What are asteroids and what is known about them? General information about asteroids
Asteroids are small celestial bodies ranging in size from a few meters to a thousand kilometers. In general, there is no clear difference between them and meteoroids. The smaller they themselves are, the greater the number of similar bodies in the solar system. Many scientists believe that most meteoroids are fragments of asteroids. Asteroids, like meteorites, are composed of iron, nickel and various rocks. In composition they are close to the terrestrial planets.
Asteroids got their name for their resemblance to stars when observed through a telescope. Being tiny, asteroids appear, like stars, as points. Asteroid means "star-like".
Most asteroids move in the so-called asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter. Jupiter disturbs their movements. As a result of this, asteroids collide with each other and change their orbits. Some of them may come closer to the Sun or, conversely, get further from it than most of the small planets.
Asteroids rarely collide with large planets. Many scientists believe that the cause of the sudden climate change that led to the extinction of the dinosaurs millions of years ago was an asteroid that crashed into the Earth. A crater was even discovered on Earth that could have been formed by such an impact. It must be said that the Earth has experienced several similar “strange” animal extinctions. For example, long before the dinosaurs, trilobites just as suddenly became extinct.
Several celestial bodies with sizes of 100-200 km have been discovered beyond the orbit of Neptune. Apparently, there is also an asteroid belt there. It is called the Kuiper belt. Belt objects have a composition more similar to comets than to asteroids themselves. Pluto's orbit passes within this belt.
In February 1997, it was suggested that another asteroid belt exists beyond the orbit of Pluto, at a distance of 50 AU. In it, as in the belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter, as in the Kuiper belt, as in the Oort Cloud, there is material unspent in the construction of large bodies of the Solar System. It is the presence of this belt that has been proposed to explain the formation of the double planet Pluto-Charon, which, apparently, were previously independent bodies. It is possible that there are bodies larger than Pluto in this belt. The inner regions of this belt were cleared by Neptune's gravity. It is even likely that this belt of small bodies should not be distinguished from the Kuiper belt.
Perhaps, in the place of the asteroid belt between Mars and Jupiter, a large planet rotated, which is commonly called Phaethon. The tidal forces of Jupiter or a catastrophic collision with a large celestial body tore it into separate small pieces. Most scientists think that there was no planet, that Jupiter, through its influence, simply did not allow many planetesimals - the embryos of planets - to come together at the beginning of the history of the Solar System. Be that as it may, the total mass of all bodies in the asteroid belt does not exceed the mass of the Moon. All the asteroids would not make a very large planet. It is estimated that there are about one hundred thousand asteroids within the orbit of Jupiter that are accessible to observation.
Asteroids, comets, meteors, meteorites are astronomical objects that seem the same to those uninitiated in the basic science of celestial bodies. In fact, they differ in several ways. The properties that characterize asteroids and comets are quite easy to remember. They also have certain similarities: such objects are classified as small bodies and are often classified as space debris. What a meteor is, how it differs from an asteroid or comet, what their properties and origin are, will be discussed below.
Tailed Wanderers
Comets are space objects consisting of frozen gases and rock. They originate in remote regions of the solar system. Modern scientists suggest that the main sources of comets are the interconnected Kuiper belt and the scattered disk, as well as the hypothetically existing
Comets have highly elongated orbits. As they approach the Sun, they form a coma and a tail. These elements consist of evaporating gases such as ammonia, methane), dust and stones. The head of a comet, or coma, is a shell of tiny particles, characterized by brightness and visibility. It has a spherical shape and reaches its maximum size when approaching the Sun at a distance of 1.5-2 astronomical units.
At the front of the coma is the comet's nucleus. As a rule, it has a relatively small size and an elongated shape. At a significant distance from the Sun, the nucleus is all that remains of the comet. It consists of frozen gases and rocks.
Types of comets
The classification of these is based on the periodicity of their revolution around the star. Comets that orbit the Sun in less than 200 years are called short-period comets. Most often they fall into the inner regions of our planetary system from the Kuiper belt or scattered disk. Long-period comets orbit with a period of more than 200 years. Their “homeland” is the Oort cloud.
"Minor planets"
Asteroids are made of hard rock. They are much smaller in size than planets, although some representatives of these space objects have satellites. Most of the small planets, as they were called before, are concentrated in the Main Planet, located between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.

The total number of such cosmic bodies known in 2015 exceeded 670 thousand. Despite such an impressive number, the contribution of asteroids to the mass of all objects in the Solar System is insignificant - only 3-3.6 * 10 21 kg. This is only 4% of the same parameter of the Moon.
Not all small bodies are classified as asteroids. The selection criterion is diameter. If it exceeds 30 m, then the object is classified as an asteroid. Bodies with smaller dimensions are called meteoroids.
Asteroid classification
The grouping of these cosmic bodies is based on several parameters. Asteroids are grouped together by the characteristics of their orbits and the spectrum of visible light that was reflected from their surface.
According to the second criterion, three main classes are distinguished:
- carbon (C);
- silicate (S);
- metal (M).
Approximately 75% of all asteroids known today belong to the first category. As equipment improves and more detailed research of such objects occurs, the classification expands.
Meteoroids
A meteoroid is another type of cosmic body. These are not asteroids, comets, meteors or meteorites. The peculiarity of these objects is their small size. Meteoroids are located between asteroids and cosmic dust in size. Thus, they include bodies with a diameter of less than 30 m. Some scientists define a meteoroid as a solid body with a diameter from 100 microns to 10 m. According to their origin, they are primary or secondary, that is, formed after the destruction of larger objects.
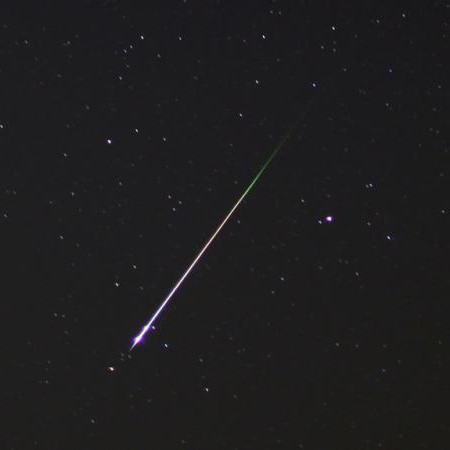
As the meteoroid enters the Earth's atmosphere, it begins to glow. And here we are already approaching the answer to the question of what a meteor is.
Falling star
Sometimes, among the flickering luminaries in the night sky, one suddenly flashes, describes a small arc and disappears. Anyone who has seen something like this at least once knows what a meteor is. These are “shooting stars” that have nothing to do with real stars. A meteor is actually an atmospheric phenomenon that occurs when small-sized objects (the same meteoroids) enter the air envelope of our planet. The observed brightness of the flare directly depends on the initial dimensions of the cosmic body. If the meteor's brilliance exceeds a fifth, it is called a fireball.
Observation
Such phenomena can only be admired from planets with an atmosphere. Meteors on the Moon or Mercury cannot be observed because they do not have an air envelope.
When conditions are right, shooting stars can be seen every night. It is best to admire meteors in good weather and at a considerable distance from a more or less powerful source of artificial lighting. Also, there should be no Moon in the sky. In this case, up to 5 meteors per hour can be seen with the naked eye. The objects that give rise to these single “shooting stars” revolve around the Sun in very different orbits. Therefore, it is impossible to accurately predict the place and time of their appearance in the sky.
Streams
Meteors, photos of which are also presented in the article, as a rule, have a slightly different origin. They are part of one of several swarms of small cosmic bodies rotating around the star along a certain trajectory. In their case, the ideal viewing period (the time when anyone can quickly figure out what a meteor is by looking at the sky) is pretty well defined.
A swarm of such space objects is also called a meteor shower. Most often they are formed during the destruction of the comet's nucleus. Individual particles of the swarm move parallel to each other. However, from the surface of the Earth, they appear to be coming from a specific small area of the sky. This section is usually called the radiant of the flow. The name of a meteor swarm is usually given by the constellation in which its visual center (radiant) is located, or by the name of the comet whose disintegration led to its appearance.
Meteors, photos of which are easy to obtain if you have special equipment, belong to such large showers as the Perseids, Quadrantids, eta Aquarids, Lyrids, and Geminids. In total, the existence of 64 streams has been recognized to date, and about 300 more are awaiting confirmation.
Heavenly stones
Meteorites, asteroids, meteors and comets are related concepts according to certain criteria. The first are space objects that fell to Earth. Most often, their source is asteroids, less often - comets. Meteorites carry invaluable data about various parts of the solar system beyond Earth.
Most of these bodies that hit our planet are very small in size. The most impressive meteorites in terms of their dimensions leave traces after impact that are quite noticeable even after millions of years. A well-known crater near the city of Winslow in Arizona. The fall of a meteorite in 1908 is believed to have caused the Tunguska phenomenon. 
Such large objects “visit” the Earth once every few million years. Most of the meteorites found are quite modest in size, but do not become less valuable for science.
According to scientists, such objects can tell a lot about the formation of the solar system. Presumably, they carry particles of the substance from which the young planets consisted. Some meteorites come to us from Mars or the Moon. Such space wanderers make it possible to learn something new about neighboring objects without the huge costs of distant expeditions.
To remember the differences between the objects described in the article, you can briefly outline the transformation of such bodies in space. An asteroid, consisting of solid rock, or a comet, which is a block of ice, when destroyed, gives rise to meteoroids, which, when entering the planet's atmosphere, burst into meteors, burn up in it, or fall, turning into meteorites. The latter enrich our knowledge of all the previous ones.
Meteorites, comets, meteors, as well as asteroids and meteoroids are participants in continuous cosmic motion. The study of these objects makes a great contribution to our understanding of the structure of the Universe. As equipment improves, astrophysicists are obtaining more and more data about such objects. The relatively recently completed mission of the Rosetta probe clearly demonstrated how much information can be obtained from a detailed study of such cosmic bodies.
On January 1, 1801, Italian astronomer Giuseppe Piazzi used his telescope to discover a new celestial body that looked like a star. It and similar bodies discovered later were called asteroids, which means “star-like” (from the Greek words “aster” - star and “oidos” - species).
Currently, more than 5 thousand asteroids have been discovered. Usually these are small, irregularly shaped celestial bodies with a diameter of one to several tens of kilometers.
Of course, asteroids are not stars. Like planets, they do not emit their own light and revolve around the Sun. Therefore, they are also called minor planets.
Asteroids are part of the solar system. Most of them move between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter.
The origin of asteroids has not yet been fully elucidated. For a long time, scientists assumed that these were the remains of some collapsed planet. But recent research shows that, most likely, these are the remnants of the “building material” from which all the planets of the solar system known to us were once formed.
Comets
Comets. These celestial bodies get their name from the Greek word cometes, which means hairy. Few natural phenomena have frightened people as much as the appearance of a bright comet. It was considered a harbinger of various troubles, such as epidemics, famine, and war.
Comets
But gradually scientists accumulated knowledge about these unusual celestial bodies, and now it is known that they are part of the solar system. Comets move in elongated orbits, sometimes approaching the Sun, sometimes moving away from it.
The main part of the comet is the solid nucleus. Its diameter usually ranges from 1 to 10 km. The core consists of ice, frozen gases and solid particles of some other substances.
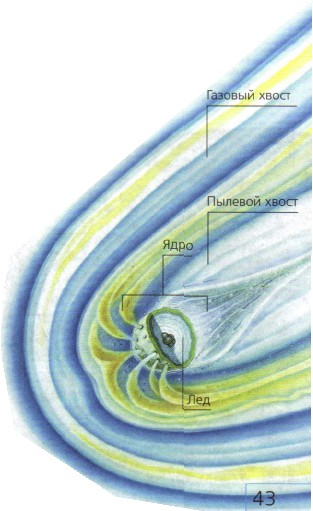
Structure of the Comet
As the comet approaches the Sun, the nucleus heats up and its substances begin to evaporate. A gas shell forms around the core, and then a long tail appears. The tail of a comet can stretch for millions of kilometers! It is always directed away from the Sun and consists of gases and fine dust. As a comet moves away from the Sun, its tail and gaseous envelope gradually disappear.

Over time, many comets are completely destroyed by the sun's heat. Their particles are scattered in outer space.
Comets visible to the naked eye rarely appear. But with the help of telescopes, scientists observe them quite often.
A huge amount of so-called cosmic dust moves in interplanetary space. In most cases, these are the remains of destroyed comets. At times they burst into the Earth's atmosphere and flare up, sweeping across the black sky as a bright luminous line: it seems as if a star is falling. These flashes of light are called meteors(from the Greek word “meteoros” - floating in the air).
Cosmic particles heat up as a result of friction with the atmosphere, flare up and burn. This usually occurs at an altitude of 80-100 km above the Earth.
In addition to cosmic dust, larger bodies also move in interplanetary space, mainly fragments of asteroids. When they enter the Earth's atmosphere, they do not have time to burn out in it. Their remains fall to the surface of the Earth. Space bodies that fall to Earth are called meteorites. Meteorites are divided into three large classes: stone, iron and stony-iron.
The fall of large meteorites to Earth is a rather rare phenomenon. Typically their weight ranges from hundreds of grams to several kilograms. The largest meteorite found weighed more than 60 tons.
Scientists carefully study these space “aliens,” as they allow us to judge the composition of celestial bodies and the processes occurring in space.

Mysterious neighbors of the Sun
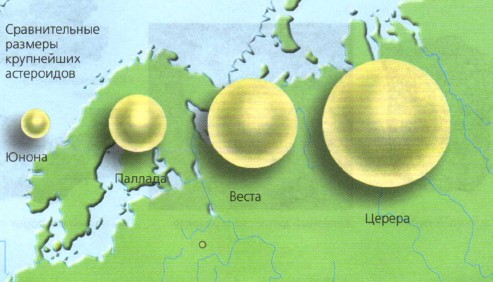
The largest of the asteroids, Ceres, has a diameter of about 1000 km. It was opened first. The total mass of all asteroids is approximately 20 times less than the mass of the Moon. Despite this, they pose some danger to our planet. Scientists do not rule out that one of the asteroids may collide with the Earth. This would lead to a terrible disaster. Scientists are now developing ways to protect the Earth from this danger.
The most famous comet, Halley's Comet, approaches the Sun once every 76 years. At this time, it flies relatively close to the Earth and can be observed with the naked eye. The last time people saw this comet was in 1986. Its next appearance is expected in 2062.
Over the course of a year, about 2,000 meteorites fall to Earth. The fall of large meteorites is accompanied by an explosion. A meteorite crater is formed at the site of the explosion. One of the largest meteorite craters is located in the USA (Arizona), its diameter is 1200 m, its depth is almost 200 m.

Test your knowledge
- What is an asteroid?
- In what part of the solar system do most asteroids move?
- What is the structure of a comet? What does its core consist of?
- How does the appearance of a comet change as it moves through its orbit?
- What is a meteor? What is a meteorite?
Think!
- Describe and compare asteroids and comets.
- Explain the difference between meteors and meteorites. Is it possible to observe meteors on the Moon?
The solar system includes asteroids and comets. Particles of cosmic dust and larger bodies - fragments of asteroids - move in interplanetary space. Flashes of light that occur when particles of cosmic dust burn in the earth's atmosphere are called meteors, and cosmic bodies that fall to Earth are called meteorites.
Asteroids? First of all, I would like to say that this is the name given to rocky solid bodies that move in elliptical orbits around the Sun, like planets. However, space asteroids are much smaller in size than the planets themselves. Their diameter is approximately within the following limits: from several tens of meters to a thousand kilometers.
When wondering what asteroids are, a person involuntarily thinks about where this term even came from and what it means. It is translated as “star-like,” and was introduced in the 18th century by an astronomer named William Herschel.
Comets and asteroids can be seen as point sources of a certain light, more or less bright. Although in the visible range, data does not emit anything - it only reflects the sunlight that falls on it. It should be noted that comets are different from asteroids. The first is their different appearance. The comet is easily recognized by its brightly glowing core and the tail that extends from it.
Most of the asteroids that are known to astronomers today move between the orbits of Jupiter and Mars at a distance of approximately 2.2-3.2 AU. e. (that is, from the Sun. To date, scientists have discovered about 20 thousand asteroids. Only fifty percent of them are registered. What are registered asteroids? These are celestial bodies that have been assigned numbers, and sometimes even proper names. Their orbits have been calculated with very great accuracy. It should be noted that these celestial bodies usually have the names that were assigned to them by their discoverers. The names for asteroids are taken, as a rule, from ancient Greek mythology.

In general, from the above definition it becomes clear what asteroids are. However, what else is characteristic of them?
As a result of observations of these celestial bodies through a telescope, an interesting fact was discovered. The brightness of a large number of asteroids can change, and in a very short time - this takes several days, or even several hours. Scientists have long hypothesized that these changes in the brightness of asteroids are associated with their rotation. It should be noted that they are determined, first of all, by their irregular forms. And the first photographs that captured these celestial bodies (the photographs were taken with the help of this theory) confirmed this theory, and also showed the following: the surfaces of the asteroids are completely pitted with deep craters and craters of various sizes.
![]()
The largest asteroid discovered in our solar system was previously considered to be the celestial body Ceres, whose dimensions were about 975 x 909 kilometers. But since 2006 it received a different status. And it began to be called And the other two large asteroids (called Pallas and Vesta) have a diameter of 500 kilometers! Another interesting fact should also be noted. The fact is that Vesta is the only asteroid that can actually be observed with the naked eye.




