye reaches a diameter of up to 30 cm, it can be larger than a plate, and the lens of its eye is the size of an orange. These huge eyes allow the squid to see in dim light, which is very useful for an animal that spends most his life hunting at depths of more than 2000 meters.
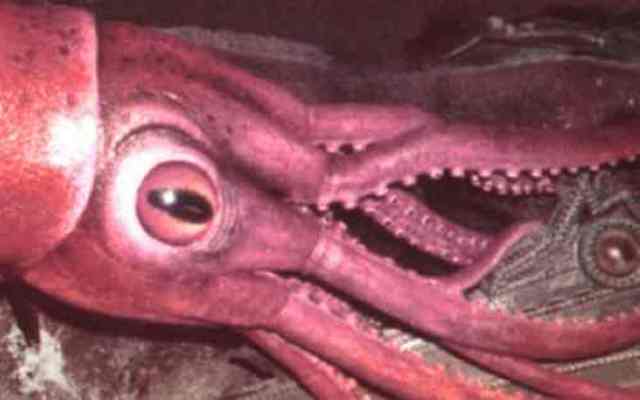

It should be noted that so far only juvenile colossal squid have been caught, but an adult can grow up to 15 meters in length. These giants have even bigger eyes. Unlike the giant squid, the colossal squid has stereoscopic vision, and has an excellent ability to accurately judge distances. An even more amazing feature is that each eye has a built-in "headlamp", an organ that can produce as much light as the squid needs to see its prey in the dark.

4. Four-eyed fish
Found in Mexico, Central America and South America, this fish, measuring up to 32 cm, usually lives in fresh or salt water (although it has been spotted on sea coasts on several occasions). It feeds mainly on insects, so it spends most of its time swimming near the surface.

Despite its name, the four-eyed fish actually has two eyes, each separated by a piece of flesh, with all four "parts" possessing their own pupils. This strange “device” allows the four-eyed fish to see perfectly both above and below the waterline, scanning for prey and predators.

The upper half of the eyeball is adapted for seeing in the air, while the lower half is designed for underwater vision. Although both halves of the eye use the same lens, the thickness of the shell is different in the upper and lower parts, therefore the behavior of the fish in the air and in the water is different.
This means that when the fish's four eyes are completely submerged in water, the upper halves of the eyes are out of focus. Fortunately, the fish spends most of its life at the surface of the water, and dives very rarely only for the purpose of protecting the upper halves of the eyes from dehydration.
4. Stem-eyed fly
These small but fascinating creatures are most often found in the jungles of Southeast Asia and Africa, however there are some species that are found in Europe and North America. They get their name from the long, stem-like structures located on the sides of the head, at the ends of which are the eyes.
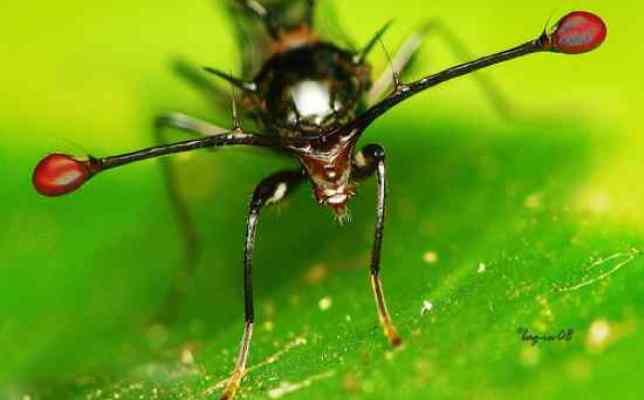

Male flies, as a rule, have longer and larger stalks than female flies. In turn, females prefer males with the longest eyestalks. Males often stand facing each other during the mating season and compare their stems; the winner is the one with the longest stem.

Moreover, the male stalk-eyed fly has extraordinary abilities that help him increase the size of his eyes and stalks: they swallow air through the mouth and “push” it through the ducts into the eyestalks. They mostly do this during mating season.
3. Dolichopteryx longipes
This is a deep-sea fish that has one of the strangest eye structures known to science. Each eye has a side swelling called a diverticulum, which is separated from the main eye by a septum. While the main part of the eye has a membrane and functions that are similar to those of the eyes of other animals, the diverticulum has a curved composite "mirror" consisting of several layers of crystals.
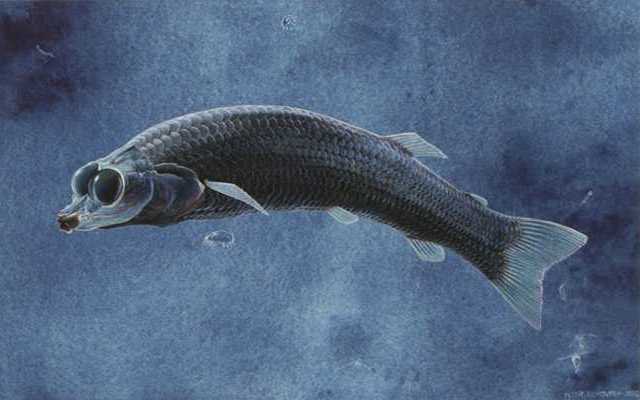

This "mirror" collects much more light than the normal eye. The diverticulum reflects light and focuses it on the retina, allowing the fish to see both above and below at the same time.

This fish is the only known vertebrate that uses the mirror structure of the eye to simply see, much like a normal lens. It can be found in different parts of the world, but it is extremely rare to see it, because the fish spends most of its life at a depth of 1000-2000 meters. They feed on small crustaceans and plankton, and their body length is about 18 cm.
2. Spiders are ogres
These spiders are widely known for having a large number of eyes (although the number varies greatly among different species, ranging from 2 to 8). The Spider-Face Ogre has six eyes, but it looks like he only has two because the middle pair is significantly larger than all the others.
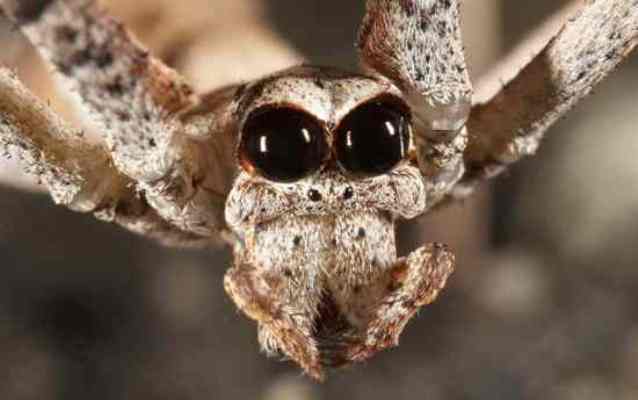

All this is created for the convenience of a nightlife lifestyle. With a slightly scary-looking face, spiders have excellent night vision not only thanks to their eyes, but also due to the presence of a layer of extremely sensitive cells covering them.

This membrane is so sensitive that at dawn it destroys itself, and at night a new one appears. This spider's face is unusual because it can see perfectly at night, but it lacks the reflective membrane that helps other spiders (and other predators) see in low light conditions. In fact, scientists believe that this spider actually has night vision that is better than that of a cat, shark, and even an owl (which can see up to 100 times at night better than man).
1. Crayfish are mantises
And finally, we come to the animal that has the strangest and most amazing eyes in the world. Crayfish - mantises - are not shrimp, but arthropods belonging to another species of crustaceans from the order Stomatopods. They are known for their aggressiveness and formidable weapons (they have very powerful and sharp claws that can easily cut a human finger or even break an aquarium glass with one blow). Mantis crayfish are voracious predators that live mainly in tropical waters.
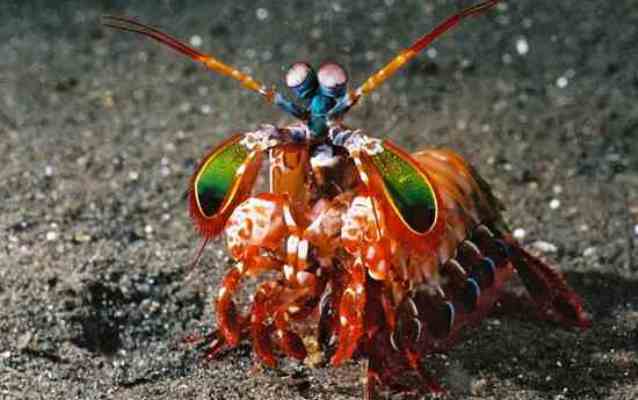

Their eyes are very complex in structure, but similar to the eyes of a dragonfly. They also have ommatidia (about 10,000 per eye), however, in mantis crayfish, each specific part of the ommatidia has a specific function. For example, some of them are used to detect light, others to detect color, etc. Mantis crayfish have much better developed color vision than humans; their eyes have 12 types of color receptors, while humans have only 3.
Moreover, they have ultraviolet, infrared and polarized vision, making their vision the most complex of all animals. The eyes are located at the end of a special stalk and can move independently of each other, rotating 70 degrees. Interestingly, visual information is processed by the eyes themselves, and not by the brain.

Even stranger is the fact that each eye of the mantis crayfish is divided into three parts, allowing the arthropod to see objects from three different perspectives of the same eye. In other words, each eye has "trinocular vision" and full depth perception, meaning that if a cancer loses an eye, the remaining eye will still be able to judge depth and distance as clearly as a person can with their two eyes.
Scientists are just beginning to understand the secrets of vision, similar to that of the crab, the mantis, so this moment we can only imagine how this creature sees the world.
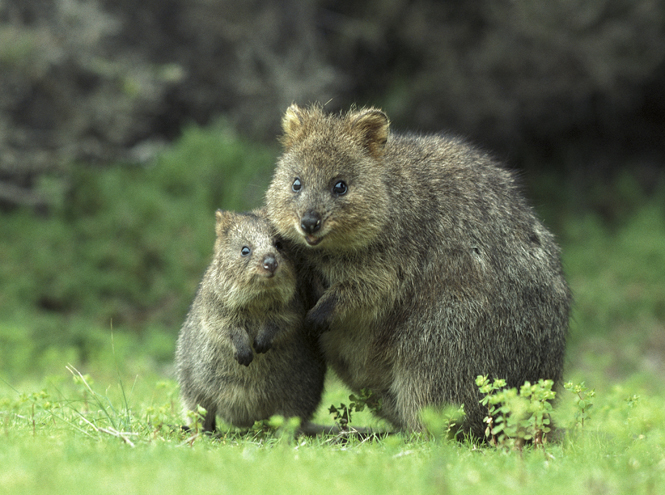

This touching animal is a real smiley marsupial! His face looks as if a quokka is smiling all the time. A miracle of nature lives in Australia, which, as you know, is generally rich in marsupials. And if kangaroos used to be very popular in this country, now the quokka has won the palm. It's all about her love... for selfies. Quokka is an extremely friendly animal, is absolutely not afraid of people and is happy to be photographed with the most modern gadgets. And one of the quokkas was even presented to the Duchess of Cambridge and her husband during their official visit to Australia. Kate even fed the smiling animal some grass.
Externally, the quokka is very similar to the kangaroo. In terms of size, it is not very large. It can be compared to a domestic cat or a small dog. It has a brown-gray color, thick and short fur, a long tail. Like all marsupials, the quokka prefers to eat leaves and grass, and live in the shade of trees, closer to moisture.
Bearded Tamarin (Emperor Tamarin)
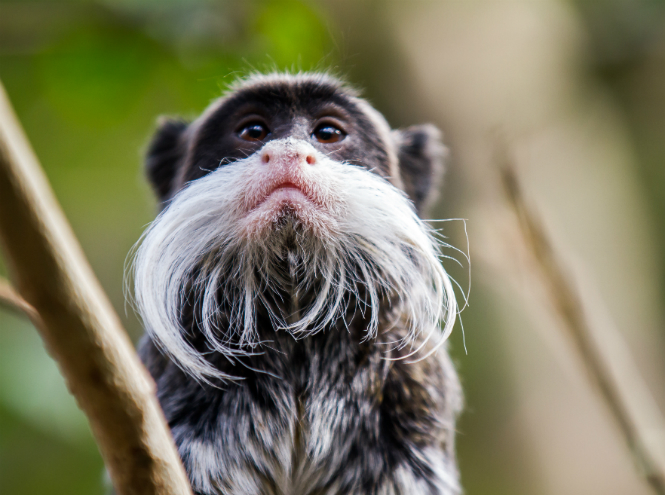
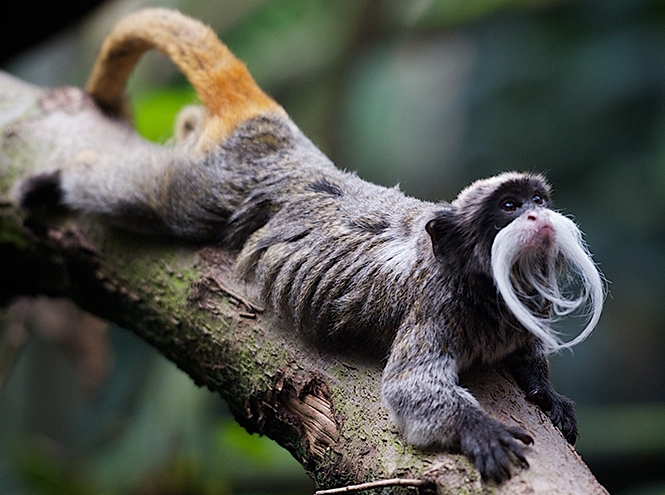


The tamarin is not just bearded, but also imperial. This species of monkey owes its name to its resemblance to the Emperor of Germany and the King of Prussia, William II. It wasn't that they were indistinguishable, but the noble mustaches were at least practically identical. The jungle emperors live in the wilds of the Amazon - they prefer to hide in impenetrable thickets, probably to rule the world on the sly.
By the way, the main ones in the family of tamarins are females - nature also does not deprive them of mustaches, and sometimes the gray beards of females look much more impressive than those of males. As for the territories, here the bearded monkeys show their regal disposition. One small group lives on an area of thirty or even forty hectares. All strangers are certainly expelled. However, imperial tamarins tolerate the proximity of tamarins of other species. Sometimes these South American monkeys even rally against common enemies. And it’s better not to encounter an angry imperial tamarin, because, despite their tiny size, these bearded monkeys have sharp claws, large fangs and desperate courage. The tamarin will fight to the last for its cubs.
Fennec fox
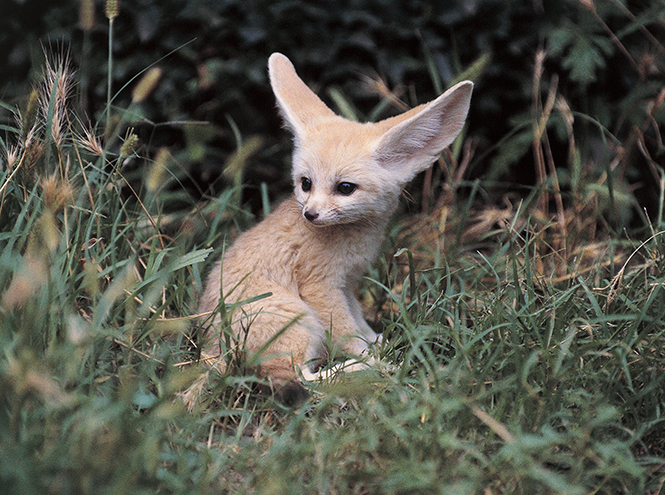
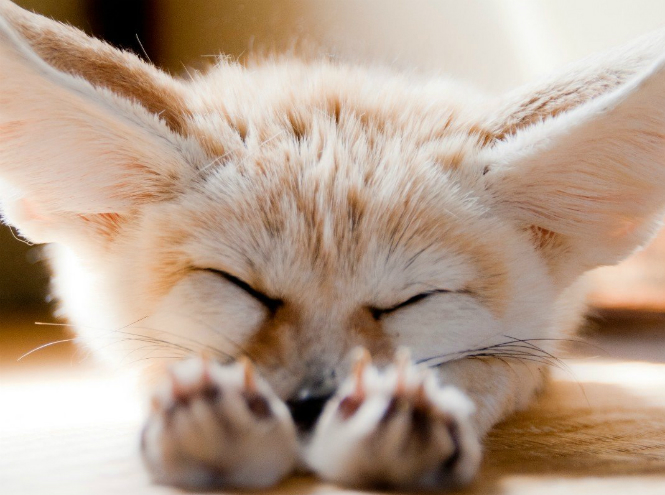


The fennec fox is a tiny animal with huge ears and a sharp, cute face. In fact, representatives of the canid family simply do not exist in the world smaller than the fennec. wildlife. At the same time, it turned out that this little fox gets along well with humans. can be tamed, and if desired, the fennec can even be taught standard commands. For example, like in this video:
The fennec mainly lives in the Sahara Desert - big ears help him cope with the heat, and also contribute to a successful hunt. With such locators, the fox catches the slightest rustle of its intended prey - the fennec feeds on insects and small vertebrates. This animal, it turns out, is completely incapable of a solitary existence - tiny foxes live in large families, in which there is always a ruling couple, which is almost impossible to overthrow from the throne.
Common Dormouse
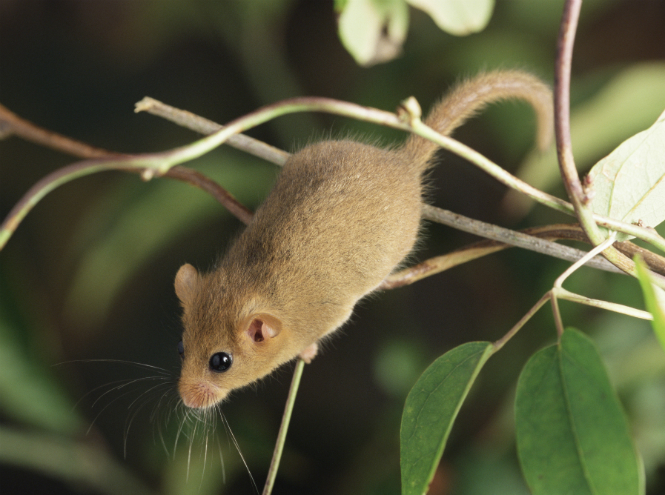
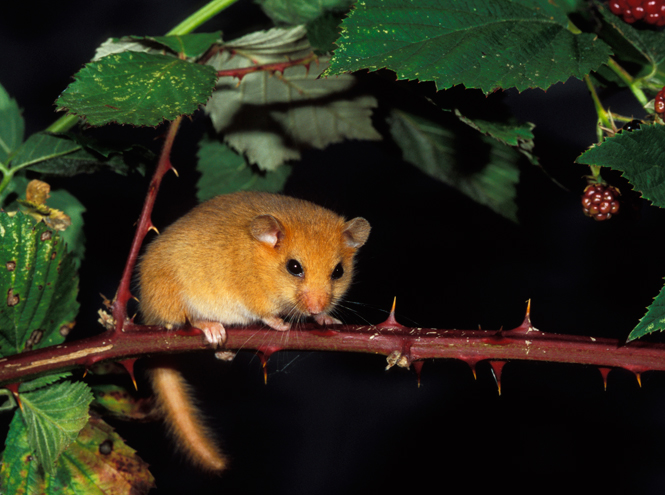


Remember Lewis Carroll's famous tea party in Alice in Wonderland? There in the teapot sat the same dormouse mouse - pretty to the point of disgrace and very small. Of course, in a fairy tale, all animals acquire almost human features, but meanwhile, the representative of rodents is incredibly pretty in real life! In general, dormouse is divided into two types - mouse-shaped and squirrel-shaped. It must be said that the squirrel-shaped dormouse is much prettier than the one that lives on the ground. It's all about her stunning tail, which is covered with fluffy fur! In addition, the dormouse is very tiny - an adult can easily fit in the palm of a person.
Their habitats: North Africa, Europe, Asia Minor, Altai, the northern regions of China and Japan, the northern parts of Scandinavia and, finally, southern Africa, where the only genus of the African dormouse of the same name is found. It turns out that quite recently it was discovered that dormice of all subspecies are rapidly disappearing from the face of the earth. So, until the last babies died out, scientists listed the animals in the “Red Book” and now mice are also bred at home.
Alpaca
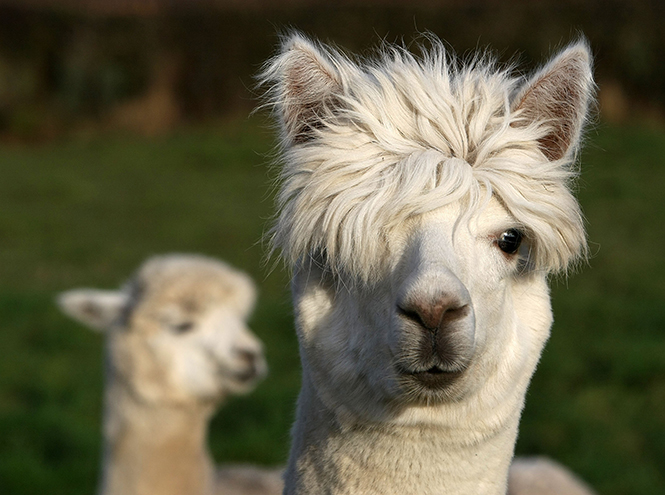
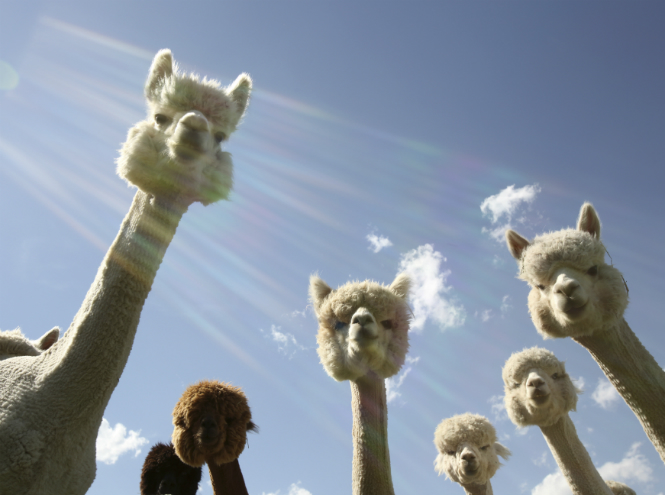


Alpaca belongs to the camel family. These touching creatures live high in the mountains in South America. The fluffy bangs give the alpaca a special charm. By the way, it is precisely by the intricate hairstyle that one can distinguish an alpaca from a llama: after all, as a rule, the latter does not have long hair on its head.
The alpaca is quite small in size: its weight does not exceed sixty kilograms, but it has luxurious wool, which is often used to make clothes. Alpaca wool is very soft and at the same time very durable and light, almost waterproof, with an excellent heat-insulating effect. For 6,000 years, alpacas were bred by the Peruvians along with llamas. But if llamas were used as a beast of burden, alpacas were cared for and cherished.
Aye-aye
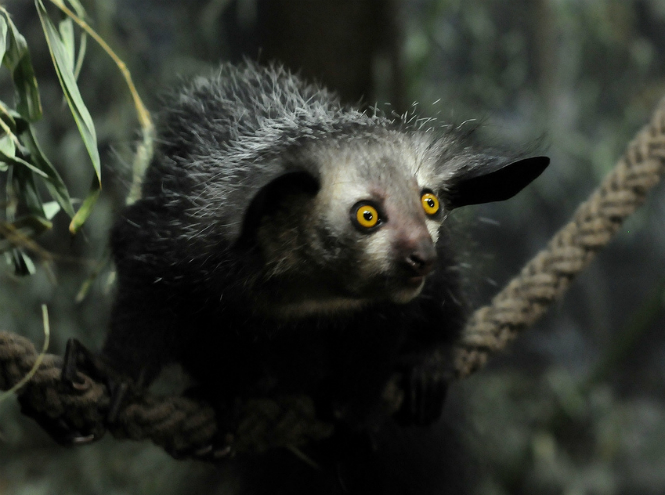
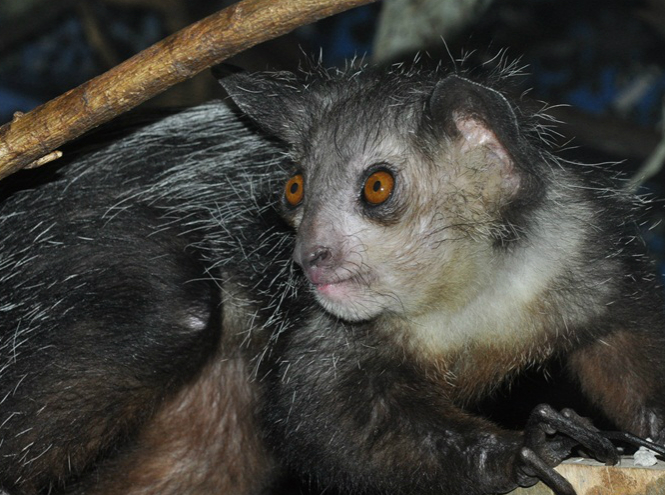


They say that the name “Aye-aye” appeared thanks to the exclamations made by anyone who saw the animal for the first time. What is this animal actually called? Madagascan hand-footed and, as you might guess, lives in Madagascar. Once upon a time they tried to classify him as a rodent, then as a primate, although Ai-ai does not resemble either one or the other. It must be said that it does not resemble anything intelligible at all: a small body covered with black fur, eternally surprised eyes and a huge tail, which is longer than the animal itself.
The only part of the aye-aye's body that is free from fur is... the middle finger on the forelimb, or rather both middle fingers. Actually, this finger is the most important tool for the arm: it uses it to clean the fur, drink water and get food. When searching for beetles and larvae hidden in the bark of a tree, the little hand always uses its miracle finger. First, he taps the trunk with it, finding suitable prey, then gnaws through the bark (here sharp teeth come into play), and finally sticks his middle finger into the resulting hole, pricks the larva onto his claw and sends it into his mouth.
Little slow loris
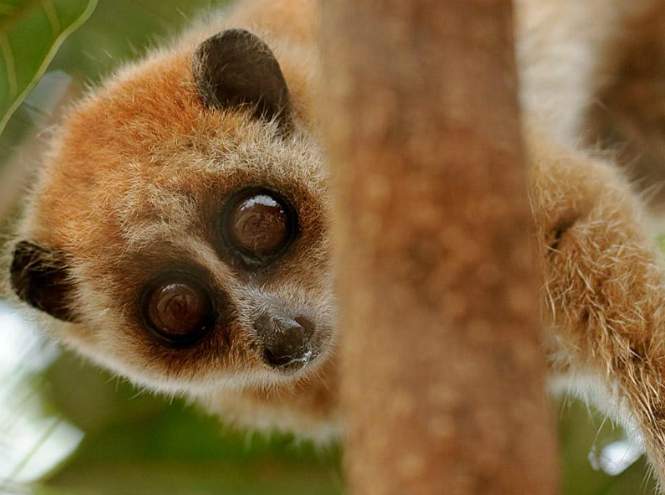
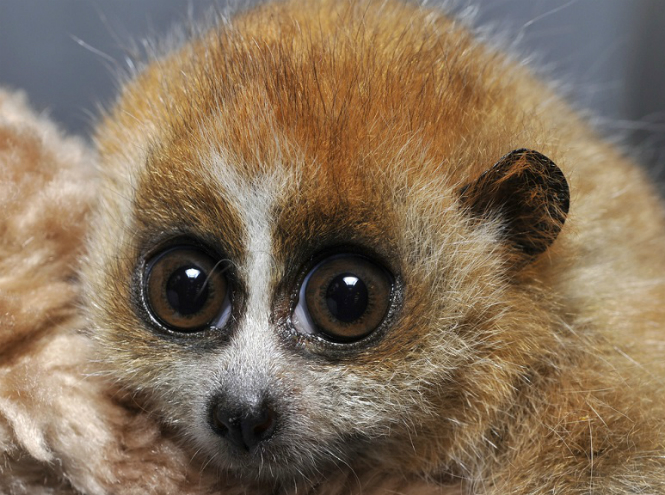


In fact, the full name of this big-eyed animal is: “Small Fat Lori”; small (its size does not exceed 23 centimeters in length), it lives in tropical forests and bamboo groves in Vietnam, Laos, Thailand, parts of China and Cambodia. Sometimes the little fat one is mistakenly considered a lemur, which in fact is not at all the case. Small and thick belongs to its own family - Loriaceae. The most amazing thing is that this handsome guy with short thick hair and incredibly touching huge eyes that are always wide open is poisonous.
On the inside of the animal’s elbow joint there are special glands, the secretions from which, combined with the saliva of the loris, turn into a powerful poison! This is so unusual for primates that the small loris received first place in the ranking of poisonous animals that are unknown to the general public. The fat fellow lives in the treetops, daring to go out only when it gets dark - the poisonous animal has a lot of enemies, so it sometimes has to hang for hours, clinging to a tree branch, which, fortunately, allows the loris to make a specific paw structure.
African black-footed cat
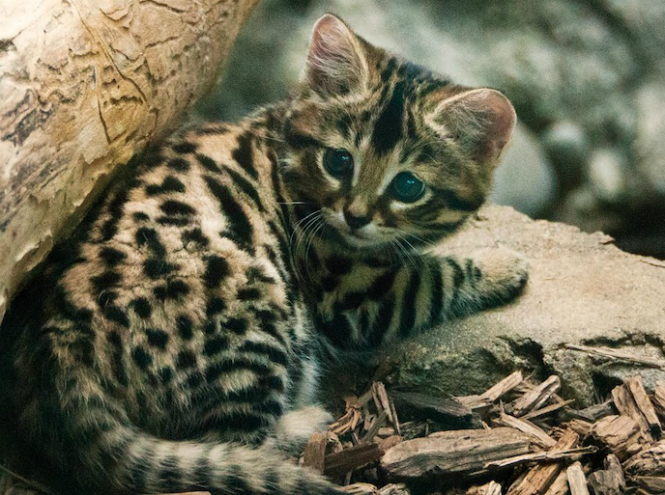
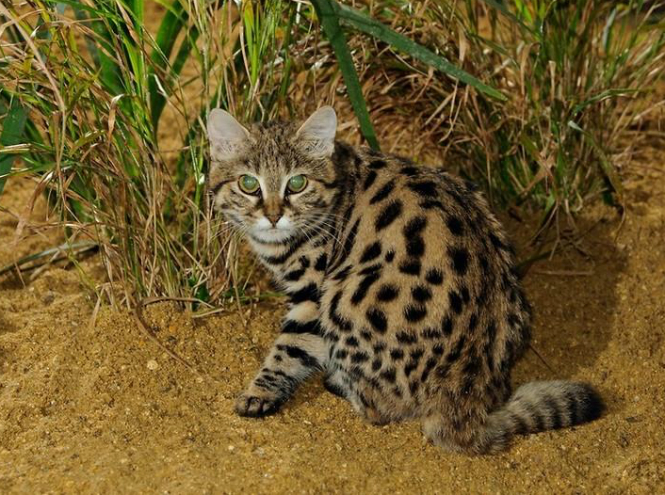


They look like real domestic cats - small, even tiny, because the weight of an adult does not even reach one and a half kilograms. In fact, these striped and charming animals living in Africa are real predators! They hunt, like any other representative of the cat family at night - their miniature shapes and appropriate colors help the seals remain completely invisible, and their large ears catch every sound - no one can hide from such animals. Behind the retina there is a special vascular layer that acts as a reflector necessary for night vision. It increases visual ability and causes the eyes to glow bright blue at night.
In Africa they are called “Antlion” - these little ones live, as a rule, in termite mounds and anthills that they themselves have emptied. By the way, insects are not the only favorite dish Black-footed cats - in addition to ants and termites, small predators prefer to eat 54 more species of a wide variety of animals - brave kids do not stop at game that is sometimes twice their own size - for example, dining on a hare is a common thing for wild cats.
Red Panda
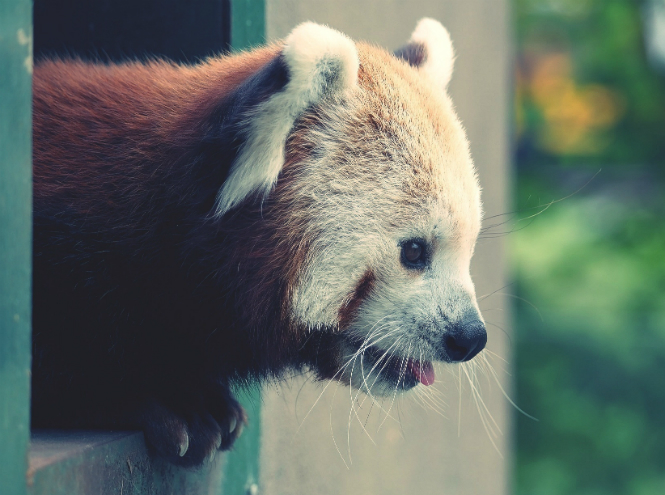
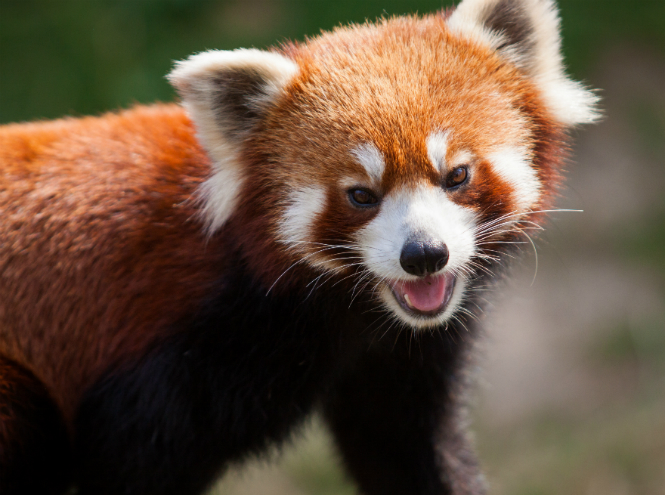


In China, where the red-haired beauty is found, this representative of the little panda family is called the “fiery fox” - the similarity is obvious: a pointed nose, fur the color of a red Sicilian orange! For a long time, the red panda hung around in space without classification: some scientists classified it as a raccoon, others as a bear, but in the end it turned out that these animals themselves are a separate, independent family of little pandas. The red panda lives not only in China - sometimes the animal can be found in Nepal.
Unlike its namesake, the common panda, the fire fox belongs to the category of predatory animals, but due to its natural clumsiness, the animal hunts extremely rarely, feeding mainly on bamboo leaves, following the example of distant relatives.
Koala
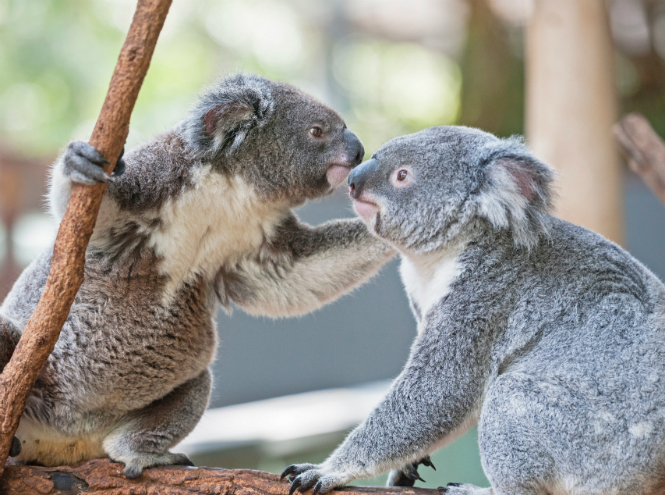
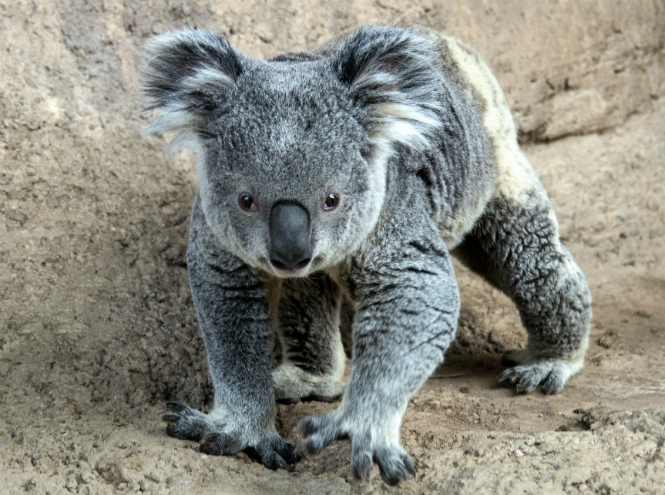


Contrary to popular belief, the koala is not a bear, although it is often called a marsupial bear. The appearance of this animal is quite unusual. Its coat is short and thick, usually smoky gray in color with a lighter belly, sometimes with a brownish tint. The eyes are small and look slightly blind, but the ears are relatively large, widely spaced, with long hair at the edges. The koala's large, leathery nose is flattened. His tail is typically “bearish” - short and almost invisible, but the claws on his paws are very long and curved.
This cute animal lives exclusively in Australia and mainly in eucalyptus forests - if for any other animal eucalyptus leaves are a deadly poison, then koalas are not at all afraid of such a nuisance. The thing is that marsupials are incredibly picky - they know how to choose only those plant flowers that are not capable of causing harm to health.
Another stereotype that haunts gray animals is the lack of thirst; allegedly, even the very name of the animal contains a decoding of a popular opinion; from the Aboriginal language the word “koala” is translated as “teetotal.” In reality, koalas, although infrequently, still drink water.
Meerkat
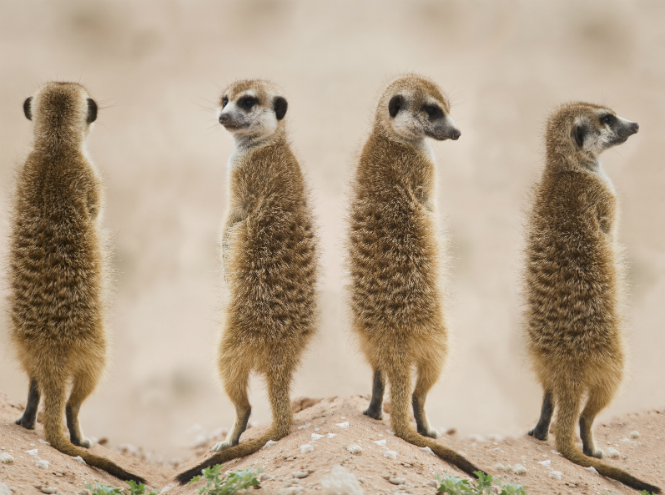
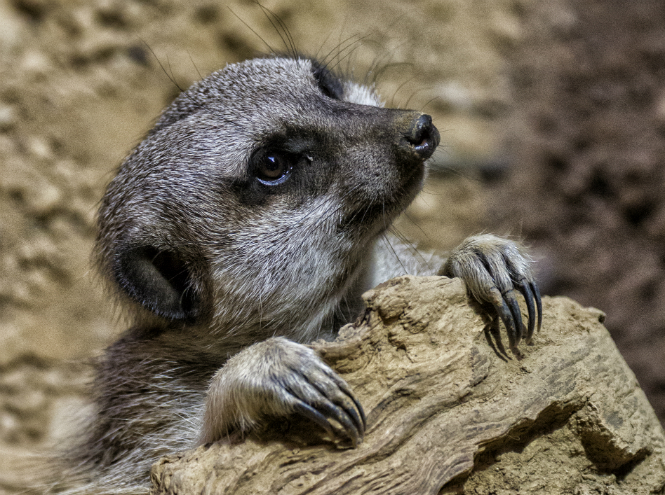


Meerkats can seem like real alarmists. Still would! As soon as these animals hear the slightest sound, they immediately rise on their hind legs, stretch out and control the space. Meerkats are indeed extremely vigilant; for their caution they even received the humorous title of “desert sentinels.”
A small people live in South Africa, mainly in the desert, since their short stature coupled with nervousness does not allow them to enter dense thickets. Among other things, these representatives of the mongoose family have phenomenal vision, which allows them to notice and assess the threat from afar.
By the way, what allows meerkats to live in the desert without any problems is not only their vision and permanent alertness, but also the structure of their eyes - the fact is that the little beauties have a well-developed third eyelid that protects the organs of vision from sand, and around the eye itself there is a dark border that works like sunglasses.
Scientists have concluded that the visual system in animals began to develop approximately 540 million years ago. At first it had a simple structure, but over time it became more complex and improved for each type of vision. For example, fish have excellent vision underwater, eagles from a great height can easily notice a small rodent on the ground, and cats can navigate perfectly in the dark.
Take a look at the selection of the most unusual animal eyes and see the uniqueness and wisdom of Mother Nature!
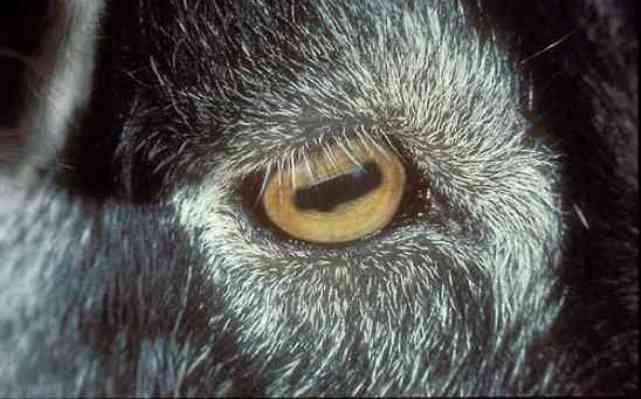
1. Mountain goat.
We are accustomed to the fact that the human pupil is round. But in most ungulates, in particular the mountain goat, it has a rectangular shape.
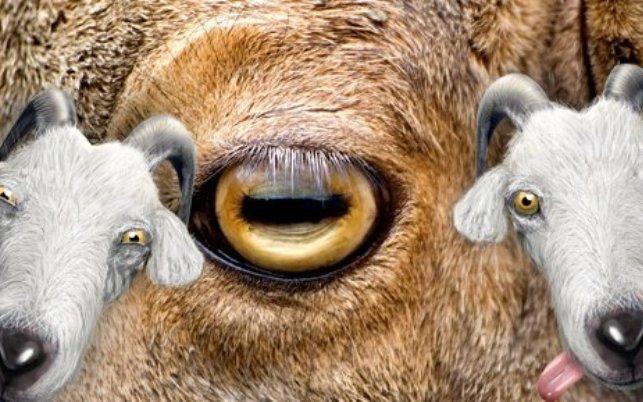

2. This pupil shape and horizontally oriented vision are the best for survival in mountain conditions. So, without turning its head, the goat sees around itself at 320-340 degrees. For comparison, a person sees only 160-200 degrees. Animals with this eye structure have excellent vision at night.
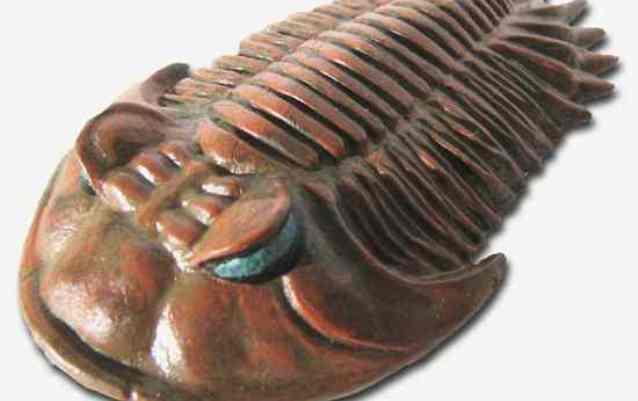

3. Trilobite.
Long before the advent of dinosaurs, the entire Earth was inhabited by marine trilobite arthropods. Paleontologists have counted about 10,000 species of these animals. At this time, this class is extinct.
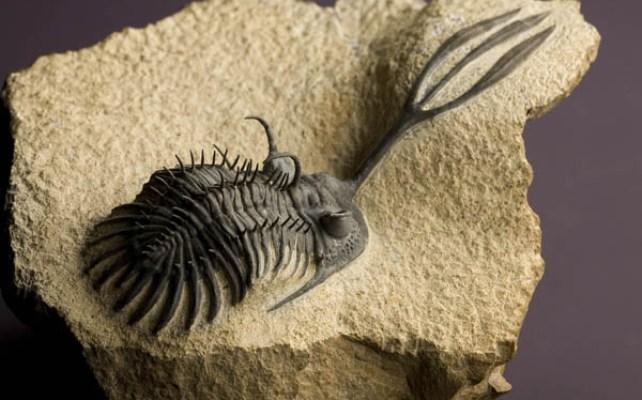

4. Some of the representatives of this class were eyeless, but the majority had eyes unique in their structure. Their eye lens was made of calcite. This is a transparent mineral that is the basis of chalk and lime.
The shell of the eyes of modern invertebrates consists of chitin, a hard, translucent substance. The unusual composition of the eye gave these arthropods the ability to simultaneously keep objects at near and far distances in focus. The vision of trilobites had a horizontal or vertical orientation. But regardless of this, the animal saw only at a distance approximately equal to the length of its own body.
Depending on their habitat, the eyes of trilobites were located either on elongated eyelids or were covered with an eye lid that protected them from the bright sun. Paleontologists have studied trilobite vision in great detail, as calcite fossils are well preserved.
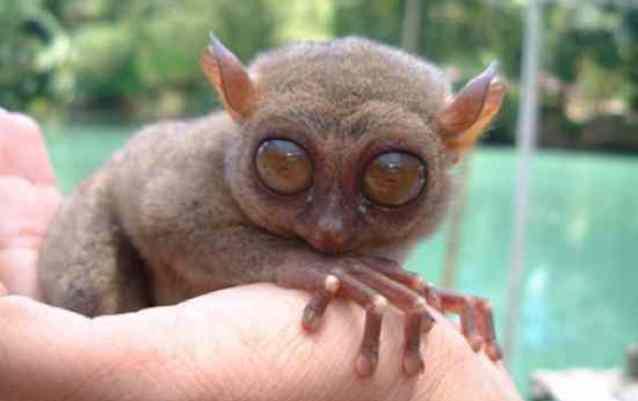

5. Tarsier.
Tarsiers are primates only 9-16 cm tall and weighing only 80-150 grams, living on the islands of Southeast Asia. Small size does not at all prevent the animal from being a predator. Moreover, tarsiers are the only primates in the world that eat only food of animal origin. They deftly catch lizards, insects and can even catch a bird during its flight. But their most important feature is their large eyes glowing in the darkness. Their diameter can reach 16 mm. In relation to body size, these are the largest eyes of any known mammal.
6. Locals They are still convinced that the tarsier is a messenger of evil spirits. And European tourists, seeing such a baby for the first time, shudder and then remember this meeting for a long time. Imagine yourself with huge, glowing eyes on a small round head. A second, and you are already looking at the back of the animal’s head. He simply turned his head...almost 360 degrees. Isn't that impressive?
In addition, tarsiers have excellent night vision. Based on this, scientists conclude that the animals recognize ultraviolet light.
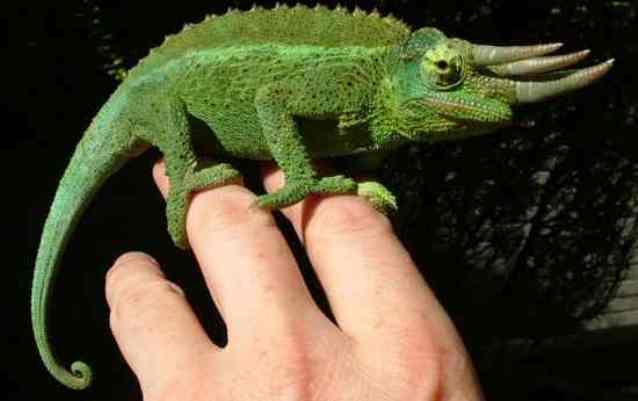

7. Chameleon.
Many people know that a chameleon can change color. This is how he disguises himself and shows his mood and demands to other lizards. The vision of these animals is also unusual - tightly fused eyelids cover the entire eyeball, leaving only a small hole for the pupil.
The eyes of these lizards seem to fall out of their sockets and can rotate independently of each other through 360 degrees.

8. A chameleon's eyes look in one direction only when its gaze is fixed on its prey. The lizard feeds on insects and small rodents. The chameleon notices its prey at a distance of several meters. Like the tarsier, it is able to see ultraviolet light.

9. Dragonfly.
The dragonfly's visual organs are also unique and unusual. They occupy almost the entire head of the insect and are able to cover the space 360 degrees.
Each dragonfly eye consists of 30,000 tiny light-sensitive cells. In addition to two huge eyes, she has 3 more small eyes. This special vision makes the insect a dangerous aerial predator, capable of reacting to any movement literally in a split second.
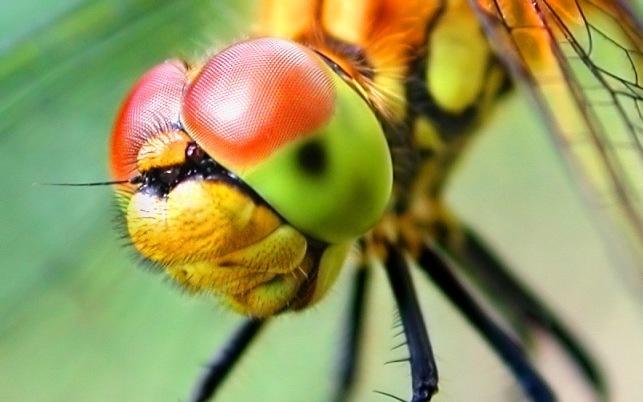

10. There are also dragonflies that successfully hunt in twilight conditions. Under these same conditions, a person is unable to see much.
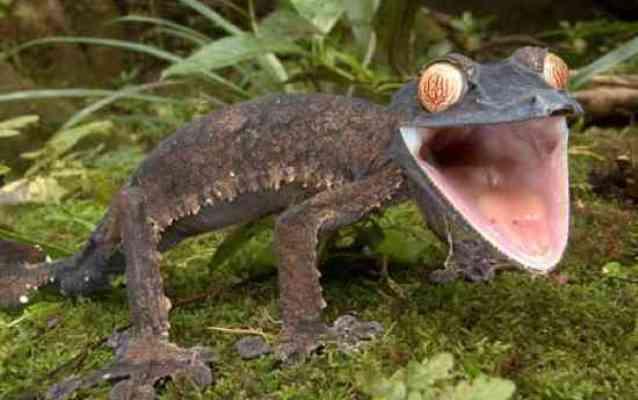

11. Leaf-tailed gecko.
The tropics of Madagascar are home to some very unusual geckos. It is very difficult to notice them, as the shape and color of this animal is very reminiscent of a dry leaf of a plant. Because of their large red eyes, these reptiles have received names such as “satanic” and “fantasy” geckos. The vision of these lizards is highly sensitive. Geckos are nocturnal animals. Even in complete darkness, they easily distinguish all objects and colors.
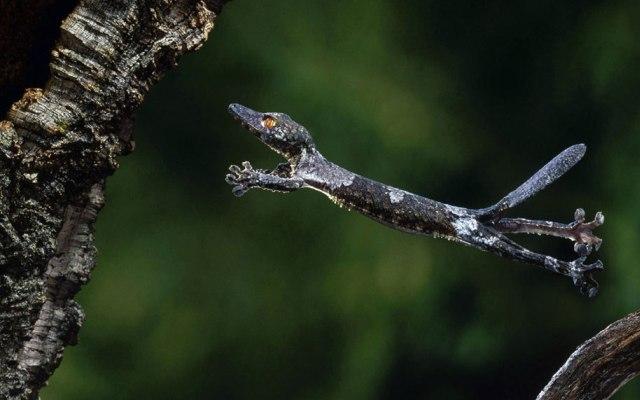

12. For comparison, cats see six times better than humans in dim lighting. Under the same conditions, geckos see 350 times better.
These reptiles owe such remarkable vision to the special structure of the pupil.
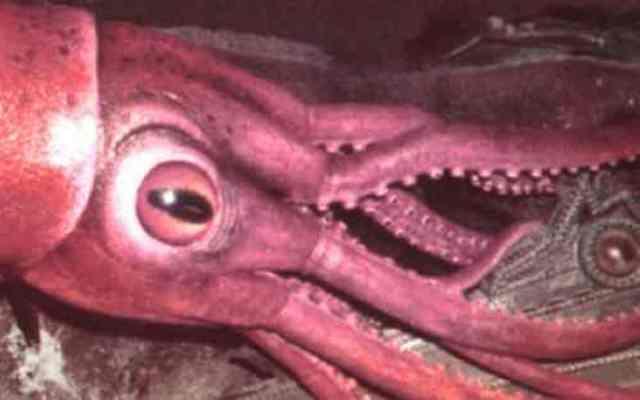

13. Colossal squid - a mystery of the ocean.
This is the largest invertebrate animal known to scientists. He is also the owner of the most big eyes among all representatives of the animal world. The diameter of its eye can reach 30 cm, and the pupil is the size of a large apple. Squids have 100 percent vision even in dim light. This is very important for him, because these animals live at a depth of at least 2000 meters.
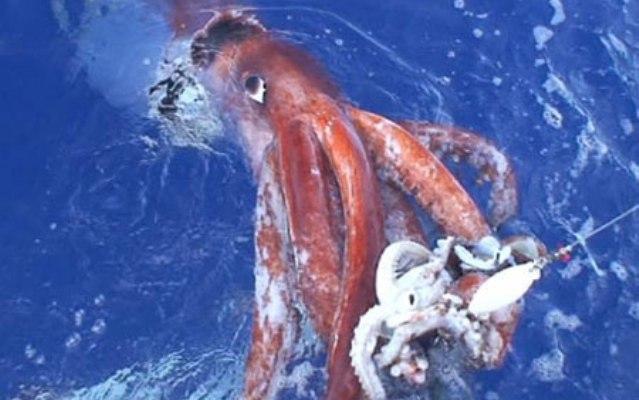

14. But besides this, the eyes of these squids have a built-in “spotlight” that turns on in the dark and provides the necessary amount of light for a successful hunt

15. Four-eyed fish.
This is a small fish up to 30 cm long, living in the waters of Mexico and South America. Its main food is insects, so it can often be seen on the water surface.

16. Despite the name, the fish only has two eyes. But they are divided by the flesh into four parts. Each part has its own lens.
The upper part of the eyes is adapted for vision in the air, the lower part for underwater observation.
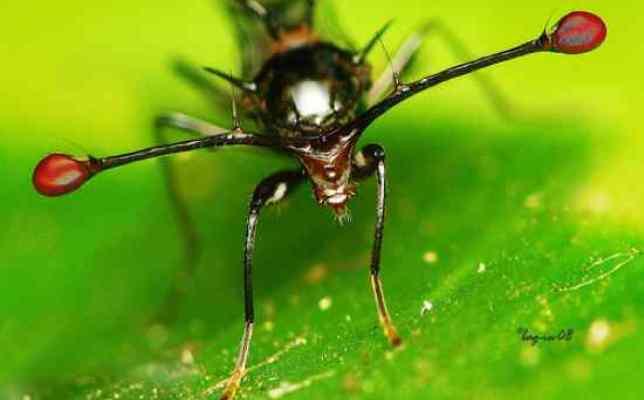

17. Stem-eyed fly.
Another unusual representative of the animal world. It got its name because of the thin, long, stem-like growths on the sides of its head. At the ends of the stems there are eyes.
Males and females have eyestalks of different lengths and thicknesses. Females choose males with the longest stalks.

18. During the mating season, males compare their stems. To win, they even use a trick - they inflate their eyes and stalks with air, which increases their size and, of course, the chances of finding the female they like.
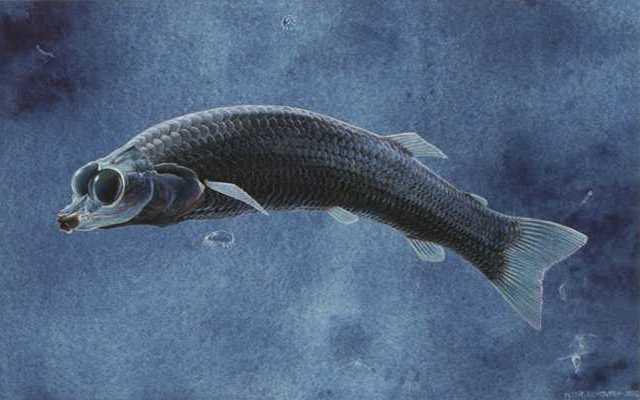

19. Dolichopteryx longipes.
This is a small deep-sea fish up to 18 cm long.
![]()
20. Only Dolichopteryx has unique mirror vision. Its organs of vision work on the principle of a lens, and allow the little predator to see both surface and underwater space at the same time.
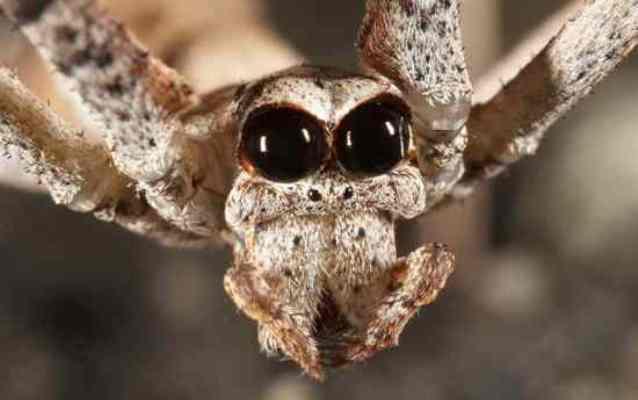

21. Spiders are ogres.
These are six-eyed spiders. But their middle pair of eyes is much larger than the others, so it seems that the spiders have two eyes.
Ogres are nocturnal predators. The spider's eyes are covered with a membrane of hypersensitive cells, providing excellent night vision.

22. Scientists believe that these spiders navigate in the dark at least a hundred times better than humans.
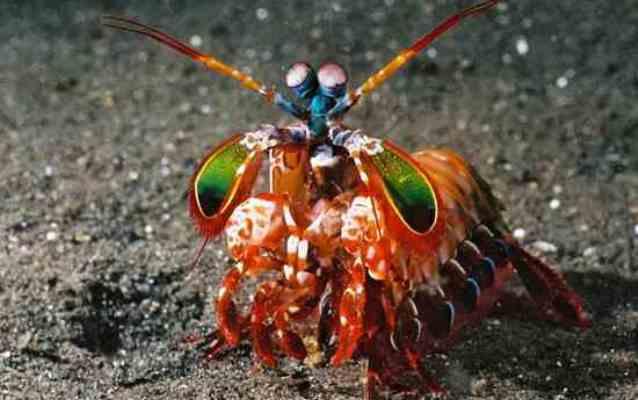

23. Crayfish are mantises.
These are the most dangerous representatives arthropods in tropical waters. With their sharp claws, they can easily leave a person without fingers. They are the owners of the most unique eyes in the world.
Their eyes consist of 10,000 hypersensitive cells. Each cell performs a strictly defined function. For example, some are responsible for determining light, others - color. This type Crayfish catch shades of colors 4 times better than humans.
They are the only ones with ultraviolet, infrared and polar vision at the same time. In addition, their eyes can rotate 70 degrees. It is also surprising that the information received in these crayfish is processed not by the brain, but by the eyes.
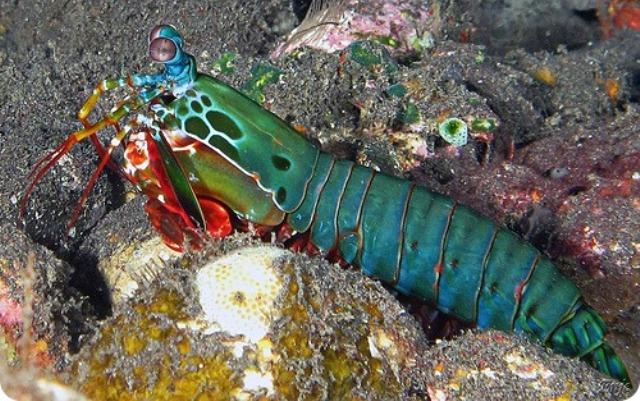

24. But that's not all. These crayfish have “trinocular vision.” Cancer's eye is divided into three parts, and he can see everything that happens from 3 different points of the same eye.
This is the most unique structure of the visual system. Scientists are still unable to fully explain it, much less recreate it. We can only marvel at the wisdom and uniqueness of nature.
There is no limit to the perfection and diversity of nature. Throughout his life, a person more than once encounters miracles of nature that in fact are not such. Animals alone can amaze any person, because they are all so different. Some animals are famous for their unusual eyes, some for their microscopic size, and others for their fantastic colors. In today's article we will talk about animals with the most variegated colors.
Panther chameleon
photo: Scruffy Hound
In an incredibly short period of time, the panther chameleon can change many colors, ranging from green to bright red. Changing color is a means of protecting the chameleon. Interestingly, he himself cannot change color, since the change occurs as a result of changes in temperature, mood or light.
Red salmon
 photo: Jon Deisher
photo: Jon Deisher
A person's skin tone may change slightly, for example after sunburn or extreme embarrassment, but the skin cannot change from red to green. Sockeye salmon easily changes its color beyond recognition when changing environment. The main color of sockeye salmon is blue and silver, but during the spawning period it completely changes to red and green.
Paradise Bird
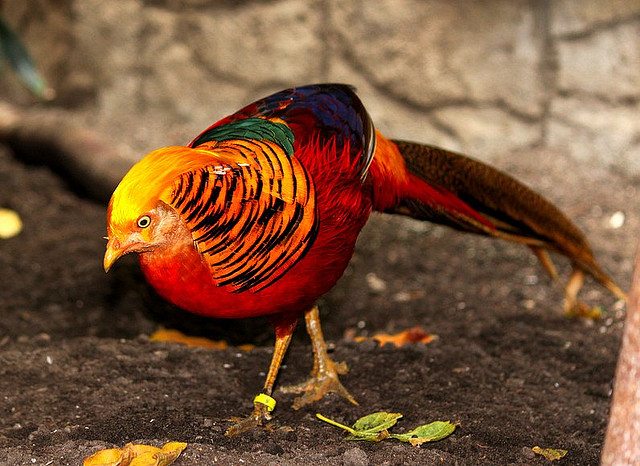 photo:Mohammed Fahad
photo:Mohammed Fahad
This beautiful name the bird received because of its amazing appearance. To conquer the female he likes, the male will show off his incredibly beautiful plumage in front of her, dance, and, if necessary, even completely change his shape. Currently, these magnificent birds are on the verge of extinction as poachers today kill them for their amazing plumage.
Ocellated Tragopan
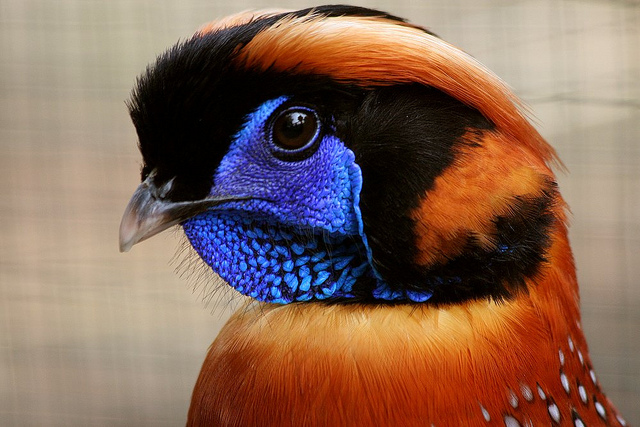

photo: Jan Harteman
One of the representatives of pheasants is able to amaze a person with its appearance alone. His fluffy bangs are orange-brown and his chest resembles a heart, on which he lies whale shark, look incredibly beautiful. If you want to see this beauty, you should go to the forests of South Asia, where birds live in large quantities. Another feature is a blue piece of skin that looks like feathers.
Herbal Sea Dragon
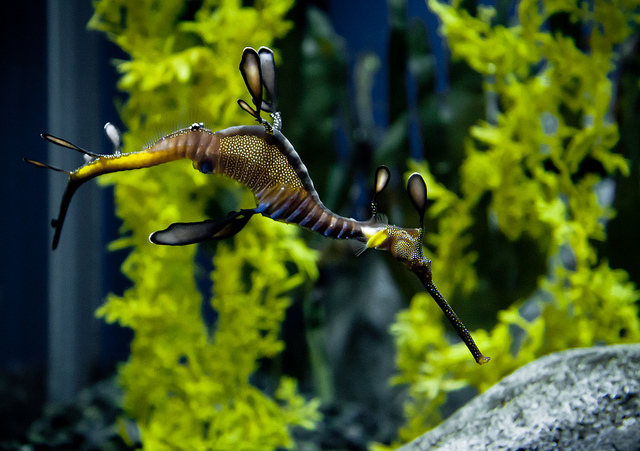

photo:Mike
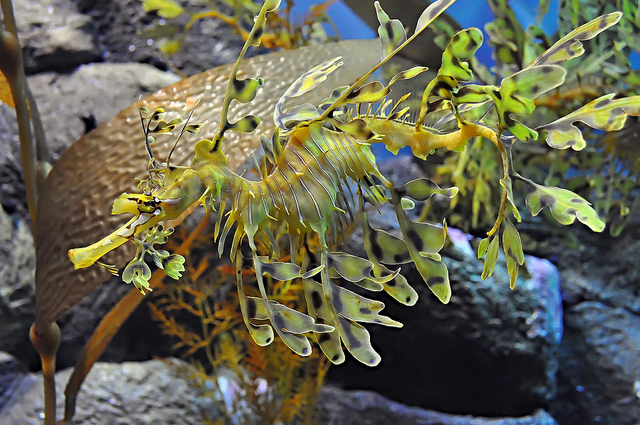

photo:John K
The underwater world is so beautiful that sometimes it seems as if it is not real. One of the most vibrant and magnificent creatures underwater world is a sea dragon. These aquatic creatures are amazing in that they are able to reproduce about 250 eggs at a time, which are monitored by a male, and not a female, as is customary. The eggs are colored bright pink, which is quite rare in nature. The grass dragon itself is very similar in appearance to algae, so it often hides among them when it is necessary to hide from predators.
Blue-footed booby
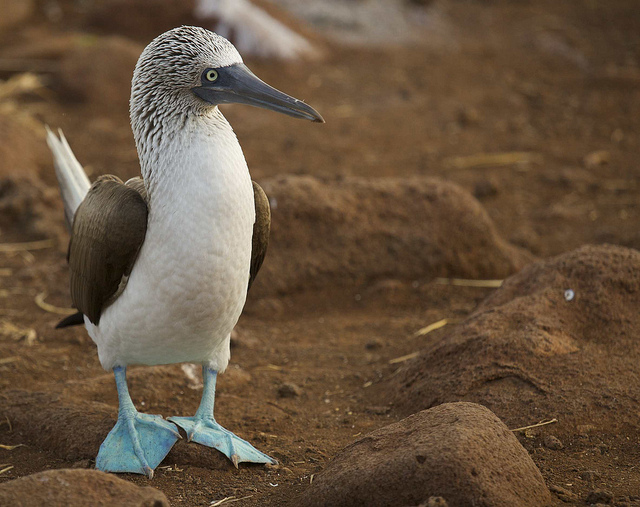 photo:
photo:
Every male wants to get the best female, so sometimes he has to fight for her. The male blue-footed booby uses his bright blue paws for this purpose. If it happens that the males miss the mating season, their legs become much brighter. The bird itself is very beautiful, but it is extremely difficult to meet it, because it lives on Galapagos Islands and on some others with subtropical and tropical climates.
Clown fish
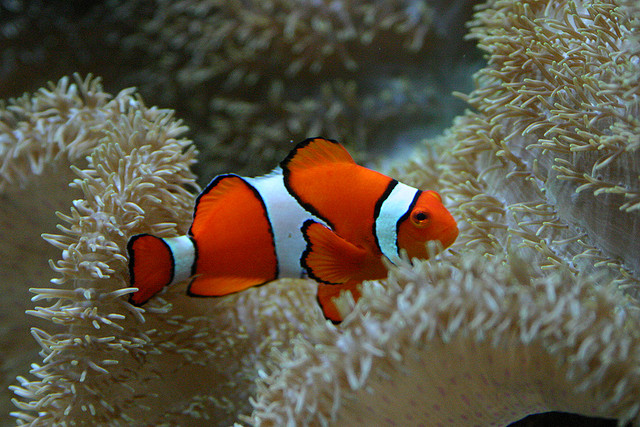

photo: Jonathan Beeston
At first glance, the fish seems very cute and funny, if not for the thick mucus that completely covers its body. Fish really need this mucus, because thanks to it they can survive and not be eaten more large predators. The fish is orange in color with white stripes.
Lesser flamingo
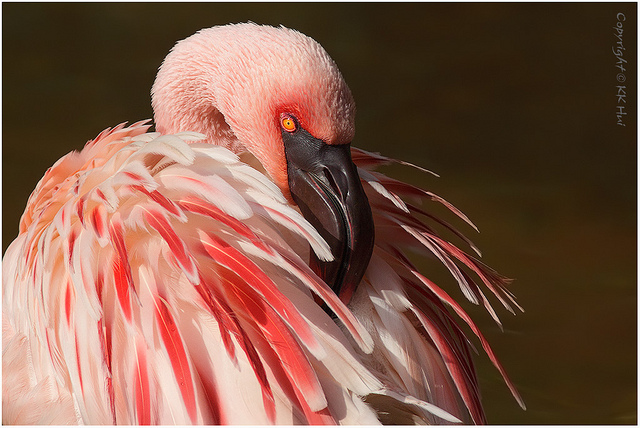

photo: KK Hui
Probably few people know that the luxurious pink color that flamingos have is actually the result of eating algae. In this case, the saying “you are what you eat” is very appropriate. Of all the representatives of the flamingo family, the smallest is the lesser flamingo, which can be understood by its name alone. Birds live in Africa and in some areas of Asia.
sailboat
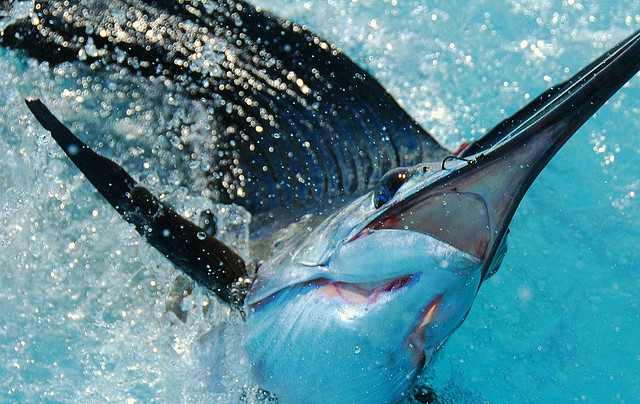

photo:Perry
The sailboat's interesting blue stripes have nothing to do with fashion. Interestingly, during the hunt, the stripes begin to burn brightly, thereby confusing their prey. Well, the sailboat uses its original color very cleverly. If necessary, the sailfish can reach speeds of up to 100 kilometers per hour, which makes it one of the best quicksand among other fish.
Danaid monarch

photo: Phuong Tran
Butterflies are very beautiful, which is why everyone loves them so much. One of the most beautiful butterflies can be called the butterfly with interesting name Danaid monarch. Its motley color helps it escape from predators, because in this way it shows that it is poisonous. The butterfly also differs from others in that it flies south every year, like many birds.
If you find an error, please highlight a piece of text and click Ctrl+Enter.
